Abstract
Purpose
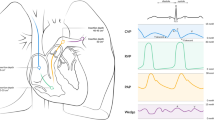
Nonlinear dynamics has enhanced the diagnostic abilities of some physiological signals. Recent studies have shown that the complexity of the intracranial pressure waveform decreases during periods of intracranial hypertension in paediatric patients with acute brain injury. We wanted to assess changes in the complexity of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure signal over the large range covered during the study of CSF circulation with infusion studies.
Methods
We performed 37 infusion studies in patients with hydrocephalus of various types and origin (median age 71 years; interquartile range 60–77 years). After 5 min of baseline measurement, infusion was started at a rate of 1.5 ml/min until a plateau was reached. Once the infusion finished, CSF pressure was recorded until it returned to baseline. We analysed CSF pressure signals using the Lempel–Ziv (LZ) complexity measure. To characterise more accurately the behaviour of LZ complexity, the study was segmented into four periods: basal, early infusion, plateau and recovery.
Results
The LZ complexity of the CSF pressure decreased in the plateau of the infusion study compared to the basal complexity (p = 0.0018). This indicates loss of complexity of the CSF pulse waveform with intracranial hypertension. We also noted that the level of complexity begins to increase when the infusion is interrupted and CSF pressure drops towards the initial values.
Conclusions
The LZ complexity decreases when CSF pressure reaches the range of intracranial hypertension during infusion studies. This finding provides further evidence of a phenomenon of decomplexification in the pulsatile component of the pressure signal during intracranial hypertension.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katzman R, Hussey F (1970) A simple constant-infusion manometric test for measurement of CSF absorption. I. Rationale and method. Neurology 20:534–544
Agren-Wilsson A, Eklund A, Koskinen LO, Bergenheim AT, Malm J (2005) Brain energy metabolism and intracranial pressure in idiopathic adult hydrocephalus syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:1088–1093
Momjian S, Czosnyka Z, Czosnyka M, Pickard JD (2004) Link between vasogenic waves of intracranial pressure and cerebrospinal fluid outflow resistance in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Br J Neurosurg 18:56–61
Schmidt EA, Czosnyka Z, Momjian S, Czosnyka M, Bech RA, Pickard JD (2005) Intracranial baroreflex yielding an early Cushing response in human. Acta Neurochir Suppl 95:253–256
Hornero R, Aboy M, Abásolo D, McNames J, Goldstein B (2005) Interpretation of approximate entropy: analysis of intracranial pressure approximate entropy during acute intracranial hypertension. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 52:1671–1680
Lempel A, Ziv J (1976) On the complexity of finite sequences. IEEE Trans Inform Theory 22:75–81
Nagarajan R (2002) Quantifying physiological data with Lempel–Ziv complexity—certain issues. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 49:1371–1373
Zhang XS, Roy RJ, Jensen EW (2001) EEG complexity as a measure of depth of anesthesia for patients. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 48:1424–1433
Zhang XS, Roy RJ (1999) Predicting movement during anaesthesia by complexity analysis of electroencephalograms. Med Biol Eng Comput 37:327–334
Zhang XS, Zhu YS, Thakor NV, Wang ZZ (1999) Detecting ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation by complexity measure. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 46:548–555
Hornero R, Aboy M, Abásolo D, McNames J, Wakeland W, Goldstein B (2006) Complex analysis of intracranial hypertension using approximate entropy. Crit Care Med 34:87–95
Hornero R, Aboy M, Abásolo D (2007) Analysis of intracranial pressure during intracranial hypertension using Lempel–Ziv complexity: further evidence. Med Bio Eng Comput 45:617–620
Radhakrishnan N, Gangadhar BN (1998) Estimating regularity in epileptic seizure time series data. A complexity–measure approach. IEEE Eng Med Biol 17:89–94
Aboy M, Hornero R, Abásolo D, Álvarez D (2006) Interpretation of the Lempel–Ziv complexity measure in the context of biomedical signal analysis. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 53:2282–2288
