Abstract
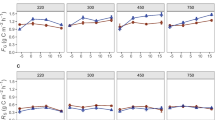
Leymus chinensis and Stipa grandis are two important plant species of temperate steppes in Inner Mongolia of North China. They differ in their life forms, e.g., L. chinensis is a type of rhizomatous clonal grass, whereas S. grandis is a type of tussock grass. Here we hypothesize that both plant species possess distinct nitrogen (N) acquisition strategies for their growth and survival. To test this hypothesis, we conducted a four-factor experimental field study using a short-term (three hours) 15N labeling technique in two plant communities mono-dominated by L. chinensis and S. grandis of the temperate steppes over two months (July and August) and at two soil depths. In both of communities, L. chinensis and S. grandis directly absorbed all three of the common forms of N, including substantial portions of N-derived from glycine (organic and inorganic forms) ranged from 2.7 to 17.8 %, although they absorbed more inorganic N. Nitrogen uptake rates showed significant effects of communities, months, soil depths, and N forms. The uptake rate was higher in August than in July and at 0–5 cm than at 5–15 cm soil depths. L. chinensis and S. grandis showed different preference on N form across months. L. chinensis shifted its uptake pattern from more nitrate (NO3 −) in July to more ammonium (NH4 +) in August, whereas S. grandis took up comparable NH4 + and NO3 − in both months. In general, L. chinensis showed a more flexible N acquisition strategy and S. grandis performed a more concentrated and relatively more stable N acquisition strategy. The distinct N acquisition strategies used by L. chinensis and S. grandis varied greatly across different months and soil depths. These findings are more helpful in further understanding the plasticity of nutrient utilization issues of different plant species in response to N-limited conditions of grassland ecosystems.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abuzinadah RA, Read DJ (1986) The role of proteins in the nitrogen nutrition of ectomycorrhizal plants. III. Protein utilization by Betula, Picea, and Pinus in mycorrhizal association with Hebeloma crustiliniforme. New Phytol 103:507–514
Abuzinadah RA, Read DJ (1989) The role of proteins in the nitrogen nutrition of ectomycorrhizal plants. IV. The utilization of peptides by birch (Betula pendula L.) infected with different mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol 112:55–60
Al-Karaki G, Mcmichael B, Zak J (2004) Field response of wheat to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and drought stress. Mycorrhiza 14:263–269
Anna W, Hill PW, Vaieretti MV, Farrar JF, Jones DL, Bardgett RD (2014) Challenging the paradigm of nitrogen cycling: no evidence of in situ resource partitioning by coexisting plant species in grasslands of contrasting fertility. Ecol Evol 5:275–287
Ashton IW, Miller AE, Bowman WD, Suding KN (2008) Nitrogen preferences and plant-soil feedbacks as influenced by neighbors in the alpine tundra. Oecologia 156:625–636
Ashton IW, Miller AE, Bowman WD, Suding KN (2010) Niche complementarity due to plasticity in resource use: plant partitioning of chemical N forms. Ecology 91:3252–3260
Bai W, Sun X, Wang Z, Li L (2009) Nitrogen addition and rhizome severing modify clonal growth and reproductive modes of Leymus chinensis population. Plant Ecol 205:13–21
Barber SA (1962) A diffusion and mass-flow concept of soil nutrient availability. Soil Sci 93:39–49
Bardgett RD, Streeter TC, Bol R (2003) Soil microbes compete effectively with plants for organic nitrogen inputs to temperate grasslands. Ecology 84:1277–1287
Bol R, Ostle NJ, Petzke KJ (2002) Compound specific plant amino acid δ15N values differ with functional plant strategies in temperate grassland. J Soil Sci Plant Nut 165:661–667
Brouwer R (1954) The regulating influence of transpiration and suction tension on the water and salt uptake by the roots of intact Vicia faba plants. Plant Biol 3:264–312
