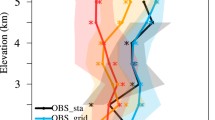
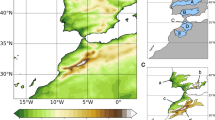
Abstract
The GLACIOCLIM-SAMBA (GS) Antarctic accumulation monitoring network, which extends from the coast of Adelie Land to the Antarctic plateau, has been surveyed annually since 2004. The network includes a 156-km stake-line from the coast inland, along which accumulation shows high spatial and interannual variability with a mean value of 362 mm water equivalent a−1. In this paper, this accumulation is compared with older accumulation reports from between 1971 and 1991. The mean and annual standard deviation and the km-scale spatial pattern of accumulation were seen to be very similar in the older and more recent data. The data did not reveal any significant accumulation trend over the last 40 years. The ECMWF analysis-based forecasts (ERA-40 and ERA-Interim), a stretched-grid global general circulation model (LMDZ4) and three regional circulation models (PMM5, MAR and RACMO2), all with high resolution over Antarctica (27–125 km), were tested against the GS reports. They qualitatively reproduced the meso-scale spatial pattern of the annual-mean accumulation except MAR. MAR significantly underestimated mean accumulation, while LMDZ4 and RACMO2 overestimated it. ERA-40 and the regional models that use ERA-40 as lateral boundary condition qualitatively reproduced the chronology of interannual variability but underestimated the magnitude of interannual variations. Two widely used climatologies for Antarctic accumulation agreed well with the mean GS data. The model-based climatology was also able to reproduce the observed spatial pattern. These data thus provide new stringent constraints on models and other large-scale evaluations of the Antarctic accumulation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arthern RJ, Winebrenner DP, Vaughan DG (2006) Antarctic snow accumulation mapped using polarization of 4.3-cm wavelength microwave emission. J Geophys Res 111:D06107. doi:10.1029/2004JD005667
Bamber JL, Gomez-Dans JL, Griggs JA (2009) Antarctic 1 km digital elevation model (DEM) from combined ERS-1 radar and ICESat laser satellite altimetry. National Snow and Ice Data Center, Boulder
Bromwich DH, Cassano JJ, Klein T, Heinemann G, Hines KM, Steffen K, Box JE (2001) Mesoscale modeling of katabatic winds over Greenland with the polar MM5. Mon Weather Rev 129(9):2290–2309
Cassano JJ, Parish TR, King JC (2001) Evaluation of turbulent surface flux parameterizations for the stable surface layer over Halley, Antarctica. Mon Weather Rev 129(1):26–46
Eisen O, Frezzotti M, Genthon C et al (2008) Ground-based measurements of spatial and temporal variability of snow accumulation in east Antarctica. Rev Geophys 46(1):RG2001. doi:10.1029/2006RG000218
Ettema J, van den Broeke MR, van Meijgaard E, van de Berg WJ, Bamber JL, Box JE, Bales RC (2009) Higher surface mass balance of the Greenland ice sheet revealed by high-resolution climate modeling. Geophys Res Lett 36:L12501. doi:10.1029/2009GL038110
Frezzotti M, Pourchet M, Flora O, Gandolfi S (2004) New estimations of precipitation and surface sublimation in East Antarctica from snow accumulation measurements. Clim Dyn 23:803–813. doi:10.1007/s00382-004-0462-5
Gallée H, Duynkerke PG (1997) Air-snow interactions and the surface energy and mass balance over the melting zone of west Greenland during the Greenland Ice margin experiment. J Geophys Res 102(D12):13813–13824
Gallée H, Pettré P (1998) Dynamical constraints on katabatic wind cessation in Adelie Land, Antarctica. J Atmos Sci 55(10):1755–1770
Gallée H, Schayes G (1994) Development of a 3-dimensional meso-gamma primitive equation model—katabatic winds simulation in the area of Terra-Nova Bay, Antarctica. Mon Weather Rev 122(4):671–685
Gallée H, Guyomarc’h G, Brun E (2001) Impact of snow drift on the Antarctic ice sheet surface mass balance: possible sensitivity to snow-surface properties. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 99:1–19
Genthon C, Kaspari S, Mayewski PA (2005) Interannual variability of the surface mass balance of West Antarctica from ITASE cores and ERA40 reanalyses, 1958–2000. Clim Dyn 24(7–8):759–770. doi:10.1007/s00382-005-0019-2
Genthon C, Lardeux P, Krinner G (2007) The surface accumulation and ablation of a coastal blue-ice area near Cap Prudhomme, Terre Adélie, Antarctica. J Glaciol 53(183):635–645. doi:10.3189/002214307784409333
Genthon C, Krinner G, Castebrunet H (2009) Antarctic precipitation and climate change predictions: horizontal resolution and margin vs plateau issues. Ann Glaciol 50:55–60
Grell GL, Dudhia J, Stauffer DR (1994) A description of the fifth-generation Penn State/NCAR mesoscale model (MM5). NCAR technical note NCAR/TN-398CSTR, p 117. National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado
Helsen MM, van den Broeke MR, van de Wal RSW, van de Berg WJ, van Meijgaard E, Davis CH, Li Y, Goodwin I (2008) Elevation changes in Antarctica mainly determined by accumulation variability. Science 320(5883):1626–1629. doi:10.1126/science.1153894
