Abstract
Introduction
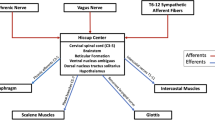
Vagus nerve stimulation for the management of intractable seizure disorders is increasingly being used, especially in younger children. Although complications such as infection or vocal cord paralysis are uncommon, some may be unreported.
Clinical presentation
A 3.5-year-old boy with intractable complex partial and generalized seizures had a left vagus nerve stimulator (VNS) successfully implanted. Two weeks later, the cervical incision showed signs of infection, antibiotics were started, and the VNS generator and leads were explanted. Three weeks later the child's mother noted a change in the voice of her son, as well as increased coughing and gagging. Flexible laryngoscopy identified a left vocal cord paralysis, which eventually resolved after 6 months.
Conclusion
Infection requiring explantation of a VNS is uncommon. The risk is higher in younger children, especially in those who are developmentally delayed. These children may continuously drool, with saliva or food soiling the fresh incision, or even pick at the incision to the point of twisting or even pulling out the electrodes. Less common is a vocal cord paralysis, especially occurring in a delayed fashion.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruce DA, Alksne JF, Bernard E, Blume H, Fraser RAR, Li, M (1998) Implantation of a vagus nerve stimulator for refractory partial seizures: surgical outcomes of 454 study patients. Epilepsia 39 [Suppl 6]:92–93
Carey ME, Kutz S (2000) Modified Malis bayonet forceps aids application of the cyberonics vagus nerve stimulator electrode: technical note. Neurosurgery 47:985–987
Espinosa J, Aiello MT, Naritoku DK (1999) Revision and removal of stimulating electrodes following long-term therapy with the vagus verve stimulator. Surg Neurol 51:659–664
Murphy JV, Pediatric VNS Study Group (1999) Left vagal nerve stimulation in children with medically refractory epilepsy. J Pediatr 134:563–565
Murphy JV, Hornig G, Schallert G (1995) Left vagal nerve stimulation in children with refractory epilepsy: preliminary observations. Arch Neurol 52:886–889
Murphy JV, Hornig GW, Schallert GS, Tilton CL (1998) Adverse events in children receiving intermittent left vagal nerve stimulation. Pediatr Neurol 19:42–44
Ortler M, Luef G, Kofler A, Bauer G, Twerdy K (2001) Deep wound infection after vagus nerve stimulator implantation: treatment without removal of the device. Epilepsia 42:133–135
Patwardhan RV, Stong B, Bebin EM, Mathisen J, Grabb PA (2000) Efficacy of vagal nerve stimulation in children with medically refractory epilepsy. Neurosurgery 47:1353–1358
Reid SA (1990) Surgical technique for implantation of the neurocybernetic prosthesis. Epilepsia 31 [Suppl 2]:38–39
Uthman BM, Wilder BJ, Penry JK, Dean C, Ramsay RE, Reid SA, Hammond EJ, Tarver WB, Wernicke JF (1993) Treatment of epilepsy by stimulation of the vagus nerve. Neurology 43:1338–1345
Vagus Nerve Stimulation Study Group (1995) A randomized controlled trial of chronic vagus nerve stimulation for treatment of medically intractable seizures. Neurology 45:224–230
Vassilyadi M, Strawsburg RH, King A, Yeh H-S (2000) Vagus nerve stimulation at the Children's Hospital Medical Center. Childs Nerv Syst 16:342–343
Wheless JW, Baumgartner J, Maggio B, Thomas AB, Constantinou JEC (1999) Complications of vagus nerve stimulation. Epilepsia 40 [Suppl 2]:91
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vassilyadi, M., Strawsburg, R.H. Delayed onset of vocal cord paralysis after explantation of a vagus nerve stimulator in a child. Childs Nerv Syst 19, 261–263 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-003-0722-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-003-0722-4