Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effects of probiotics on bacterial translocation in the obstructive common bile duct with comparison to an enteral product containing arginine and glutamine.
Material and method
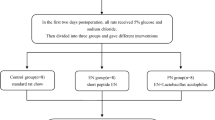
In our study, 40 Sprague–Dawley rats each weighing 250–300 g were used. Animals in Group 1 (sham) were laparatomized and fed standard chow supplemented with physiologic saline at daily doses of 2 ml through orogastric tube for 7 days. Common bile ducts of the animals in the other groups were ligated with 3/0 silk sutures. Group 2 (control group) was fed standard chow supplemented with daily doses of 2 ml physiologic saline. Group 3 (probiotic group) was fed standard chow supplemented with a probiotic solution (Acidophilus plus) containing strains of Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactobacillus bulgaricus at a daily doses of 2 × 109 colony forming units (CFU). Group 4 (formula group) was fed only an enteral solution (Stresson Multi Fiber) containing glutamine, arginine and a medium-chain fatty acid at daily doses of 2 g/kg. At the end of the 7th day, all animals were relaparatomized, and to determine bacterial translocation, aerobic, and anaerobic cultures were obtained from the specimens of mesenteric lymph nodes, intestinal mucosa, and blood samples. Smear cultures prepared from caecum were examined to determine the number of CFU. Finally, for histological examination specimens were excised from terminal ileum, and oxidative damage was assessed in liver tissues. Afterwards all animals were killed.
Results
Moderately lesser degrees of bacterial translocation, and mucosal damage were seen in Groups 3, and 4 relative to Group 2 (p < 0.05). In Group 4, any difference was not seen in the number of cecal bacteria relative to baseline values, while in Group 3, significant decrease in cecal colonization was seen. Among all groups, a significant difference between levels of malondialdehyde, and glutathione was not observed.
Conclusion
At the end of our study, we have concluded that both probiotics, and enteral diets which contain immunomodulators such as glutamine, and arginine alleviate bacterial translocation, and impairment of intestinal mucosa.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albillos A, Hera A (2002) Multifactorial gut barrier failure in cirrhosis and bacterial translocation: working out the role of probiotics and antioxidants. J Hepatol 37:523–526
Alexander JW, Boyce ST, Babcock GF, Gianotti L, Peck MD, Dunn DL, Pyles T, Childress CP, Ash SK (1990) The process of microbial translocation. Ann Surg 212(4):496–510
Barber AE, Jones WG 2nd, Minei JP, Fahey TJ 3rd, Lowry SF, Shires GT (1991) Bacterial overgrowth and intestinal atrophy in the etiology of gut barrier failure in the rat. Am J Surg 161(2):300–304
Başaran UN, Celayir S, Eray N, Oztürk R, Senyüz OF (1998) The effect of an H2-receptor antagonist on small bowel colonization and bacterial translocation in newborn rats. Pediatr Surg Int 13:118–120
Duffy LC (2000) Interactions mediating bacterial translocation in the immature intestine. J Nutr 130:432–436
Saadia R, Schein M, MacFarlane C, Boffard KD (1990) Gut barrier function and the surgeon. Br J Surg 77(5):487–492
Ziegler TR, Smith RJ, O’Dwyer ST, Demling RH, Wilmore DW (1988) Increased intestinal permeability associated with infection in burn patients. Arch Surg 123:1313–1319
Ding JW, Anderson R, Stenham U, Lunderquist A, Bengmark S (1992) Effect of biliary decompression on reticuloendothelial function in jaundiced rats. Br J Surg 79:648–652
Kimmings AN, van Deventer SJH, Obertop H, Rauws EA, Gouma DJ (1995) Inflammatory and immunologic effects of obstructive jaundice: pathogenesis and treatment. J Am Coll Surg 181:567–581
Lorenzo-Zùniga V, Bartolí R, Planas R, Hofmann SF, Vinado B, Hagey LR, Hernández JM, Mané J, Alvarez MA, Ausina V, Gassull MA (2003) Oral bile acids reduce bacterial overgrowth, bacterial translocation and endotoxemia in cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 37:551–557
Parks RW, Stuart Cameron CH, Gannon CD, Pope C, Diamond T, Rowlands BJ (2000) Changes in gastrointestinal morphology associated with obstructive jaundice. J Pathol 192:526–532
Ishibashi N, Yamazaki S (2001) Probiotics and safety. Am J Clin Nutr 73:465–470
Isolauri E (2001) Probiotics in human disease. Am J Clin Nutr 73:1142–1146
Kopp-Hoolihan L (2001) Prophylactic and therapeutic uses of probiotics: a review. J Am Diet Assoc 101(2):229–238
Molin G (2001) Probiotics in foods not containing milk or milk constituents, with special reference to Lactobacillus plantarum 299v. Am J Clin Nutr 73:380–385
Reid G (2002) Safety of Lactobacillus strains as probiotic agents. Clin Infect Dis 35:349–350
