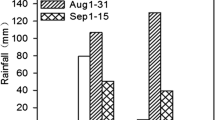
Abstract
Returning crop residues to soil is an effective approach for sustaining organic matter concentrations and increasing nutrient availability in soils. A 2-year micro-plot field experiment was conducted in dryland to determine the green manure, straw, and fertilizer nitrogen (N)-15 uptake by wheat, their residual N in soil and losses; the effect of straw application on the fate of N from green manure and vice versa was also determined, as well as the effect of crop residue additions on the fate of fertilizer N. All the micro-plots were treated with the same amount of 15N-labeled or unlabeled fertilizer. The green manure N uptake by wheat, residual N, and N loss were 22.4, 51.7, and 25.9 % of the total added green manure N over the 2-year experiment. Straw addition significantly decreased the green manure residual soil N but increased the cumulative losses. The straw N taken up by wheat, residual N in soil, and N loss were 8.3, 31.0, and 60.7 %, respectively. Green manure addition significantly decreased the straw N taken up by wheat, increased the residual soil N, and reduced the N loss. Furthermore, the fertilizer N taken up by wheat, residual N in soil, and N loss were 32.4, 32.3, and 35.2 %, respectively. Crop residue additions significantly increased the uptake of fertilizer N by wheat in the second year. The application of inorganic N fertilizer in combination with appropriate crop residues may be an effective approach to improve the long-term fertilizer N use efficiency, soil quality, and crop yield in wheat–summer fallow rotation systems in dryland.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker M, Ladha JK (1997) Synchronizing residue N mineralization with rice N demand in flooded conditions. In: Cadisch G, Giller KE (eds) Driven by nature: plant litter quality and decomposition. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 231–238
Bergstrom L, Kirchmann H (2004) Leaching and crop uptake of nitrogen from nitrogen-15-labelled green manures and ammonium nitrate. J Environ Qual 33:1786–1792
Blankenau K, Olfs HW, Kuhlmann H (2002) Strategies to improve the use efficiency of mineral fertilizer nitrogen applied to winter wheat. J Agron Crop Sci 188:146–154. doi:10.1046/j.1439-037X.2002.00548.x
Bremmer JM, Mulvaney CS (1982) Nitrogen-total. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 595–624
Bussiere F, Cellier P (1994) Modification of the soil–temperature and water-content regimes by a crop residue mulch- experiment and modeling. Agric Forest Meteorol 68:1–28. doi:10.1016/0168-1923(94)90066-3
Cassman KG, Dobermann A, Walters DT (2002) Agroecosystems, nitrogen-use efficiency, and nitrogen management. Ambio 31:132–140. doi:10.1639/0044-7447(2002)031[0132:anuean]2.0.co;2
Chen BQ, Liu EK, Tian QZ, Yan CR, Zhang YQ (2014) Soil nitrogen dynamics and crop residues. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 34:429–442. doi:10.1007/s13593-014-0207-8
Chen XP, Cui ZL, Vitousek PM, Cassman KG, Matson PA, Bai JS, Meng QF, Hou P, Yue SC, Römhelde V, Zhang FS (2011) Integrated soil-crop system management for food security. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:6399–6404. doi:10.1073/pnas.1101419108
Chivenge P, Vanlauwe B, Gentile R, Six J (2011a) Organic resource quality influences short-term aggregate dynamics and soil organic carbon and nitrogen accumulation. Soil Biol Biochem 43:657–666. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.12.002
Chivenge P, Vanlauwe B, Six J (2011b) Does the combined application of organic and mineral nutrient sources influence maize productivity? A meta-analysis. Plant Soil 342:1–30. doi:10.1007/s11104-010-0626-5
Crews TE, Peoples MB (2005) Can the synchrony of nitrogen supply and crop demand be improved in legume and fertilizer-based agroecosystems? A review. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 72:101–120. doi:10.1007/s10705-004-6480-1
Cui ZL, Yue SC, Wang GL, Zhang FS, Chen XP (2013) In-season root-zone N management for mitigating greenhouse gas emission and reactive N losses in intensive wheat production. Environ Sci Technol 47:6015–6022. doi:10.1021/es4003026
Douxchamps S, Frossard E, Bernasconi SM, van der Hoek R, Schmidt A, Rao IM, Oberson A (2011) Nitrogen recoveries from organic amendments in crop and soil assessed by isotope techniques under tropical field conditions. Plant Soil 341:179–192. doi:10.1007/s11104-010-0633-6
