Abstract
Objects
Puncture of the ventricular system as one of the most frequently performed operative procedures in neurosurgery is usually done in a freehand way without guiding devices. The objective of this study is to examine whether ultrasonic guidance is able to heighten the accuracy of ventricular tapping.
Methods
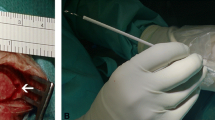
Real-time imaging via a single burr hole approach is achieved by aid of a bajonet-like shaped transducer with a footprint of 8x8 mm only (EUP-NS32, Hitachi Medical Systems). The needle is advanced towards the frontal horn along a displayed guideline. 51 punctures in 48 patients were performed with ultrasonic guidance and compared to 85 punctures in 67 patients without a guiding device.
Conclusion
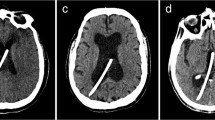
The presented ultrasound method was not able to heighten the access rate of ventricular tapping, but it improved correct positioning of the catheter tip inside the frontal horn of the ventricular system significantly.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bode H, Strassburg HM, Bohlayer R, Gilsbach HJ (1985) Sonographic position and functional diagnosis of ventricular positioned shunt systems in infants with hydrocephalus. Klin Padiatr 197:94–97, (Ger)
Choudhury AR (1993) CT measurement of the ventricular catheter length in shunt surgery. Br J Neurosurg 7:541–544
Dickerman RD, McConathy WJ, Morgan J, Stevens QE, Jolley JT, Schneider S, Mittler MA (2005) Failure rate of frontal versus parietal approaches for proximal catheter placement in ventriculoperitoneal shunts: revisited. J Clin Neurosci 12:781–783
Frank E, Kohler E, Hein L (1989) A modification of the Brown–Roberts–Wells stereotactic frame for implantation of ventricular access reservoirs. Neurosurgery 25:839–841
Ghajar JB (1985) A guide for ventricular catheter placement. J Neurosurg 63:985–986
Gil Z, Siomin V, Beni-Adani L, Ben Sira L, Constantini S (2002) Ventricular catheter placement in children with hydrocephalus and small ventricles: the use of a frameless neuronavigation system. Child’s Nerv Syst 18:26–29
Gomez CR (1995) Ultrasonic ventriculostomy stylet. Neurosurgery 37:1020–1021
Howard MA 3rd, Srinivasan J, Bevering CG, Winn HR, Grady MS (1995) A guide to placement of parietooccipital ventricular catheters. Technical note. J Neurosurg 82:300–304
Imaizumi S, Onuma T, Mino M, Kameyama M, Motohashi O (2001) Free hand aspiration for large periventricular hemorrhage. Case report. Surg Neurol 55:376–377
Kaufman BA, Park TS (1999) Ventricular anatomy and shunt catheters. Pediatr Neurosurg 31:1–6
Kellnar S, Boehm R, Ring E (1995) Ventriculoscopy-aided implantation of ventricular shunts in patients with hydrocephalus. J Pediatr Surg 30:1450–1451
Kestle JR, Drake JM, Cochrane DD, Milner R, Walker ML, Abbott R 3rd, Boop FA, Endoscopic Shunt Insertion Trial participants (2003) Lack of benefit of endoscopic ventriculoperitoneal shunt insertion: a multicenter randomized trial. J Neurosurg 98:284–290
Kim YB, Lee JW, Lee KS, Lee KC (2006) Image-guided placement of ventricular shunt catheter. J Clin Neurosci 13:50–54
Krombach G, Ganser A, Fricke C, Rohde V, Reinges M, Gilsbach J, Spetzger U (2000) Virtual placement of frontal ventricular catheters using frameless neuronavigation: an “unbloody training” for young neurosurgeons. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 43:171–175
Krötz M, Linsenmaier U, Kanz KG, Pfeifer KJ, Mutschler W, Reiser M (2004) Evaluation of minimally invasive percutaneous CT-controlled ventriculostomy in patients with severe head trauma. Eur Radiol 14:227–233
Melada A, Heinrich Z, Chudy D, Scap M, Rotim K (2000) The difference between ultrasound-guided and stereotactic-guided neurosurgical procedures. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 43:149–152
Missori P, Artizzu S, Salvati M (2000) Immediate postoperative CT to assess the correct positioning of a ventricular catheter. Br J Neurosurg 14:44–45
O’Leary ST, Kole MK, Hoover DA, Hysell SE, Thomas A, Shaffrey CI (2000) Efficacy of the Ghajar guide revisited: a prospective study. J Neurosurg 92:801–803
Pang D, Grabb PA (1994) Accurate placement of coronal ventricular catheter using stereotactic coordinate-guided free-hand passage. Technical note. J Neurosurg 80:750–755
Paramore CG, Turner DA (1994) Relative risks of ventriculostomy infection and morbidity. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 127:79–84
Ruchholtz S, Waydhas C, Müller A, Lewan UM, Nast-Kolb D, Euler E, Pfeiffer KJ, Schweiberer L (1998) Percutaneous computed tomographic-controlled ventriculostomy in severe traumatic brain injury. J Trauma 45:505–511
Seeger W (1978) Atlas of topographical anatomy of the brain and surrounding structures. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Stangl AP, Meyer B, Zentner J, Schramm J (1998) Continuous external CSF drainage—a perpetual problem in neurosurgery. Surg Neurol 50:77–82
Strowitzki M, Moringlane JR, Steudel WI (2000) Ultrasound-based navigation during intracranial burr-hole procedures. Experience in a series of 100 cases. Surg Neurol 54:134–144
Strowitzki M, Schwerdtfeger K, Steudel WI (2001) Ultrasound-guided aspiration of brain abscesses through a single burr-hole. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 44:135–140
Theodosopoulos PV, Abosch A, McDermott MW (2001) Intraoperative fiber-optic endoscopy for ventricular catheter insertion. Can J Neurol Sci 28:56–60
Tirakotai W, Riegel T, Sure U, Bozinov O, Hellwig D, Bertalanffy H (2004) Clinical application of neuro-navigation in a series of single burr-hole procedures. Zentralbl Neurochir 65:57–64
Tuli S, O’Hayon B, Drake J, Clarke M, Kestle J (1999) Change in ventricular size and effect of ventricular catheter placement in pediatric patients with shunted hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 45:1329–1333
Ure BM, Holschneider AM (1997) Ventriculoscopic implantation of ventricular shunts in children with hydrocephalus. Eur J Pediatr Surg 7:299–300
Woodworth GF, McGirt MJ, Elfert P, Sciubba DM, Rigamonti D (2005) Frameless stereotactic ventricular shunt placement for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 83:12–16
Funding
The authors do not have any commercial or other associations that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the presented method.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strowitzki, M., Komenda, Y., Eymann, R. et al. Accuracy of ultrasound-guided puncture of the ventricular system. Childs Nerv Syst 24, 65–69 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-007-0410-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-007-0410-x