Abstract
Object
The aim of this study is to evaluate the outcome of young children hospitalized for non-accidental head trauma in our PICU, to evaluate PRISM II score in this sub-population of pediatric trauma and to identify factors that might influence the short-term outcome.
Materials and methods
Files of all children less than 2 years old with the diagnosis of non-accidental head trauma over a 10-years period were systematically reviewed. We collected data on demographic information, medical history, clinical status, and management in the PICU. Three severity scores were then calculated: PRISM II, Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), and Pediatric Trauma Score (PTS). Prognosis value of qualitative variables was tested with a univariate procedure analysis (anemia, diabetes insipidus...). Then, quantitative variables were tested with univariate procedure too (age, weight, PRISM II, GCS, Platelet count, fibrin, prothrombine time (PT)...). Potential association between variables and death was tested using univariate procedure. Variables identified by univariate analysis were then analyzed with multivariate analysis through a forward-stepping logistic regression.
Results
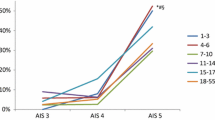
Thirty-six children were included. Mean age was 5.5 months (8 days–21.5 months). Mortality rate was 27.8%. At admission, PTS, PRISM II, GCS, PT, PTT, and diabetes insipidus were significantly altered or more frequent in non survivors. Cutoff value for PRISM II at which risk of mortality increased was 17.5 (sensitivity = 0.8; specificity = 0.88).
Conclusion
PRISM II is a reliable and easy performing tool for assessing the prognosis of non-accidental cranial traumatism in young children. GCS and PTS, scores even simpler than PRISM II, showed good accuracy regarding survival prediction.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahloul M, Chelly H, Ben Hmida M, Ben Hamida C, Ksibi H, Kallel H, Chaari A, Kassis M, Rekik N, Bouaziz M (2004) Prognosis of traumatic head injury in South Tunisia: a multivariate analysis of 437 cases. J Trauma 57:255–261
Baulieu F, Fournier P, Baulieu JL, Dalonneau M, Chiaroni P, Eder V, Pottier JM, Legros B (2001) Technetium-99m ECD single photon emission computed tomography in brain trauma: comparison of early scintigraphic findings with long-term neuropsychological outcome. J Neuroimaging 11:112–120
Bayreuther J, Wagener S, Woodford M, Edwards A, Lecky F, Bouamra O, Dykes E (2009) Paediatric trauma: injury pattern and mortality in the UK. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed 94:37–41
Behan LA, Phillips J, Thompson CJ, Agha A (2008) Neuroendocrine disorders after traumatic brain injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79:753–759
Bode H (1989) Transcranial Doppler sonography in childhood. 1. Study technic and biological effect magnitudes. Ultraschall Med 10:54–59
Bode H, Eden A (1989) Transcranial Doppler sonography in children. J Child Neurol 4(Suppl):S68–S76
Born JD, Albert A, Hans P, Bonnal J (1985) Relative prognostic value of best motor response and brain stem reflexes in patients with severe head injury. Neurosurgery 16:595–601
Boughey JC, Yost MJ, Bynoe RP (2004) Diabetes insipidus in the head-injured patient. Am Surg 70:500–503
Braakman R, Gelpke GJ, Habbema JD, Maas AI, Minderhoud JM (1980) Systematic selection of prognostic features in patients with severe head injury. Neurosurgery 6:362–370
Caffey J (1972) On the theory and practice of shaking infants. Its potential residual effects of permanent brain damage and mental retardation. Am J Dis Child 124:161–169
Cantais E, Paut O, Giorgi R, Viard L, Camboulives J (2001) Evaluating the prognosis of multiple, severely traumatized children in the intensive care unit. Intensive Care Med 27:1511–1517
Case ME (2007) Abusive head injuries in infants and young children. Leg Med (Tokyo) 9:83–87
Case ME (2008) Accidental traumatic head injury in infants and young children. Brain Pathol 18:583–589
Castellanos-Ortega A, Delgado-Rodriguez M (2000) Comparison of the performance of two general and three specific scoring systems for meningococcal septic shock in children. Crit Care Med 28:2967–2973