Drinkwater LE, Wagoner P, Sarrantonio M (1998) Legume-based cropping systems have reduced carbon and nitrogen losses. Nature 396:262–265. doi:10.1038/24376
Edmeades DC (2003) The long-term effects of manures and fertilisers on soil productivity and quality: a review. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 66:165–180. doi:10.1023/a:1023999816690
Ehaliotis C, Cadisch G, Giller KE (1998) Substrate amend ments can alter microbial dynamics and N availability from maize residues to subsequent crops. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1281–1292. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(98)00035-2
Erisman JW, Bleeker A, Galloway J, Sutton MS (2007) Reduced nitrogen in ecology and the environment. Environ Pollut 150:140–149. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.033
Fontainea S, Mariotti A, Abbadie L (2003) The priming effect of organic matter: a question of microbial competition? Soil Biol Biochem 35:837–843. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(03)00123-8
Gentile R, Vanlauwe B, van Kessel C, Six J (2009) Managing N availability and losses by combining fertilizer-N with different quality residues in Kenya. Agric Ecosyst Environ 131:308–314. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2009.02.003
Glendining MJ, Poulton PR, Powlson DS, Macdonald AJ, Jenkinson DS (2001) Availability of the residual nitrogen from a single application of N-15-labelled fertilizer to subsequent crops in a long-term continuous barley experiment. Plant Soil 233:231–239. doi:10.1023/a:1010508914895
Guo SL, Wu JS, Dang TH, Liu WZ, Li Y, Wei WX, Syers JK (2010) Impacts of fertilizer practices on environmental risk of nitrate in semiarid farmlands in the Loess Plateau of China. Plant Soil 330:1–13. doi:10.1007/s11104-009-0204-x
Handayanto E, Giller KE, Cadisch G (1997) Regulating N release from legume tree prunings by mixing residues of different quality. Soil Biol Biochem 29:1417–1426. doi:10.1016/s0038-0717(97)00047-3
Hart PBS, Powlson DS, Poulton PR, Johnston AE, Jenkinson DS (1993) The availability of the nitrogen in the crop residues of winter-wheat to subsequent crops. J Agric Sci 121:355–362
Henriksen A, Selmer-Olsen AR (1970) Automatic methods for determining nitrate and nitrite in water and soil extracts. Analyst 95:514–518
Ichir LL, Ismaili M, Hofman G (2003) Recovery of N-15 labelled wheat residue and residual effects of N fertilization in a wheat - wheat cropping system under Mediterranean conditions. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 66:201–207. doi:10.1023/a:1023976600760
Janzen HH, Bole JB, Biederbeck VO, Slinkard AE (1990) Fate of N applied as green manure or ammonium fertilizer to soil subsequently cropped with spring wheat at three sites in western Canada. Can J Soil Sci 70:313–323. doi:10.4141/cjss90-032
Jensen LS, Pedersen IS, Hansen TB, Nielsen NE (2000) Turnover and fate of N-15-labelled cattle slurry ammonium-N applied in the autumn to winter wheat. Eur J Agron 12:23–35. doi:10.1016/s1161-0301(99)00040-4
Ju XT, Xing GX, Chen XP, Zhang SL, Zhang LJ, Liu XJ, Cui ZL, Yin B, Christie P, Zhu ZL, Zhang FS (2009) Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:3041–3046. doi:10.1073/pnas.0813417106
Kampradit W et al (2009) Mixing groundnut residues and rice straw to improve rice yield and N use efficiency. Field Crops Res 110:130–138. doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2008.07.011
Kirchmann H, Johnston AEJ, Bergstrom LF (2002) Possibilities for reducing nitrate leaching from agricultural land. Ambio 31:404–408. doi:10.1639/0044-7447(2002)031[0404:pfrnlf]2.0.co;2
Ladd JN, Amato M (1986) The fate of nitrogen from legume and fertilizer sources in soils successively cropped with wheat under field conditions. Soil Biol Biochem 18:417–425. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(86)90048-9
Li FC, Wang ZH, Dai J, Li Q, Xue C, Zhao HB, Wang X, Olesen JE (2014) Summer fallow soil management—impact on rainfed winter wheat. Acta Agr Scand B-S P 64:398–407. doi:10.1080/09064710.2014.919347
Li SX, Wang ZH, Malhi SS, Li SQ, Gao YJ, Tian XH (2009) Nutrient and water management effects on crop production, and nutrient and water use efficiency in dryland areas of China. Adv Agron 102:223–265
Liang B, Yang XY, Murphy DV, He XH, Zhou JB (2013) Fate of 15N-labelled fertilizer in soils under dryland agriculture after 19 years of different fertilizations. Biol Fertil Soil 49:977–986. doi:10.1007/s00374-013-0789-3