Rolfe RD (2000) The role of probiotic cultures in the control of gastrointestinal health. J Nutr 130:396–402
Buchman LA (1996) Glutamine: is it a conditionally required nutrient for the human gastrointestinal system? J Am Coll Nutr 15(3):199–205
Kennedy JA, Parks RW, Clements WDB, Rowlands BJ (1995) Failure of macrophage activation in experimental obstructive jaundice: association with bacterial translocation. Br J Surg 82:1433–1434
McAnena OJ, Moore FA, Jones TN, Parsons P (1991) Selective uptake of glutamine in the gastrointestinal tract: confirmation in a human study. Br J Surg 78:480–482
Salvalaggio PRO, Campos ACL (2002) Bacterial translocation and glutamine. Nutrition 18:435–436
Tenenhaus M, Hansbrough JF, Zapata-Sirvent RL, Ohara M, Nyhan W (1994) Supplementation of an elemental enteral diet with alanyl-glutamine decreases bacterial translocation in burned mice. Burns 20(3):220–225
Adawi D, Ahrné S, Molin G (2001) Effects of different probiotic strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium on bacterial translocation and liver injury in an acute liver injury model. Int J Food Microbiol 70(3):213–220
Bauer TM, Fernández J, Navasa M, Vila J, Rodés J (2002) Failure of Lactobacillus spp. to prevent bacterial translocation in a rat model of experimental cirrhosis. J Hepatol 36(4):501–506
Chiva M, Soriano G, Rochat I, Peralta C, Rochat F, Llovet T, Mirelis B, Schiffrin EJ, Guarner C, Balanzó J (2002) Effect of Lactobacillus johnsonii La1 and antioxidants on intestinal flora and bacterial translocation in rats with experimental cirrhosis. J Hepatol 37:456–462
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxidase in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Beutler E, Duran O, Kelly BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61(5):882–888
Deleve LD, Kaplowitz N (1991) Glutathione metabolism and it is role in hepatotoxicity. Pharmacol Ther 52:287–305
Chiu CJ, McArdle AH, Brown R, Scott HJ, Gurd FN (1970) Intestinal mucosal lesion in low flow states. Arch Surg 101:478–483
Akın ML, Erenoglu C, Dal A, ErdemElbuken E, Batkin A (2001) Hyperbaric oxygen prevents bacterial translocation in rats with obstructive jaundice. Dig Dis Sci 46(8):1657–1662
Jones WG 2nd, Minei JP, Barber AE, Rayburn JL, Fahey TJ 3rd, Shires GT 3rd, Shires GT (1990) Bacterial translocation and intestinal atrophy after thermal injury and burn wound sepsis. Ann Surg 211:399–405
Parks RW, Clements WDB, Pope C, Halliday MI, Rowlands BJ, Diamond T (1996) Bacterial translocation and gut microflora in obstructive jaundice. J Anat 189:561–565
Salman FT, Buyruk N, Gürler N, Çelik A (1992) The effect of surgical trauma on the bacterial translocation from the gut. J Pediatr Surg 27:802–804
Spaeth G, Berg RD, Specian RD, Deitch EA (1990) Food without fiber promotes bacterial translocation from the gut. Surgery 108:240–246
Tadros T, Traber DL, Heggers JP, Herndon DN (2003) Effects of interleukin-1 alfa administration on intestinal ischemia and reperfusion injury, mucosal permeability and bacterial translocation in burn and sepsis. Ann Surg 237(1):101–109
Nieuwenhuijs VB, Dijk JE, Gooszen HG, Akkermans LM (2000) Obstructive jaundice, bacterial translocation and interdigestive small bowel motility in rats. Digestion 62:255–261
Braga M, Gianotti L, Cestari A, Vignali A, Pellagatta F, Dolci A, Di Carlo V (1996) Gut function and immune and inflammatory responses in patients perioperatively fed with supplemented enteral formulas. Arch Surg 131:1257–1265
Chen K, Nezu R, Sando K, Haque SM, Iiboshi Y, Masunari A, Yoshida H, Kamata S, Takagi Y, Okada A (1996) Influence of glutamine supplemented parenteral nutrition on intestinal aminoacid metabolism in rats after small bowel resection. Jpn J Surg 26:618–623
Farges MC, Berard MP, Raul F, Cézard JP, Joly B, Davot P, Vasson MP, Cynober L (1999) Oral administration of glutamine enriched diet before or after endotoxin challenge in aged rats has limited effects. J Nutr 129(10):1799–1806
MacFie J, McNaught C (2003) Glutamine and gut barrier function. Nutrition 18(5):433–434
Erbil Y, Berber E, Ozarmağan S, Sever R, Eminoglu L, Calis A, Olgaç V, Gürler N (1999) The effects of sodium deoxycholate, lactulose and glutamine on bacterial translocation in common bile duct ligated rats. Hepatogastroenterology 46:2791–2795
Schimple G, Pesendorfer P, Steinwender G, Feierl G, Ratschek M, Höllwarth ME (1996) Allopurinol and glutamine attenuate bacterial translocation in chronic portal hypertensive and common bile duct ligated growing rats. Gut 39:48–53
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarac, F., Salman, T., Gun, F. et al. Effect of probiotic supplementation on bacterial translocation in common bile duct obstruction. Pediatr Surg Int 31, 155–161 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-014-3643-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-014-3643-2