Abstract
Purpose
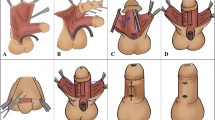
Soft tissue interposition (STI) during hypospadias repair (HR) purportedly prevents postoperative urethrocutaneous fistula (PUF) by supporting the neourethra. We report our experience.
Methods
Data from 243 hypospadias patients treated by a single surgeon from 1997 to 2014 by urethroplasty (UP) with STI (n = 229; UP + STI) and UP without STI (n = 14; UP-STI) were collated prospectively and compared for incidence of PUF. Re-operative UP were excluded.
Results
Hypospadias was distal (n = 55), mid-shaft (n = 59), proximal/penoscrotal (n = 109), scrotal (n = 15), and perineal (n = 5). UP was single-staged in 86, multi-staged in 157; mean age at UP was 3.1 ± 2.4 years. Soft tissue used for STI was prepucial inner dartos fascia (inner dartos: n = 88), ventral dartos fascia (ventral dartos: n = 15), pedicled external spermatic fascia (ESF: n = 84), adipose tissue surrounding the spermatic cord (pericordal: n = 9), scrotal adipose tissue (n = 8), or a combination of tissues (combined: n = 25). Mean follow-up was 6.4 ± 4.6 (range 0.6–16.8) years. Overall incidence of PUF was 10/243 (4.1 %); 7/229 (3.1 %) for UP + STI and 3/14 (21.4 %) in UP-STI (p < 0.05); incidence versus type of hypospadias was 1/55 for distal (1.8 %), 3/59 for mid-shaft (5.1 %), 5/109 for proximal/penoscrotal (4.6 %), 0/15 for scrotal (0 %), and 1/5 for perineal (20 %); incidence versus type of STI was 7/88 for inner dartos, 0/15 for ventral dartos, 0/84 for ESF, 0/9 for pericordal adipose tissue, 0/8 for scrotal adipose tissue, and 0/25 for combined. All PUF were repaired successfully. Satisfaction with penile cosmesis was acceptable (10.3 %) or good (89.7 %) without any testicular complications or scrotal deformity.
Conclusion
STI, especially ESF, would appear to effectively prevent PUF in HR.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kass EJ, Bolomg D (1999) Single stage hypospadias reconstruction without fistula. J Urol 144:520–522
Sarhan OM, El-Hefnawy AS, Hafez AT et al (2009) Factor affecting outcome of tubularized incised plate (TIP) urethroplasty: single-center experience with 500 cases. J Pediatr Urol 5:378–382
Khan M, Majeed A, Hayat W et al (2014) Hypospadias repair: a single center experience. Hindawi Publishing Corporation. doi:10.1155/2014/453039. Accessed 20 Jan 2014
Snodgrass WT, Nguyen MT (2002) Current technic of tubularized incised plate hypospadias repair. Urology 60:157–162
Churchill BM, Van Savage JG, Khoury AE et al (1996) The Dartos flap as an adjunct in preventing urethrocutaneous fistulas in repeat hypospadias surgery. J Urol 156:2047–2049
Lau JKT, Saing H, Tam PKH et al (1982) Interposing fascial pedicle flap for the repair of urethral fistulae after hypospadias surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 70:206–208
Retwik AB, Mandell J, Bauer SB et al (1994) Meatal based hypospadias repair with the use of a dorsal subcutaneous flap to prevent urethrocutaneous fistula. J Urol 152:1229–1231
Snow BW (1986) Use of tunica vaginalis to prevent fistula in hypospadias surgery. J Urol 136:861–863
Snow BW, Cartwright PC, Unger K (1995) Tunica vaginalis blanket wrap to prevent urethrocutaneous fistula: an 8-year experience. J Urol 153:427–473
Yamataka A, Ando K, Lane GJ et al (1998) Pedicled external spermatic fascia flap for urethroplasty in hypospadias and closure of urethrocutaneous fistula. J Pediatr Surg 33:1788–1789
Elder JS, Duckett JW, Snyder HM (1987) Onlay island flap in the repair of mid and distal penile hypospadias without chordee. Urol Clin N Am 29:285–290
Shimotakahara A, Nakazawa N, Wada A (2011) Tubularized incised plate urethroplasty with dorsal inlay graft prevents meatal/neourethral stenosis: a single surgeon’s experience. J Pediatr Surg 46:2370–2372
Hanna M, Weiser AC (2004) Thiersch-Duplay principle. In: Hadidi AT, Azmy AF (eds) Hypospadias surgery, 1st edn. Springer, New York, pp 127–134
Buskin L, Duckett JW (1994) Dorsal tunica albuginea plication (TAP) for hypospadias curvature. J Urol 151:1668–1671
Yamataka A, Shimotakahara A, Miyano G (2008) Repair of hypospadias with severe chordee using a long, wide, U-shaped flap that preserves ventral penile tissues intact for second-stage urethroplasty. J Pediatr Surg 43:2260–2263
Cimador M, Pensabene M, Sergio M et al (2013) Coverage of urethroplasty in pediatric hypospadias: randomized comparison between different flaps. Int J Urol 20:1000–1005
Chung JW, Choi SH, Kim BS et al (2012) Risk factor for the development of urethrocutaneous fistula after hypospadias repair: a retrospective study. Korean J Urol 53:711–715
Dhua AK, Aggarwal SK, Sinha S et al (2012) Soft tissue covers in hypospadias surgery. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg 17:16–19
Duckett JW (1998) Hypospadias. In: Walsh PC, Retik AB, Vaughan ED et al (eds) Campbell’s Urology, 7th edn. WB Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp 2094–2116
Subramanian R, Spinot AF, Hoebeke P et al (2011) Hypospadias repair: an overview of the actual techniques. Semin Plast Surg 25:206–212
Kraft KH, Shukla AR, Canning DA (2010) Hypospadias. Urol Clin North Am 37:167–181
Spinoit AF, Poelaert F, Groen LA et al (2013) Hypospadias repair at a tertiary care center: long-term follow-up is mandatory to determine the real complication rate. J Urol 189:2276–2281
Snodgrass W, Ziada A, Yucel S et al (2008) Comparison of outcomes of tubularized incised plate hypospadias repair and circumcision: a questionnaire based survey of parents and surgeon. J Pediatr Urol 4:250–254
Bush NC, Holzer M, Zhang S et al (2012) Age dose not impact risk for urethroplasty complications after tubularized incised plate repair of hypospadias in prepubertal boys. J Pediatr Urol 9:252–258
Snodgrass W, Bush N (2011) Tubularized incised plate proximal hypospadias repair: continued evolution and extended applications. J Pediatr Urol 7:2–9
Baskin L (2001) Hypospadias: acritical analysis of cosmetic outcomes using photography. BUJ Int 87:534–539
Liu G, Yuan J, Feng J et al (2006) Factors affecting the long-term results of hypospadias repairs. J Pediatr Urol 41:554–559
Mouriquand PD, Gorduza DB, Noche ME et al (2011) Long-term outcome of hypospadias surgery: current dilemmas. Curr Opin Urol 21:465–469
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, S., Ochi, T., Yazaki, Y. et al. Soft tissue interposition is effective for protecting the neourethra during hypospadias surgery and preventing postoperative urethrocutaneous fistula: a single surgeon’s experience of 243 cases. Pediatr Surg Int 31, 297–303 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-015-3655-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-015-3655-6