Liu JG, Diamond J (2005) China’s environment in a globalizing world. Nature 435:1179–1186. doi:10.1038/4351179a
López-Bellido RJ, López-Bellido L, Castillo JE, López-Bellido FJ (2004) Chickpea response to tillage and soil residual nitrogen in a continuous rotation with wheat: II. Soil nitrate, N uptake and influence on wheat yield. Field Crops Res 88:201–210. doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2004.01.012
Manzoni S, Jackson RB, Trofymow JA, Porporato A (2008) The global stoichiometry of litter nitrogen mineralization. Science 321:684–686. doi:10.1126/science.1159792
Myers RJK, Palm CA, Cuevas E, Gunatilleke IUN, Brossard M (1994) The synchronization of nutrient mineralization and plant nutrient demand. In: Woomer PL, Swift MJ (eds) The biological management of tropical soil fertility. Wiley, Chichester, pp 81–116
Ortiz Monasterio JI, Sayre KD, Rajaram S, McMahon M (1997) Genetic progress in wheat yield and nitrogen use efficiency under four nitrogen rates. Crop Sci 37:898–904
Palm CA, Gachengo CN, Delve RJ, Cadisch G, Giller KE (2001) Organic inputs for soil fertility management in tropical agroecosystems: application of an organic resource database. Agric Ecosyst Environ 83:27–42. doi:10.1016/s0167-8809(00)00267-x
Pansu M, Thuries L (2003) Kinetics of C and N mineralization, N immobilization and N volatilization of organic inputs in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 35:37–48. doi:10.1016/s0038-0717(02)00234-1
Powlson DS, Jenkinson DS, Pruden G, Johnston AE (1985) The effect of straw incorporation on the uptake of nitrogen by winter wheat. J Sci Food Agric 36:26–30. doi:10.1002/jsfa.2740360105
Raun WR, Solie JB, Johnson GV, Stone ML, Mullen RW, Freeman KW, Thomason WE, Lukina EV (2002) Improving nitrogen use efficiency in cereal grain production with optical sensing and variable rate application. Agron J 94:815–820
Schwendener CM, Lehmann J, de Camargo PB, Luizao RCC, Fernandes ECM (2005) Nitrogen transfer between high- and low-quality leaves on a nutrient-poor Oxisol determined by N-15 enrichment. Soil Biol Biochem 37:787–794. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.10.011
Sebilo M, Mayer B, Grably M, Billiou D, Mariotti A (2004) The use of the ‘ammonium diffusion’ method for delta 15N-NH4 + and delta 15N-NO3 − measurements: comparison with other techniques. Environ Chem 1:99–103. doi:10.1071/en04037
Sebilo M, Mayer B, Nicolardot B, Pinay G, Mariotti A (2013) Long-term fate of nitrate fertilizer in agricultural soils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:18185–18189. doi:10.1073/pnas.1305372110
Smith JL, Papendick RI, Bezdicek DF, Lynch JM (1992) Soil organic matter dynamics and crop residue management. In: Metting FB Jr (ed) Soil microbial ecology: applications in agricultural and environmental management. Marcel Dekker, pp 65–94
Thorup-Kristensen K, Magid J, Jensen LS (2003) Catch crops and green manures as biological tools in nitrogen management in temperate zones. Adv Agron 79:227–302. doi:10.1016/s0065-2113(02)79005-6
Yanni SF, Whalen JK, Simpson MJ, Janzen HH (2011) Plant lignin and nitrogen contents control carbon dioxide production and nitrogen mineralization in soils incubated with Bt and non-Bt corn residues. Soil Biol Biochem 43:63–69. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.09.012
Zhang SL, Lövdahl L, Grip H, Tong YA, Yang XY, Wang QJ (2009) Effects of mulching and catch cropping on soil temperature, soil moisture and wheat yield on the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Till Res 102:78–86. doi:10.1016/j.still.2008.07.019
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the China Agricultural Research System (CARS-3-1-31), the Agricultural Scientific Research Talent and Team Program, the National Key Basic Research Special Funds under Grant (2015CB150404), the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest under Grant (201303104, 201103005), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (41401330). We would like to thank the editor and three reviewers for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F., Wang, Z., Dai, J. et al. Fate of nitrogen from green manure, straw, and fertilizer applied to wheat under different summer fallow management strategies in dryland. Biol Fertil Soils 51, 769–780 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-015-1023-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-015-1023-2