Abstract
Background and aims
Tempol (4-hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-N-oxyl) is a water-soluble analogue of the spin label TEMPO. As an antioxidative agent, it is a member of nitroxides, which detoxifies superoxide and possibly other toxic radicals in vivo. In this study, we aimed to investigate whether tempol prevents harmful systemic effects of superior mesenteric ischemia-reperfusion on left colonic anastomosis in rats.
Materials and methods
Anastomosis of the left colon was performed in 30 rats that were divided into three groups each having ten animals: sham-operated control (group I), 60 min of intestinal ischemia-reperfusion by superior mesenteric artery occlusion (group II), and tempol-treated group (30 mg/kg before and after the ischemia-reperfusion (group III). On postoperative day 5, all animals were killed and anastomotic bursting pressures were measured in vivo. Tissue samples were obtained for further investigation of anastomotic hydroxyproline content, perianastomotic malondialdehyde, and glutathione levels.
Results
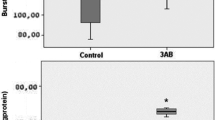
There was a statistically significant increase in the quantity of myeloperoxidase activity and malondialdehyde levels in group II, along with a decrease in glutathione levels, anastomotic hydroxyproline content, and bursting pressure values when compared to controls. However, all of the investigated parameters were normalized in tempol-treated animals (group III).
Conclusion
We conclude that tempol significantly prevents harmful systemic effects of reperfusion injury on colonic anastomoses in a rat model of superior mesenteric artery occlusion.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hill J, Lindsay TF, Ortiz F, Yeh CG, Hechtman HB, Moore FD Jr (1992) Soluble complement receptor type 1 ameliorates the local and remote organ injury after intestinal ischemia-reperfusion in the rat. J Immunol 149(5):1723–1728
Sisley AC, Desai T, Harig JM, Gewertz BL (1994) Neutrophil depletion attenuates human intestinal reperfusion injury. J Surg Res 57(1):192–196
McMillen MA, Huribal M, Sumpio B (1993) Common pathway of endothelial–leukocyte interaction in shock, ischemia, and reperfusion. Am J Surg 166(5):557–562
Sorkine P, Setton A, Halpern P, Miller A, Rudick V, Marmor S et al (1995) Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors reduce bowel ischemia-induced lung permeability and neutrophil sequestration. Crit Care Med 23(8):1377–1381
Lucchesi BR (1994) Complement, neutrophils and free radicals: mediators of reperfusion injury. Arzneimittelforschung 44(3A):420–432
Kologlu M, Yorganci K, Renda N, Sayek I (2000) Effect of local and remote ischemia-reperfusion injury on healing of colonic anastomoses. Surgery 128(1):99–104
Tekin K, Aytekin F, Ozden A, Bilgihan A, Erdem E, Sungurtekin U et al (2002) Antithrombin III prevents deleterious effects of remote ischemia-reperfusion injury on healing of colonic anastomoses. Am J Surg 184(2):160–165
McDonald MC, Zacharowski K, Bowes J, Cuzzocrea S, Thiemermann C (1999) Tempol reduces infarct size in rodent models of regional myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Free Radic Biol Med 27(5–6):493–503
Chatterjee PK, Cuzzocrea S, Brown PA, Zacharowski K, Stewart KN, Mota-Filipe H et al (2000) Tempol, a membrane-permeable radical scavenger, reduces oxidant stress-mediated renal dysfunction and injury in the rat. Kidney Int 58(2):658–673
Rak R, Chao DL, Pluta RM, Mitchell JB, Oldfield EH, Watson JC (2000) Neuroprotection by the stable nitroxide Tempol during reperfusion in a rat model of transient focal ischemia. J Neurosurg 92(4):646–651
Cuzzocrea S, McDonald MC, Mazzon E, Siriwardena D, Costantino G, Fulia F et al (2000) Effects of tempol, a membrane-permeable radical scavenger, in a gerbil model of brain injury. Brain Res 875(1–2):96–106
Sledzinski Z, Wozniak M, Antosiewicz J, Lezoche E, Familiari M, Bertoli E et al (1995) Protective effect of 4-hydroxy-TEMPO, a low molecular weight superoxide dismutase mimic, on free radical toxicity in experimental pancreatitis. Int J Pancreatol 18(2):153–160
Kuzu MA, Tanik A, Kale IT, Aslar AK, Koksoy C, Terzi C (2000) Effect of ischemia/reperfusion as a systemic phenomenon on anastomotic healing in the left colon. World J Surg 24(8):990–994
Reddy GK, Enwemeka CS (1996) A simplified method for the analysis of hydroxyproline in biological tissues. Clin Biochem 29(3):225–229
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95(2):351–358
Suzuki K, Ota H, Sasagawa S, Sakatani T, Fujikura T (1983) Assay method for myeloperoxidase in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Anal Biochem 132(2):345–352
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82(1):70–77
Udassin R, Haskel Y, Samuni A (1998) Nitroxide radical attenuates ischaemia/reperfusion injury to the rat small intestine. Gut 42(5):623–627
Thiemermann C (2003) Membrane-permeable radical scavengers (tempol) for shock, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and inflammation. Crit Care Med 31(1 Suppl):S76–S84
Essani NA, Fisher MA, Farhood A, Manning AM, Smith CW, Jaeschke H (1995) Cytokine-induced upregulation of hepatic intercellular adhesion molecule-1 messenger RNA expression and its role in the pathophysiology of murine endotoxin shock and acute liver failure. Hepatology 21(6):1632–1639
Barbul A (2005) Wound healing. In: Brunicardi FC (eds) Schwartz’s principles of surgery, 8th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 223–249
Ahrendt GM, Tantry US, Barbul A (1996) Intra-abdominal sepsis impairs colonic reparative collagen synthesis. Am J Surg 171(1):102–117 (discussion 107–108)
Hoer JJ, Junge K, Schachtrupp A, Klinge U, Schumpelick V (2002) Influence of laparotomy closure technique on collagen synthesis in the incisional region. Hernia 6(3):93–98
Jefferies H, Coster J, Khalil A, Bot J, McCauley RD, Hall JC (2003) Glutathione. ANZ J Surg 73(7):517–522
Nakamura S, Sugiyama S, Fujioka D, Kawabata K, Ogawa H, Kugiyama K (2003) Polymorphism in glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier subunit gene is associated with impairment of nitric oxide-mediated coronary vasomotor function. Circulation 108(12):1425–1427
Haciyanli M, Fuzun M, Unek T, Tokgoz Z (2001) Does the administration route of leucovorin have any influence on the impairment of colonic healing caused by intraperitoneal 5-fluorouracil treatment? Eur Surg Res 33(2):80–85
Irvin TT (1978) Effects of malnutrition and hyperalimentation on wound healing. Surg Gynecol Obstet 146(1):33–37
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aydin, C., Teke, Z., Aytekin, F. et al. Tempol prevents harmful effects of remote ischemia reperfusion injury on healing of experimental colonic anastomoses. Int J Colorectal Dis 22, 325–331 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-006-0149-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-006-0149-y