Hourdin F, Musat I, Bony S et al (2006) The LMDZ4 general circulation model: climate performance and sensitivity to parametrized physics with emphasis on tropical convection. Clim Dyn 27:787–813. doi:10.1007/s00382-006-0158-0
IPCC (2007) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
King JC, Turner J (1997) Antarctic meteorology and climatology. Cambridge atmospheric and space science series. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kitanidis PK (1997) Introduction to geostatistics: applications to hydrogeology. Cambridge University Press, New York
König-Langlo G, King JC, Pettré P (1998) Climatology of the three coastal Antarctic stations Dumont d’Urville, Neumayer, and Halley. J Geophys Res 103(D9):10935–10946
Krinner G, Genthon C, Li ZX, Le Van P (1997) Studies of the Antarctic climate with a stretched-grid general circulation model. J Geophys Res 102(D12):13731–13745
Krinner G, Magand O, Simmonds I, Genthon C, Dufresne J (2007) Simulated Antarctic precipitation and surface mass balance at the end of the twentieth and twenty-first centuries. Clim Dyn 28(2–3):215–230. doi:10.1007/s00382-006-0177-x
Lenaerts JTM, van den Broeke MR, Déry SJ, König-Langlo G, Ettema J, Munneke PK (2010) Modelling snowdrift sublimation on an Antarctic ice shelf. The Cryosphere 4(2):179–190. doi:10.5194/tc-4-179-2010
Magand O, Genthon C, Fily M, Krinner G, Picard G, Frezzotti M, Ekaykin AA (2007) An up-to-date quality-controlled surface mass balance data set for the 90 degrees-180 degrees E Antarctica sector and 1950–2005 period. J Geophys Res 112(D12):D12106. doi:10.1029/2006JD007691
Magand O, Picard G, Brucker L, Fily M, Genthon C (2008) Snow melting bias in microwave mapping of Antarctic snow accumulation. The Cryosphere 2:109–115
Marti O, Braconnot P, Bellier J et al (2006) The new IPSL climate system model: IPSL-CM4. Note du Pôle de Modélisation n. 26. IPSL, ISSN 1288–1619
Mayewski PA, Meredith MP, Summerhayes CP et al (2009) State of the Antarctic and Southern Ocean climate system. Rev Geophys 47:RG1003. doi:10.1029/2007RG000231
Monaghan AJ, Bromwich DH, Fogt RL et al (2006a) Insignificant change in Antarctic snowfall since the International Geophysical Year. Science 313(5788):827–831. doi:10.1126/science.1128243
Monaghan AJ, Bromwich DH, Wang S (2006b) Recent trends in Antarctic snow accumulation from polar MM5 simulations. Philos Trans R Soc A 364(1844):1683–1708. doi:10.1098/rsta.2006.1795
Pettré P, Pinglot JF, Pourchet M, Reynaud L (1986) Accumulation distribution in Terre Adélie, Antarctica: effect of meteorological parameters. J Glaciol 32(112112):486–500
Richardson-Näslund C (2004) Spatial characteristics of snow accumulation in Dronning Maud Land, Antarctica. Glob Planet Chang 42(1–4):31–43. doi:10.1016/j.gloplacha.2003.11.009
Rignot E, Bamber JL, van den Broeke MR, Davis C, Li Y, van de Berg WJ, van Meijgaard E (2008) Recent Antarctic ice mass loss from radar interferometry and regional climate modelling. Nat Geosci 1(2):106–110. doi:10.1038/ngeo102
Simmons A, Uppala S, Dee D, Kobayashi S (2006) ERA-interim: new ECMWF reanalysis products from 1989 onwards. ECMWF Newslett 110:25–35
Uppala SM, Kallberg PW, Simmons AJ et al (2005) The ERA-40 re-analysis. Q J R Meteorol Soc 131(612):2961–3012. doi:10.1256/qj.04.176
van de Berg WJ, van den Broeke MR, Reijmer C, van Meijgaard E (2006) Reassessment of the Antarctic surface mass balance using calibrated output of a regional atmospheric climate model. J Geophys Res 111:D11104. doi:10.1029/2005JD006495
Vaughan DG, Russell J (1997) Compilation of surface mass balance measurements in Antarctica. Internal rep. ES4/8/1/1997/1. British Antarctic Survey, Cambridge, UK
Acknowledgments
The GLACIOCLIM-SAMBA observatory is supported by IPEV (Institut Polaire Paul-Emile Victor) and INSU (Institut National des Sciences de l’Univers). IPEV also provided archives of older SMB measurements. Data mining, processing and analysis were done as part of Europe’s FP4 Ice2sea and the French INSU/LEFE CHARMANT programs. We acknowledge the ice2sea project, funded by the European Commission’s 7th Framework Programme through grant number 226375, ice2sea manuscript number 023. IDRIS (Institut du Développement et des Ressources en Informatique Scientifique) provided computing time for the MAR and LMDZ4 models. We thank the Antartic Hindcast Project (http://www.polarmet.osu.edu/PolarMet/ant_hindcast.html) for sharing Polar MM5 simulation results. Many people at IPEV and at LGGE have contributed to make the GLACIOCLIM-SAMBA system deployment and annual campaigns successful. We thank the three anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agosta, C., Favier, V., Genthon, C. et al. A 40-year accumulation dataset for Adelie Land, Antarctica and its application for model validation. Clim Dyn 38, 75–86 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-011-1103-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-011-1103-4