Abstract
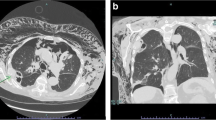
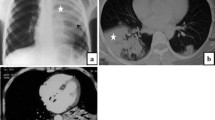
The aim of this work is to prospectively study the value of thoracic ultrasound (US) before pleural drainage in children with parapneumonic effusion (PPE). All children hospitalized for PPE, identified by thoracic radiography, underwent US to assess pleural loculation, echogenicity, and pleural fluid quantity. From August 2001 to July 2003, 52 children were examined. US was performed on 48 of these children, of whom 35 received chest tube drainage and 13 only received clinical treatment. US identified 38 patients with free flowing and 10 with loculated pleural fluid. About 25 of the free flowing (65.8%) and 10 (100%) of the loculated patients received chest tube drainage. Echogenicity was anechoic in 13, echoic without septations in 17 and echoic with septations in 18. Chest tube drainage was required in 6 anechoic (46.15%), 14 echoic without septations (82.35%), and 15 echoic with septations (83.33%). Quantity of fluid estimated by US varied from 20 to 860 ml. Effusion volume was higher in patients that were echoic with septations and loculated effusions. Pleural glucose and pH were lower, and LDH was higher in loculated PPE patients. In conclusion, US is an auxiliary exam for determining whether thoracic drainage is needed in parapneumonic effusion; loculated or echoic effusion should be drained, and free anechoic fluid needs further investigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
*Toshiba® Sonolayer SSH – 140 A/G.
References
DATASUS. Morbidade hospitalar do SUS: por local de internação: Brasil CID. 10 [Accessed 2006 Jan 10]. Available from: http://www.tabnet.datasus.gov.br
Light RW, Girard WM, Jenkinson SG, George RB (1980) Parapneumonic effusions. Am J Med 69:507–512
Beckh S, Bölcskei PL, Lessnau KD (2002) Real-time chest ultrasonography, a comprehensive review for the pulmonologist. Chest 122:1759–1773
Yang PC, Luh KT, Chang DB, Wu HD, Yu CJ, Kuo SH (1992) Value of sonography in determining the nature of pleural effusion: analysis of 320 cases. AJR Am J Roentgenol 152:29–33
Kunyioshi V, Cataneo DC, Cataneo AJM (2006) Complicated pneumonias with empyema and/or pneumatocele in children. Pediatr Surg Int 22:186–190
Hilliard TN, Henderson AJ, Langton HSC (2003) Management of parapneumonic effusion and empyema. Arch Dis Child 88:915–917
Himelman RB, Callen PW (1986) The prognostic value of loculations in parapneumonic pleural effusions. Chest 90:852–856
Shankar KR, Kenny SE, Okoye BO, Carty HM, Lloyd DA, Losty PD (2000) Evolving experience in the management of empyema thoracis. Acta Paediatr 89:417–420
Lemeense GP, Strange C, Sahn SA (1995) Empyema thoracis—therapeutic management and outcome. Chest 107:532–537
Adde A, Oliveira Filho JF, Iazetti AV, Barreiros EE, Gianini JA, Aied M (1979) Derrame pleural na infância. J Pneumol 1:14–21
Davies CWH, Gleeson FV, Davies RJO (2003) BTS guidelines for the management of pleural infection. Thorax 58:18–28
King S, Thomson A (2002) Radiological perspectives in empyema. Br Med Bull 61:203–214
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pinotti, K.F., Ribeiro, S.M. & Cataneo, A.J.M. Thorax ultrasound in the management of pediatric pneumonias complicated with empyema. Pediatr Surg Int 22, 775–778 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-006-1754-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-006-1754-0