Chapin FS III (1995) New cog in the nitrogen cycle. Nature 377:199–200
Chinese Soil Taxonomy Research Group (2001) Index on Chinese soil taxonomy. Univ Sci Technol China, Hefei
Clemmensen KE, Sorensen PL, Michelsen A, Jonasson S, Ström L (2008) Site-dependent N uptake from N-form mixtures by arctic plants, soil microbes and ectomycorrhizal fungi. Oecologia 155:771–783
Crawford NM, Glass ADM (1998) Molecular and physiological aspects of nitrate uptake in plants. Trends Plant Sci 3:389–395
Danielson RE, Russell MB (1957) Ion absorption by corn roots as influenced by moisture and aeration. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 21:3–6
Dijkstra FA, Augustine DJ, Brewer P, Fischer JCV (2012) Nitrogen cycling and water pulses in semiarid grasslands: are microbial and plant processes temporally asynchronous? Oecologia 170:799–808
Doust LL (1981) Population dynamics and local specialization in a clonal perennial (Ranunculus repens): I. the dynamics of ramets in contrasting habitats. J Ecol 69:743–755
Doust LL (1987) Population dynamics and local specialization in a clonal perennial (Ranunculus repens): iii. responses to light and nutrient supply. J Ecol 75:555–568
Duke SE, Caldwell MM (2001) Nitrogen acquisition from different spatial distributions by six Great Basin plant species. West N Am Naturalist 61:93–102
Engels C, Marschner H (1995) Plant uptake and utilization of nitrogen. In: Bacon P (ed) Nitrogen fertilization in the environment. Marcel Decker, New York, pp 41–81
Farrell M, Hill PW, Farrar JF, Bardgett RD, Jones DL (2011) Seasonal variation in soluble soil carbon and nitrogen across a grassland productivity gradient. Soil Biol Biochem 43:835–844
Finlay RD, Frostegård Å, Sonnerfeldt AM (1992) Utilization of organic and inorganic nitrogen sources by ectomycorrhizal fungi in pure culture and symbiosis with Pinus contorta Dougl. ex Loud. New Phytol 120:105–115
Finzi AC, Berthrong ST (2005) The uptake of amino acids by microbes and trees in three cold-temperate forests. Ecology 86:3345–3353
Fry B (2006) Stable isotope ecology. Springer, New York
Gao JQ, Yi M, Xu XL, Zhang XW, Yu FH (2014) Spatiotemporal variations affect uptake of inorganic and organic nitrogen by dominant plant species in an alpine wetland. Plant Soil 381:271–278
Gebauer RLE, Ehleringer JR (2000) Water and nitrogen uptake patterns following moisture pulses in a cold desert community. Ecology 81:1415–1424
Gillespie AR (1989) Modelling nutrient flux and interspecies root competition in agroforestry interplantings. Agroforest Syst 8:257–265
Gioseffi E, Neergaard AD, Schjoerring JK (2011) Interactions between uptake of amino acids and inorganic nitrogen in wheat plants. Biogeosciences 8:11311–11335
Gu R, Chao LM, Zhang LX, Su LD, Wan ZQ, Yan YL, Chen YL, Gao QZ (2015) The influence of hydrothermal factors on soil respiration and soil temperature sensitivity of Stipa krylovii steppe, Inner Mongolia Chinese. Acta Pratac Sin 24:21–29
Harper JL (1977) Population biology of plants. Academic Press, London
Harrison KA, Bol R, Bardgett RD (2007) Preferences for different nitrogen forms by coexisting plant species and soil microbes. Ecology 88:989–999
Hill PW, Quilliam RS, Deluca TH, Farrar J, Farrell M, Roberts P, Newsham KK, Hopkins DW, Bardgett RD, Jones DL (2011) Acquisition and assimilation of nitrogen as peptide-bound and d-enantiomers of amino acids by wheat. PLoS One 6(4):e19220
Hodge A, Campbell CD, Fitter AH (2001) An arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus accelerates decomposition and acquires nitrogen directly from organic material. Nature 413:297–299
Jacob A, Leuschner C (2014) Complementarity in the use of nitrogen forms in a temperate broad-leaved mixed forest. Plant Ecol Divers 8:243–258
Jämtgård S, Näsholm T, Huss-Danell K (2010) Nitrogen compounds in soil solution of agricultural land. Soil Biol Biochem 42:2325–2330
