Abstract
Background
Shape-memory compression bowel anastomosis using a nickel and titanium alloy may reduce leak rates and eliminate foreign anastomotic material. Its safety and efficacy had been demonstrated by animal studies. We conducted the first prospective multi-center clinical evaluation of the safety and effectiveness of BioDynamix anastomosis with ColonRing™ for large-bowel end-to-end or side-to-end anastomosis.
Materials and methods
The ColonRing™ was compared to the standard double-stapled colorectal/colocolonic anastomosis. Intraoperative and immediate postoperative and 1- and 3-month postoperative follow-up data were recorded.
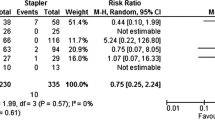
Results
Ten study patients (four males, median age 62 years, range 35–75) were compared to 13 demographically matched controls (six males, median age 62 years, range 47–82). Colorectal neoplasia was the most frequent indication for surgery (21/23 patients, 91%). The median anastomotic distance from the anal verge for both groups was 10 cm (6–20 cm). The first postoperative bowel movement was on day 5 ±2.2 (study group) and on day 4 ±1.8 (controls), and the median hospital stay was 8 days (6–14 days) and 7 days (6–13 days), respectively. There were no anastomotic leaks. There were three minor complications in each group, unrelated to the device in the study group. Two patients required transanal digital extraction of the ring which was detached but not expelled (one had a soft anastomotic stricture).
Conclusions
Our preliminary results in this first study on humans indicate that the safety and efficacy of BioDynamix anastomosis with ColonRing™ in colorectal anastomosis in human is comparable to standard staples technology and warrant larger studies for further validation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hardy KJ (1990) Non-suture anastomosis: the historical development. Aust N Z J Surg 60:625–633
McCue JL, Phillips RK (1991) Sutureless intestinal anastomoses. Br J Surg 78:1291–1296
Thiede A, Geiger D, Dietz UA, Debus ES, Engemann R, Lexer GC et al (1988) Overview on compression anastomoses: biofragmentable anastomosis ring multicenter prospective trial of 1666 anastomoses. World J Surg 22:78–86
Wullstein C, Gross E (2000) Compression anastomosis (AKA-2) in colorectal surgery: results in 442 consecutive patients. Br J Surg 87:1071–1075
Kapanen A, Ryhänen J, Danilov A, Tuukkanen J (2001) Effect of nickel–titanium shape memory metal alloy on bone formation. Biomaterials 22:2475–2480
Aggarwal R, Darzi A (2005) Compression anastomoses revisited. J Am Coll Surg 201:965–971
Baynosa RC, Stutman R, Mahabir RC, Zamboni WA, Khiabani KT (2008) Use of a novel penetrating, sutureless anastomotic device in arterial microvascular anastomoses. J Reconstr Microsurg 24:39–42
Lustosa SAS, Matos D, Atallah AN, Castro AA (2001) Stapled versus hand sewn methods for colorectal anastomosis surgery (Review). Cochrane Database Syst Rev 3:CD003144
Ravitch MM (1982) Development of intestinal anastomotic devices. S Med J 75:1520–1524
Murphy JB (1982) Chloecysto-intestinal, gastrointestinal, enterointestinal anastomosis and approximation without sutures. Med Rec 42:665–676
Hardy TG Jr, Pace WG, Maney JW, Katz AR, Kaganov AL (1985) A biofragmentable ring for sutureless bowel anastomosis. An experimental study. Dis Colon Rectum 28:484–490
Kanshin NN, Lytkin MI, Knysh VI, Klur VIu, Khamidov AI (1984) First experience with application of compression anastomoses with the apparatus AKA-2 in operations on the large intestine. Vestn Khir Im I I Grek 132:52–57
Waxman BP, Yii MK, Pahlman L (1995) Stapling in colorectal surgery. In: Mazier WP (ed) Surgery of the colon, rectum and anus. WB Saunders, Philadelphia
Kopelman D, Lelcuk S, Sayfan J, Matter I, Willenz EP, Zaidenstein L et al (2007) End-to-end compression anastomosis of the rectum: a pig model. World J Surg 31:532–537
Stewart D, Hunt S, Pierce R, Mao D, Frisella M, Cook K et al (2007) Validation of the NITI endoluminal compression anastomosis ring (EndoCAR) device and comparison to the traditional circular stapled colorectal anastomosis in a porcine model. Surg Innov 14:252–260
Nudelman I, Fuko V, Waserberg N, Niv Y, Rubin M, Szold A et al (2005) Colonic anastomosis performed with a memory-shaped device. Am J Surg 190:434–438
D'Hoore A, Hompes D, Folkesson J, Penninckx F, Pahlman L (2008) Circular 'superelastic' compression anastomosis: from the animal lab to the clinical practice. Minim Invasive Ther 17(3):172–175
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Stephen Cohen for generously providing the colonoscopy pictures. Esther Eshkol is thanked for the editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was funded by NiTi™ Surgical Solutions, Inc.,.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tulchinsky, H., Kashtan, H., Rabau, M. et al. Evaluation of the NiTi Shape Memory BioDynamix ColonRing™ in colorectal anastomosis: first in human multi-center study. Int J Colorectal Dis 25, 1453–1458 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-010-0985-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-010-0985-7