Gusev VD, Memytikova LA, Chuzhanova NA (1999) On the complexity measures of genetic sequences. Bioinformatics 15:994–999
Orlov YL, Potapov VN (2004) Complexity: an internet resource for analysis of DNA sequence complexity. Nucleic Acids Res 32:W628–W633
Abásolo D, Hornero R, Gomez C, Garcia M, Lopez M (2006) Analysis of EEG background activity in Alzheimer’s disease patients with Lempel–Ziv complexity and central tendency measure. Med Eng Phys 28:315–322
Godin PJ, Buchman TG (1996) Uncoupling of biological oscillators: a complementary hypothesis concerning the pathogenesis of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Crit Care Med 24:1107–1116
Goldberger AL, Amaral LA, Hausdorff JM, Inanov P, Peng CK, Stanley HE (2002) Fractal dynamics in physiology: alterations with disease and aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99(1):2466–2472
Goldberger AL (1996) Non-linear dynamics for clinicians: chaos theory, fractals and complexity at the bedside. Lancet 347:1312–1314
Di Rocco C, Pettorossi VE, Caldarelli M, Mancinelli R, Velardi F (1977) Experimental hydrocephalus following mechanical increment of intraventricular pressure. Experientia 33:1470–1472
Eide PK (2006) Intracranial pressure parameters in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus patients treated with ventriculo-peritoneal shunts. Acta Neurochir 148:21–29
Holm S, Eide PK (2008) The frequency domain versus time domain methods for processing of intracranial pressure signals. Med Eng Phys 30:164–170
Schuhman M, Sood S, McAllister J, Jaeger M, Ham S, Czosnyka Z, Czosnyka M (2008) Value of overnight monitoring of intracranial pressure in hydrocephalic children. Pediatr Neurosurg 44:269–279
Cushing H (1901) Concerning a definite regulatory mechanism of vasomotor centre which controls blood pressure during cerebral compression. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp 12:290–292
Johnston IH, Rowan JO, Harper AM, Jennett WB (1972) Raised intracranial pressure and cerebral blood flow. I. Cisterna magna infusion in primates. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 35(3):285–296
Rowan JO, Teasdale G (1997) Brain stem blood flow during raised intracranial pressure. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 64:520–521
Nakamura K, Osborn JW Jr, Cowley AW Jr (1987) Pressure response to small elevations of cerebroventricular pressure in conscious rats. Hypertension 10(6):635–641
Pincus SM (1994) Greater signal regularity may indicate increased system isolation. Math Biosci 122:161–181
Goldstein B, Toweill D, Lai S, Sonnenthal K, Kimberly B (1998) Uncoupling of the autonomic and cardiovascular systems in acute brain injury. Am J Physiol 275:1287–1292
Goldstein B, DeKing DE, DeLong D, Kempski M, Cox C, Kelly M, Nichols DD, Woolf PD (1993) Autonomic cardiovascular state following severe head injury and brain death. Crit Care Med 21:228–233
Ellenby MS, McNames J, Lai S et al (2001) Uncoupling and recoupling of autonomic regulation of the heart beat in pediatric septic shock. Shock 16:274–277
Kyriazis M (2003) Practical applications of chaos theory to the modulation of human ageing: nature prefers chaos to regularity. Biogerontology 4:75–90
Gomez C, Hornero R, Abásolo D, Fernandez A, Lopez M (2006) Complexity analysis of the magnetoencephalogram background activity in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Med Eng Phys 28:851–859
Na SH, Jin SH, Kim SY, Ham BJ (2002) EEG in schizophrenic patients: mutual information analysis. Clin Neurophysiol 113:1954–1960
Jeong J, Chae JH, Kim SY, Han SH (2001) Nonlinear dynamic analysis of the EEG in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. J Clin Neurophysiol 18:58–67
Acknowledgements
This study has been partially supported by the Consejería de Sanidad, Junta de Castilla y León (project code SOCIO126/LE04/09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santamarta, D., Hornero, R., Abásolo, D. et al. Complexity analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid pulse waveform during infusion studies. Childs Nerv Syst 26, 1683–1689 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-010-1244-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-010-1244-5