Johnsson L, Berggren D, Kårén O (1999) Content and bioavailability of organic forms of nitrogen in the O horizon of a podzol. Eur J Soil Sci 50:591–600
Kahmen A, Renker C, Unsicker SB, Buchmann N (2006) Niche complementarity for nitrogen: an explanation for the biodiversity and ecosystem functioning relationship? Ecology 87:1244–1255
Kahmen A, Livesley SJ, Arndt SK (2009) High potential, but low actual, glycine uptake of dominant plant species in three Australian land-use types with intermediate n availability. Plant Soil 325:109–121
Kaštovská E, Šantrůčková H (2011) Comparison of uptake of different N forms by soil microorganisms and two wet-grassland plants: a pot study. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1285–1291
Krom MD, Berner RA (1980) The diffusion coefficients of sulfate, ammonium, and phosphate ions in anoxic marine-sediments. Limnol Oceanogra 25:327–337
Lambers H, Iii FSC, Pons TL (1998) Plant physiological ecology. Springer, New York
Lebauer DS, Treseder KK (2008) Nitrogen limitation of net primary productivity in terrestrial ecosystems is globally distributed. Ecology 89:371–379
Li YH (1988) The divergence and convergence of Aneurolepidium Chinese steppe and Stipa grandis steppe under the grazing influence in Xilin River valley, Inner Mongolia. Chin J Plant Ecol 3:189–196
Li J, Ma XF, Guo P, Bao GZ (2007) Studies on clonal plasticity of Leymus chinensis from habitats with different degree of salt and alkali in the Songnen Plain. J Shenyang Normal Univ 25:506–509
Mckane RB, Johnson LC, Shaver GR, Nadelhoffer KJ, Rastetter EB, Brian F, Giblin AE, Kielland K, Kwiatkowski BL, Laundre JL, Murray G (2002) Resource-based niches provide a basis for plant species diversity and dominance in Arctic Tundra. Nature 415:68–71
Mederski HJ, Wilson JH (1960) Relation of soil moisture to ion absorption by corn plants. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 24:149–152
Miller AJ, Cramer MD (2004) Root nitrogen acquisition and assimilation. Plant Soil 274:1–36
Miller AE, Bowman WD, Katharine Nash S (2007) Plant uptake of inorganic and organic nitrogen: neighbor identity matters. Ecology 88:1832–1840
Miller AE, Schimel JP, Sickman JO, Skeen K, Meixner T, Melack JM (2009) Seasonal variation in nitrogen uptake and turnover in two high elevation soils: mineralization responses are site-dependent. Biogeochemistry 93:253–270
Näsholm T, Kielland K, Ganeteg U (2009) Uptake of organic nitrogen by plants. New Phytol 182:31–48
Nye PH (1977) The rate-limiting step in plant nutrient absorption from soil. Soil Sci 123:292–297
Paungfoo-Lonhienne C, Lonhienne TGA, Rentsch D, Robinson N, Christie M, Webb RI, Gamage HK, Carroll BJ, Schenk PM, Schmidt S (2008) Plants can use protein as a nitrogen source without assistance from other organisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:4524–4529
Pii Y, Mimmo T, Tomasi N, Terzano R, Cesco S, Crecchio C (2015) Microbial interactions in the rhizosphere: beneficial influences of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on nutrient acquisition process. a review. Biol Fertil Soils 51:403–415
Pornon A, Nathalie E, Thierry L (2007) Complementarity in mineral nitrogen use among dominant plant species in a subalpine community. Am J Bot 94:1778–1785
Raab TK, Lipson DA, Monson RK (1999) Soil amino acid utilization among species of the Cyperaceae: plant and soil processes. Ecology 80:2408–2419
Schenk HJ (2006) Root competition: beyond resource depletion. J Ecol 94:725–739
Schenk HJ, Jackson RB (2002) The global biogeography of roots. Ecol Monogr 72:311–328
Schimel JP, Bennett J (2004) Nitrogen mineralization: challenges of a changing paradigm. Ecology 85:591–602
Schleuss PM, Heitkamp F, Sun Y, Miehe G, Xu XL, Kuzyakov Y (2015) Nitrogen uptake in an alpine Kobresia pasture on the Tibetan Plateau: localization by 15N labeling and implications for a vulnerable ecosystem. Ecosystems 18:1–12
Schofield RK, Graham BIJ (1960) Diffusion of ions in soils. Nature 188:195–200
