Abstract
Objects
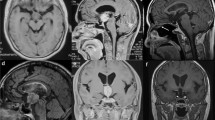
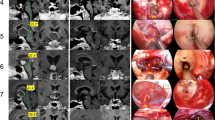
Fourth ventricle is conventionally accessed via resection of the part of the vermis for total excision of the tumors at the expense of significant morbidity. Numerous avenues have been identified to minimize the morbidity; some of which include transforaminal, subtonsillar, telovelar approaches, etc. These approaches are devised on the basis that accurate dissection along the natural avascular planes will avoid injury to the important structures in this area minimizing morbidity. We attempt to emphasize the technique of telovelar approach and the problems encountered while employing this technique for excision of large fourth ventricle tumors.
Materials and methods
Fifteen patients with fourth ventricle tumors were operated during January to September 2005 at Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, India. Fourteen of these cases were medulloblastomas, and one was ependymoma. All the patients were operated in prone oblique position via telovelar approach.
Conclusion
Clear understanding of the normal anatomy will help in meticulous dissection and will result in reduced morbidity. Significant incidence of postoperative ataxia and mutism is seen with this approach in large tumors, and this can be avoided by staged dissection of the uvulotonsillar cleft.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mussi ACM, Rhoton AL Jr (2000) Telovelar approach to the fourth ventricle: microsurgical anatomy. J Neurosurg 92:812–823
Matsushima T, Inoue T, Inamura T, Natori Y, Ikezaki K, Fukui M (2001) Transcerebellomedullary fissure approach with special reference to methods of dissecting the fissure. J Neurosurg 94:257–264
Kellogg JX, Piatt JH Jr (1997) Resection of fourth ventricle tumors without splitting the vermis: the cerebellomedullary fissure approach. Pediatr Neurosurg 27:28–33
Tanriover N, Ulm AJ, Rhoton AL Jr, Yasuda A (2004) Comparison of transvermian and telovelar approach to the fourth ventricle. J Neurosurg 101:484–498
Deshmukh VR, Figuueiredo EG, Deshmukh P, Crawford NR, Preul MC, Spetzler RF (2006) Quantification and comparison of telovelar and transvermian approaches to the fourth ventricle. Neurosurgery 58(ONS suppl 2):ONS 202–ONS 207
Ziyal IM, Sekhar LN, Salas E (1999) Subtonsillar–transcerebellomedullary approach to the lesions involving the fourth ventricle, the cerebellomedullary fissure and lateral brainstem. Br J Neurosurg 13(3):276–284
El-Bahy K (2005) Telovelar approach to the fourth ventricle: operative findings and results in 16 cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 147:137–142
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajesh, B.J., Rao, B.R.M., Menon, G. et al. Telovelar approach: technical issues for large fourth ventricle tumors. Childs Nerv Syst 23, 555–558 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-006-0295-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-006-0295-0