Castello FV, Cassano A, Gregory P, Hammond J (1999) The Pediatric Risk of Mortality (PRISM) Score and Injury Severity Score (ISS) for predicting resource utilization and outcome of intensive care in pediatric trauma. Crit Care Med 27:985–988
Chan KH, Miller JD, Dearden NM, Andrews PJ, Midgley S (1992) The effect of changes in cerebral perfusion pressure upon middle cerebral artery blood flow velocity and jugular bulb venous oxygen saturation after severe brain injury. J Neurosurg 77:55–61
Chiesa A, Duhaime AC (2009) Abusive head trauma. Pediatr Clin N Am 56:317–331
Claret Teruel G, Palomeque Rico A, Cambra Lasaosa FJ, Catala Temprano A, Noguera Julian A, Costa Clara JM (2007) Severe head injury among children: computed tomography evaluation as a prognostic factor. J Pediatr Surg 42:1903–1906
Cold G, Enevoldsen E, Malmros R (1975) Ventricular fluid lactate, pyruvate, bicarbonate and PH in unconscious brain-injured patients subjected to controlled ventilation. Acta Neurol Scand 52:187–195
Deerojanawong J, Prapphal N, Udomittipong K (2001) PRISM score and factors predicting mortality of patients with respiratory failure in the pediatric intensive care unit. J Med Assoc Thai 84(Suppl 1):S68–75
Diamond IR, Parkin PC, Wales PW, Bohn D, Kreller MA, Dykes EH, McLellan BA, Wesson DE (2009) Preventable pediatric trauma deaths in Ontario: a comparative population-based study. J Trauma 66:1189–1194, discussion 1194–1185
Duhaime AC, Christian CW, Rorke LB, Zimmerman RA (1998) Nonaccidental head injury in infants—the “shaken-baby syndrome”. N Engl J Med 338:1822–1829
Duhaime AC, Gennarelli TA, Thibault LE, Bruce DA, Margulies SS, Wiser R (1987) The shaken baby syndrome. a clinical, pathological, and biomechanical study. J Neurosurg 66:409–415
Elner VM (2008) Ocular manifestations of child abuse. Arch Ophthalmol 126:1141–1142
Faleiro RM, Faleiro LC, Caetano E, Gomide I, Pita C, Coelho G, Bras E, Carvalho B, Gusmao SN (2008) Decompressive craniotomy: prognostic factors and complications in 89 patients. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 66:369–373
Farin A, Marshall LF (2004) Lessons from epidemiologic studies in clinical trials of traumatic brain injury. Acta Neurochir Suppl 89:101–107
Fernandez C, Lopez-Herce J, Flores JC, Galaviz D, Ruperez M, Brandstrup KB, Bustinza A (2005) Prognosis in critically ill children requiring continuous renal replacement therapy. Pediatr Nephrol 20:1473–1477
Figaji AA, Zwane E, Fieggen AG, Peter JC, Leroux PD (2008) Acute clinical grading in pediatric severe traumatic brain injury and its association with subsequent intracranial pressure, cerebral perfusion pressure, and brain oxygenation. Neurosurg Focus 25:E4
Geddes JF, Hackshaw AK, Vowles GH, Nickols CD, Whitwell HL (2001) Neuropathology of inflicted head injury in children. I. Patterns of brain damage. Brain 124:1290–1298
Geddes JF, Vowles GH, Hackshaw AK, Nickols CD, Scott IS, Whitwell HL (2001) Neuropathology of inflicted head injury in children. II. Microscopic brain injury in infants. Brain 124:1299–1306
Geddes JF, Whitwell HL (2004) Inflicted head injury in infants. Forensic Sci Int 146:83–88
Gerardin P, Rogier C, Leteurtre S, Jouvencel P, Ka AS, Imbert P (2006) Evaluation of Pediatric Risk of Mortality (PRISM) scoring in African children with falciparum malaria. Pediatr Crit Care Med 7:45–47
Gilliland MG, Folberg R (1996) Shaken babies—some have no impact injuries. J Forensic Sci 41:114–116
Gonzalez-Luis G, Pons M, Cambra FJ, Martin JM, Palomeque A (2001) Use of the Pediatric Risk of Mortality Score as predictor of death and serious neurologic damage in children after submersion. Pediatr Emerg Care 17:405–409
Gutterman P, Shenkin HA (1970) Prognostic features in recovery from traumatic decerebration. J Neurosurg 32:330–335
Hadjizacharia P, Beale EO, Inaba K, Chan LS, Demetriades D (2008) Acute diabetes insipidus in severe head injury: a prospective study. J Am Coll Surg 207:477–484