Shelden MC, Dong B, de Bruxelles GL, Trevaskis B, Whelan J, Ryan PR, Howitt SM, Udvardi MK (2001) Arabidopsis ammonium transporters, AtAMT1;1 and AtAMT1;2, have different biochemical properties and functional roles. Plant Soil 231:151–160
Soil Survey Staff (1987) Keys to soil taxonomy, 3rd printing. SMSS Tech Monogr No 6. Cornell University, Ithaca, New York
Soper FM, Paungfoo-Lonhienne C, Brackin R, Rentsch D, Schmidt S, Robinson N (2011) Arabidopsis and Lobelia anceps access small peptides as a nitrogen source for growth. Funct Plant Biol 38:788–796
Stefanie VF, Andrew H, Nina B, Niklaus PA, Bernhard S, Michael SL (2009) Belowground nitrogen partitioning in experimental grassland plant communities of varying species richness. Ecology 90:1389–1399
Stefanie VF, Niklaus PA, Michael SL, Andrew H, Nina B (2012) Do grassland plant communities profit from N partitioning by soil depth? Ecology 93:2386–2396
Sun L, Du S, Zhang YC, Liu YH, Sun L, Gegentu JYS (2015) Dynamic analyses of grass yield and nutrition of natural Stipa grandis grassland in Xilinhot. Acta Agres Sin 4:870–873
Vitousek PM, Howarth RW (1991) Nitrogen limitation on land and sea: how can it occur? Biogeochemistry 5:7–34
Wang Y, Gong JR, Liu M, Luo Q, Xu S, Pan Y, Zhai ZW (2015) Effects of land use and precipitation on above- and below-ground litter decomposition in a semi-arid temperate steppe in Inner Mongolia, China. Appl Soil Ecol 96:183–191
Wei L, Yu CCS (2014) Uptake of organic nitrogen and preference for inorganic nitrogen by two Australian native Araucariaceae species. Plant Ecol Divers 8:259–264
Weigelt A, Bol R, Bardgett RD (2005) Preferential uptake of soil nitrogen forms by grassland plant species. Oecologia 142:627–635
Wu ZS, Gu L (2013) The effects of mowing on characteristics of photosynthesis and community water use of Stipa grandis. Dissertation, Inner Mongolia University, Hohhot
Xu X, Ouyang H, Cao G, Richter A, Wanek W, Kuzyakov Y (2011a) Dominant plant species shift their nitrogen uptake patterns in response to nutrient enrichment caused by a fungal fairy in an alpine meadow. Plant Soil 341:495–504
Xu X, Ouyang H, Richter A, Wanek W, Cao G, Kuzyakov Y (2011b) Spatio-temporal variations determine plant-microbe competition for inorganic nitrogen in an alpine meadow. J Ecol 99:563–571
Xu X, Li Q, Wang J, Zhang L, Tian S, Lin Z, Li Q, Sun Y (2014) Inorganic and organic nitrogen acquisition by a fern Dicranopteris dichotoma in a subtropical forest in South China. Plos One 9(5):e90075
Ye X, Yu F, Dong M (2006) A trade-off between guerrilla and phalanx growth forms in Leymus secalinus under different nutrient supplies. Ann Bot-London 98:187–191
Zhao NX, Gao YB, Wang JL, Ren AZ, Wei-Bin R, Chen L, Liu HF (2004) An analysis of genetic differentiation between Stipa grandis populations in Middle and Eastern Inner Mongolia steppe. Acta Ecol Sin 24:2178–2185
Zhong Y, Sun W, Bao Q (1998) Effect of mowing on leymus chinensis in typical steppe region. Acta Sci Nat Univ Neimongol 2:202–213
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the “National Key Basic Research Program of China” (Grant No. 2014CB138803), the “National Key Research and Development Program of China” (Grant No. 2016YFC0500502), the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (Grant No. 2014KJJCB01) and the State Key Laboratory of Earth Surface Processes and Resource Ecology, Beijing Normal University (Grant No. 2009-RC-03), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31470560 and 41071209), as well as Central Non-profit Research Institutes Fundamental Research Funds of China (1610332015020) and Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region of China (2014BS0328).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R., Tian, Y., Ouyang, S. et al. Nitrogen acquisition strategies used by Leymus chinensis and Stipa grandis in temperate steppes. Biol Fertil Soils 52, 951–961 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-016-1128-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-016-1128-2