Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study is to investigate the role of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and the effect of vitamin A administration on liver damage induced by bile duct ligation (BDL) and administration of CCl4.
Methods
Two types of animal model were used; one was BDL as a model of biliary atresia, the other was CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis. Pathological changes of the liver with or without administration of vitamin A were compared by light and electron microscopy with focusing on HSCs in each experimental group. Immunohistochemical examination was performed with anti-keratinocyte growth factor (KGF), anti-alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), and anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) antibodies, as markers of fibrosis.
Results
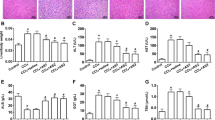
On light microscopic findings, periportal inflammation with bile ductular proliferation was obvious in BDL group and pericentral necrosis with fatty degeneration was observed in CCl4 group, both of which were ameliorated by subcutaneous injection of vitamin A. Electron microscopy showed lipid droplets were almost depleted in the HSCs treated with BDL or CCl4, which improved with vitamin A administration. Immunohistochemistry demonstrated that enhanced expression of all three fibrotic markers in the BDL group was diminished by vitamin A administration.
Conclusions
Although most of our data are qualitative observation, vitamin A may ameliorate hepatic fibrosis in the BDL model by restoring vitamin A in the HSCs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kasai M (1974) Treatment of biliary atresia with special reference to hepatic porto-enterostomy and its modifications. Prog Pediatr Surg 6:5–52
Bates MD, Bucuvalas JC, Alonso MH, Ryckman FC (1998) Biliary atresia: pathogenesis and treatment. Semin Liver Dis 18(3):281–293
Ramm GA, Carr SC, Bridle KR, Li L, Britton RS, Crawford DH, Vogler CA, Bacon BR, Tracy TF (2000) Morphology of liver repair following cholestatic liver injury: resolution of ductal hyperplasia, matrix deposition and regression of myofibroblasts. Liver 20(5):387–396
Canbay A, Higuchi H, Bronk SF, Taniai M, Sebo TJ, Gores GJ (2002) Fas enhances fibrogenesis in the bile duct ligated mouse: a link between apoptosis and fibrosis. Gastroenterology 123(4):1323–1330
Esrefoglu M, Gül M, Emre MH, Polat A, Selimoglu MA (2005) Protective effect of low dose of melatonin against cholestatic oxidative stress after common bile duct ligation in rats. World J Gastroenterol 11(13):1951–1956
Tuchweber B, Desmoulière A, Bochaton-Piallat ML, Rubbia-Brandt L, Gabbiani G (1996) Proliferation and phenotypic modulation of portal fibroblasts in the early stages of cholestatic fibrosis in the rat. Lab Invest 74(1):265–278
Seifert WF, Bosma A, Brouwer A, Hendriks HF, Roholl PJ, van Leeuwen RE, van Thiel-de Ruiter GC, Seifert-Bock I, Knook DL (1994) Vitamin A deficiency potentiates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats. Hepatology 19(1):193–201
Senoo H, Wake K (1985) Suppression of experimental hepatic fibrosis by administration of vitamin A. Lab Invest 52(2):182–194
Noyan S, Cavusoglu I, Minbay FZ (2006) The effect of vitamin A on CCl4-induced hepatic injuries in rats: a histochemical, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. Acta Histochem 107(6):421–434
Vollmar B, Heckmann C, Richter S, Menger MD (2002) High, but not low, dietary retinoids aggravate manifestation of rat liver fibrosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 17(7):791–799
Okuno M, Muto Y, Moriwaki H, Kato M, Noma A, Tagaya O, Nozaki Y, Suzuki Y (1990) Inhibitory effect of acyclic retinoid (polyprenoic acid) on hepatic fibrosis in CCl4-treated rats. Gastroenterol Jpn 25(2):223–229
Amédée-Manesme O, Mourey MS, Therasse J, Couturier M, Alvarez F, Hanck A, Bernard O (1988) Short- and long-term vitamin A treatment in children with cholestasis. Am J Clin Nutr 47(4):690–693
Cassiman D, Libbrecht L, Desmet V, Denef C, Roskams T (2002) Hepatic stellate cell/myofibroblast subpopulations in fibrotic human and rat livers. J Hepatol 36(2):200–209
Murata K, Kamata Y, Munakata H, Sugai M, Sasaki M (2008) Immunohistochemical study on liver fibrosis in biliary atresia. Hepatogastroenterology 55(81):179–183
Floreani A, Baragiotta A, Martines D, Naccarato R, D’odorico A (2000) Plasma antioxidant levels in chronic cholestatic liver diseases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 14(3):353–358
Gundimeda U, Hara SK, Anderson WB, Gopalakrishna R (1993) Retinoids inhibit the oxidative modification of protein kinase C induced by oxidant tumor promoters. Arch Biochem Biophys 300(1):526–530
Steiling H, Mühlbauer M, Bataille F, Schölmerich J, Werner S, Hellerbrand C (2004) Activated hepatic stellate cells express keratinocyte growth factor in chronic liver disease. Am J Pathol 165(4):1233–1241
Akpolat N, Yahsi S, Godekmerdan A, Yalniz M, Demirbag K (2005) The value of alpha-SMA in the evaluation of hepatic fibrosis severity in hepatitis B infection and cirrhosis development: a histopathological and immunohistochemical study. Histopathology 47(3):276–280
Khan MA, Poulos JE, Brunt EM, Li L, Solomon H, Britton RS, Bacon BR, Di Bisceglie AM (2001) Hepatic alpha-smooth muscle actin expression in hepatitis C patients before and after interferon therapy. Hepatogastroenterology 48(37):212–215
Carpino G, Franchitto A, Morini S, Corradini SG, Merli M, Gaudio E (2004) Activated hepatic stellate cells in liver cirrhosis. A morphologic and morphometrical study. Ital J Anat Embryol 109(4):225–238
Malhotra SK, Bhatnagar R, Shnitka TK, Herrera JJ, Koke JR, Singh MV (1995) Rat glioma cell line as a model for astrogliosis. Cytobios 82(328):39–51
Morini S, Carotti S, Carpino G, Franchitto A, Corradini SG, Merli M, Gaudio E (2005) GFAP expression in the liver as an early marker of stellate cells activation. Ital J Anat Embryol 110(4):193–207
Jiroutová A, Majdiaková L, Cermáková M, Köhlerová R, Kanta J (2005) Expression of cytoskeletal proteins in hepatic stellate cells isolated from normal and cirrhotic rat liver. Acta Med (Hradec Kralove) 48(3–4):137–144
Maubach G, Lim MC, Zhang CY, Zhuo L (2006) GFAP promoter directs lacZ expression specifically in a rat hepatic stellate cell line. World J Gastroenterol 12(5):723–730
De Minicis S, Seki E, Uchinami H, Kluwe J, Zhang Y, Brenner DA, Schwabe RF (2007) Gene expression profiles during hepatic stellate cell activation in culture and in vivo. Gastroenterology 132(5):1937–1946
García DM, Weigum SE, Koke JR (2003) GFAP and nuclear lamins share an epitope recognized by monoclonal antibody J1–31. Brain Res 976(1):9–21
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murakami, Ki., Kaji, T., Shimono, R. et al. Therapeutic effects of vitamin A on experimental cholestatic rats with hepatic fibrosis. Pediatr Surg Int 27, 863–870 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-011-2853-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-011-2853-0