Hukkelhoven CW, Steyerberg EW, Habbema JD, Farace E, Marmarou A, Murray GD, Marshall LF, Maas AI (2005) Predicting outcome after traumatic brain injury: development and validation of a prognostic score based on admission characteristics. J Neurotrauma 22:1025–1039
Hymel KP, Abshire TC, Luckey DW, Jenny C (1997) Coagulopathy in pediatric abusive head trauma. Pediatrics 99:371–375
Jackson RG, Samra GS, Radcliffe J, Clark GH, Price CP (2000) The early fall in levels of S-100 beta in traumatic brain injury. Clin Chem Lab Med 38:1165–1167
Klem SA, Pollack MM, Glass NL, Spohn WA, Kanter RK, Zucker AR, Ruttimann UE (1990) Resource use, efficiency, and outcome prediction in pediatric intensive care of trauma patients. J Trauma 30:32–36
Marcin JP, Pretzlaff RK, Pollack MM, Patel KM, Ruttimann UE (2004) Certainty and mortality prediction in critically ill children. J Med Ethics 30:304–307
Marmarou A, Lu J, Butcher I, McHugh GS, Murray GD, Steyerberg EW, Mushkudiani NA, Choi S, Maas AI (2007) Prognostic value of the Glasgow Coma Scale and pupil reactivity in traumatic brain injury assessed pre-hospital and on enrollment: an IMPACT analysis. J Neurotrauma 24:270–280
Matos RI, Holcomb JB, Callahan C, Spinella PC (2008) Increased mortality rates of young children with traumatic injuries at a US army combat support hospital in Baghdad, Iraq, 2004. Pediatrics 122:e959–966
Mazurek A (1994) Pediatric injury patterns. Int Anesthesiol Clin 32:11–25
Meyer PG, Ducrocq S, Carli P (2001) Pediatric neurologic emergencies. Curr Opin Crit Care 7:81–87
Meyer S, Gottschling S, Biran T, Georg T, Ehlayil K, Graf N, Gortner L (2005) Assessing the risk of mortality in paediatric cancer patients admitted to the paediatric intensive care unit: a novel risk score? Eur J Pediatr 164:563–567
Mok JY (2008) Non-accidental injury in children—an update. Injury 39:978–985
Narci A, Solak O, Turhan-Haktanir N, Aycicek A, Demir Y, Ela Y, Ozkaraca E, Terzi Y (2009) The prognostic importance of trauma scoring systems in pediatric patients. Pediatr Surg Int 25:25–30
Ong L, Selladurai BM, Dhillon MK, Atan M, Lye MS (1996) The prognostic value of the Glasgow Coma Scale, hypoxia and computerised tomography in outcome prediction of pediatric head injury. Pediatr Neurosurg 24:285–291
Ono J, Yamaura A, Kubota M, Okimura Y, Isobe K (2001) Outcome prediction in severe head injury: analyses of clinical prognostic factors. J Clin Neurosci 8:120–123
Orliaguet GA, Meyer PG, Blanot S, Jarreau MM, Charron B, Buisson C, Carli PA (1998) Predictive factors of outcome in severely traumatized children. Anesth Analg 87:537–542
Pollack MM, Ruttimann UE, Getson PR (1988) Pediatric risk of mortality (PRISM) score. Crit Care Med 16:1110–1116
Riffel B, Stohr M, Graser W, Trost E, Baumgartner H (1989) Early prognosis in severe cranio-cerebral trauma using the Glasgow Coma Score and evoked potentials. Anaesthesist 38:51–58
Selladurai BM, Jayakumar R, Tan YY, Low HC (1992) Outcome prediction in early management of severe head injury: an experience in Malaysia. Br J Neurosurg 6:549–557
Steiger HJ, Aaslid R, Stooss R, Seiler RW (1994) Transcranial Doppler monitoring in head injury: relations between type of injury, flow velocities, vasoreactivity, and outcome. Neurosurgery 34:79–85, discussion 85–76
Zakhary MM, Wesolowski JR, Sewick AE, Carlson M, Mehrotha N, Maly P, Sundgren PC (2009) Prevalence and etiology of intracranial hemorrhage in term children under the age of two years: a retrospective study of computerized tomographic imaging and clinical outcome in 798 children. Acad Radiol 16:572–577
Zuckerman GB, Gregory PM, Santos-Damiani SM (1998) Predictors of death and neurologic impairment in pediatric submersion injuries. The Pediatric Risk of Mortality Score. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 152:134–140
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
We have no financial support for this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scavarda, D., Gabaudan, C., Ughetto, F. et al. Initial predictive factors of outcome in severe non-accidental head trauma in children. Childs Nerv Syst 26, 1555–1561 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-010-1150-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-010-1150-x