Abstract
Background
Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) is an autosomal dominant disorder, mainly in childhood presents epilepsy due to cortical tubers. TSC1/TSC2 pathogenic variants cannot be detected in regular molecular genetic testing in around 10-15% of TSC patients.
Methods
We analyzed TSC genes in both cortical tuber, blood and skin samples from a pediatric patient with refractory epilepsy.
Results
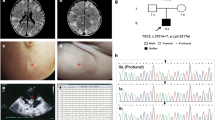
We found no germline mutations by whole-exome sequencing. Well in targeted sequencing of TSC1/2 data, we identified de novo mutations only in cortical tuber: TSC2 NM_000548.5: exon34:c.4183C>T (p.Gln1395*) in 3% of the alleles. No other TSC mutations were found in patient’s blood and skin samples and her parents’ blood sample.
Conclusion
Our case report found TSC2 mosaic mutations can be only limited to cortical tuber in patients with TSC.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TSC:
-
Tuberous sclerosis complex
- NGS:
-
Next generation sequencing
- NMI:
-
No mutations identified
- WES:
-
Whole-exome sequencing
References
Peron A, Au KS, Northrup H (2018) Genetics, genomics, and genotype-phenotype correlations of TSC: Insights for clinical practice. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 178(3):281–290. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.c.31651
Ding Y, Wang J, Zhou S, Zhou Y, Zhang L, Yu L, Wang Y (2020) Genotype and phenotype analysis of chinese children with tuberous sclerosis complex: a pediatric cohort study. Front Genet 11:204. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00204
Avgeris S, Fostira F, Vagena A, Ninios Y, Delimitsou A, Vodicka R, Vrtel R, Youroukos S, Stravopodis DJ, Vlassi M, Astrinidis A, Yannoukakos D, Voutsinas GE (2017) Mutational analysis of TSC1 and TSC2 genes in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex patients from Greece. Sci Rep 7(1):16697. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16988-w
Au KS, Williams AT, Roach ES, Batchelor L, Sparagana SP, Delgado MR, Wheless JW, Baumgartner JE, Roa BB, Wilson CM, Smith-Knuppel TK, Cheung MY, Whittemore VH, King TM, Northrup H (2007) Genotype/phenotype correlation in 325 individuals referred for a diagnosis of tuberous sclerosis complex in the United States. Genet Med 9(2):88–100. https://doi.org/10.1097/gim.0b013e31803068c7
Tyburczy ME, Dies KA, Glass J, Camposano S, Chekaluk Y, Thorner AR, Lin L, Krueger D, Franz DN, Thiele EA, Sahin M, Kwiatkowski DJ (2015) Mosaic and intronic mutations in TSC1/TSC2 explain the majority of TSC patients with no mutation identified by conventional testing. PLoS Genet 11(11):e1005637. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen
Curatolo P, Moavero R, de Vries PJ (2015) Neurological and neuropsychiatric aspects of tuberous sclerosis complex. Lancet Neurol 14(7):733–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00069-1
Samueli S, Abraham K, Dressler A, Groeppel G, Jonak C, Muehlebner A, Prayer D, Reitner A, Feucht M, Pädiatrisches TSC-Zentrum Wien (2015) Tuberous sclerosis complex: new criteria for diagnostic work-up and management. Wien Klin Wochenschr 127(15-16):619–630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-015-0758-y
Nellist M, Brouwer RW, Kockx CE, van Veghel-Plandsoen M, Withagen-Hermans C, Prins-Bakker L, Hoogeveen-Westerveld M, Mrsic A, van den Berg MM, Koopmans AE, de Wit MC, Jansen FE, Maat-Kievit AJ, van den Ouweland A, Halley D, de Klein A, van IJcken WF (2015) Targeted next generation sequencing reveals previously unidentified TSC1 and TSC2 mutations. BMC Med Genet 16:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12881-015-0155-4
Martin KR, Zhou W, Bowman MJ, Shih J, Au KS, Dittenhafer-Reed KE, Sisson KA, Koeman J, Weisenberger DJ, Cottingham SL, DeRoos ST, Devinsky O, Winn ME, Cherniack AD, Shen H, Northrup H, Krueger DA, MacKeigan JP (2017) The genomic landscape of tuberous sclerosis complex. Nat Commun 8:15816. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15816
Goswami S, Hsieh J (2019) One-hit wonders and 2-hit tubers: a second-hit to TSC2 Causes tuber-like cells in spheroids. Epilepsy Curr 19(1):49–50. https://doi.org/10.1177/1535759718822036
Bongaarts A, Giannikou K, Reinten RJ, Anink JJ, Mills JD, Jansen FE, Spliet GMW, den Dunnen WFA, Coras R, Blümcke I, Paulus W, Scholl T, Feucht M, Kotulska K, Jozwiak S, Buccoliero AM, Caporalini C, Giordano F, Genitori L, Söylemezoğlu F, Pimentel J, Nellist M, Schouten-van Meeteren AYN, Nag A, Mühlebner A, Kwiatkowski DJ, Aronica E (2017) Subependymal giant cell astrocytomas in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex have consistent TSC1/TSC2 biallelic inactivation, and no BRAF mutations. Oncotarget 8(56):95516–95529. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20764
Winden KD, Sundberg M, Yang C, Wafa SMA, Dwyer S, Chen PF, Buttermore ED, Sahin M (2019) Biallelic mutations in TSC2 lead to abnormalities associated with cortical tubers in human iPSC-derived neurons. J Neurosci 39(47):9294–9305. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0642-19.2019
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank to patient and family who contributed to this study. We also thank Lei Liu for his assistance in genetic analysis.
Availability of data and materials
The hg38/GRCh38 human reference genome (https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgTracks?db=hg38&position=lastDbPos) was used as the reference dataset in this study. The reference sequence used for the validation of the c.4183C>T (p.Gln1395*) variant in TSC2 was obtained from NCBI Nucleotide using the accession number NM_000548.5. The variation is available in the Clinvar and HGMD PRO database, with accession ID: VCV000280596 and CM174666 respectively.
Funding
This study was supported by Research Project of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (201940351) and the science and technology commission of Shanghai (18411962000). The funding bodies played no direct role in the design of the study, the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data, or the writing of the manuscript. The cost of sequencing was borne by the two funding projects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YFZ is the first author and performed data analysis and interpretation, and drafted the manuscript. XHW, JW, and YFD performed interpretation of clinical data. HL and YW conceived the idea for the study and supervised the study. BBW and RZH are the corresponding authors and conceived the idea for the study, designed the experiments, responsible for the analysis and interpretation of sequencing data, and drafted and revised the manuscript content. All authors participated in the proofreading. The authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The local ethics committee of Children’s Hospital of Fudan University approved the study protocol.
Consent to participate
Parents gave written informed consent for study participation
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication for identifying images or other personal or clinical details was obtained from both the patient’s parents.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Wang, X., Wang, J. et al. Identification of TSC2 mosaic mutation limited to cortical tuber with TSC targeted sequencing: a case report and literature review. Childs Nerv Syst 37, 3945–3949 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-021-05059-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-021-05059-1