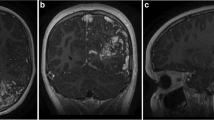
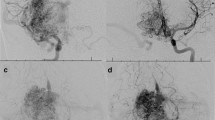
Abstract
Objects
The goal of cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVM) therapy in pediatric patients should be complete resection or obliteration of the AVM to eliminate subsequent hemorrhage, because of high mortality and morbidity rates related to hemorrhage in addition to the longer life expectation. Despite advances in Gamma knife radiosurgery and in endovascular embolization, surgical resection is still the gold standard for treating cerebral AVMs.
Methods
Between 1986 and 2003, 20 children were surgically treated for cerebral AVMs. The AVMs were graded I, II, and III using the Spetzler–Martin (S–M) Grading Scale. Good recovery was achieved in 18 out of 20 patients (90%) and only 1 patient was moderately disabled (5%). There was one mortality (5%) related to the preoperative deep comatose state of the patient. The total obliteration rate was 89% (17 out of 19).
Conclusion
For S–M grade I–III AVMs, surgical resection is the treatment of choice, considering its high cure rate and low morbidity and mortality rates.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akimoto H, Komatsu K, Kubota Y (2003) Symptomatic de novo arteriovenous malformation appearing 17 years after the resection of two other arteriovenous malformations in childhood: case report. Neurosurgery 52:228–232
Ali MJ, Bendok BR, Rosenblatt S, Rose JE, Getch CC, Batjer HH (2003) Recurrence of pediatric cerebral arteriovenous malformations after angiographically documented resection. Pediatr Neurosurg 39:32–38
Di Rocco C, Tamburrini G, Rollo M (2000) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations in children. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 142:145–158
Fong D, Chan ST (1988) Arteriovenous malformation in children. Childs Nerv Syst 4:199–203
Gerosa MA, Cappellotto P, Licata C, Iraci G, Pardatscher K, Fiore DL (1981) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations in children (56 cases). Childs Brain 8:356–371
Hladky JP, Lejeune JP, Blond S, Pruvo JP, Dhellemmes P (1994) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations in children: report on 62 cases. Childs Nerv Syst 10:328–333
Hoh BL, Ogilvy CS, Butler WE, Loeffler JS, Putman CM, Chapman PH (2000) Multimodality treatment of nongalenic arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients. Neurosurgery 47:346–358
Humphreys RP, Hoffman HJ, Drake JM, Rutka JT (1996) Choices in the 1990s for the management of pediatric cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Pediatr Neurosurg 25:277–285
Lasjaunias P, Hui F, Zerah M, Garcia-Monaco R, Malherbe V, Rodesch G, Tanaka A, Alvarez H (1995) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations in children. Management of 179 consecutive cases and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst 11:66–79
Levy EI, Niranjan A, Thompson TP, Scarrow AM, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2000) Radiosurgery for childhood intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 47:834–842
Lindqvist M, Karlsson B, Guo WY, Kihlstrom L, Lippitz B, Yamamoto M (2000) Angiographic long-term follow-up data for arteriovenous malformations previously proven to be obliterated after gamma knife radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 46:803–810
Malik GM, Sadasivan B, Knighton RS, Ausman JI (1991) The management of arteriovenous malformations in children. Childs Nerv Syst 7:43–47
Menovsky T, van Overbeeke JJ (1997) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations in childhood: state of the art with special reference to treatment. Eur J Pediatr 156:741–746
Millar C, Bissonnette B, Humphreys RP (1994) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations in children. Can J Anaesth 41:321–331
Mori K, Murata T, Hashimoto N, Handa H (1980) Clinical analysis of arteriovenous malformations in children. Childs Brain 6:13–25
Schaller C, Schramm J (1997) Microsurgical results for small arteriovenous malformations accessible for radiosurgical or embolization treatment. Neurosurgery 40:664–672
Smith ER, Butler WE, Ogilvy CS (2002) Surgical approaches to vascular anomalies of the child’s brain. Curr Opin Neurol 15:165–171
Smyth MD, Sneed PK, Ciricillo SF, Edwards MS, Wara WM, Larson DA, Lawton MT, Gutin PH, McDermott MW (2002) Stereotactic radiosurgery for pediatric intracranial arteriovenous malformations: the University of California at San Francisco experience. J Neurosurg 97:48–55
Spetzler RF, Martin NA (1986) A proposed grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 65:476–483
Valavanis A, Yasargil MG (1998) The endovascular treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations. Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg 24:131–214
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A commentary on this paper is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00381-004-1026-z
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kırış, T., Sencer, A., Şahinbaş, M. et al. Surgical results in pediatric Spetzler–Martin grades I–III intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Childs Nerv Syst 21, 69–74 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-004-1025-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-004-1025-0