Abstract
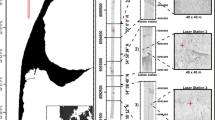
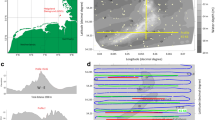
Marine habitats worldwide are increasingly pressurized by climate change, especially along the Antarctic Peninsula. Well-studied areas in front of rapidly retreating tidewater glaciers like Potter Cove are representative for similar coastal environments and, therefore, shed light on habitat formation and development on not only a local but also regional scale. The objective of this study was to provide insights into habitat distribution in Potter Cove, King George Island, Antarctica, and to evaluate the associated environmental processes. Furthermore, an assessment concerning the future development of the habitats is provided. To describe the seafloor habitats in Potter Cove, an acoustic seabed discrimination system (RoxAnn) was used in combination with underwater video images and sediment samples. Due to the absence of wave and current measurements in the study area, bed shear stress estimates served to delineate zones prone to sediment erosion. On the basis of the investigations, two habitat classes were identified in Potter Cove, namely soft-sediment and stone habitats that, besides influences from sediment supply and coastal morphology, are controlled by sediment erosion. A future expansion of the stone habitat is predicted if recent environmental change trends continue. Possible implications for the Potter Cove environment, and other coastal ecosystems under similar pressure, include changes in biomass and species composition.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aller JY (1989) Quantifying sediment disturbance by bottom currents and its effect on benthic communities in a deep-sea western boundary zone. Deep-Sea Res I 36:901–934
Bartholomä A (2006) Acoustic bottom detection and seabed classification in the German Bight, southern North Sea. Geo-Mar Lett 26:177–184. doi:10.1007/s00367-006-0030-6
Blott SJ, Pye K (2001) Gradistat: a grain size distribution and statistics package for the analysis of unconsolidated sediments. Earth Surf Process Landforms 26(11):1237–1248
Booij N, Ris RC, Holthuijsen LH (1999) A third-generation wave model for coastal regions. 1. Model description and validation. J Geophys Res 104(C4):7649–7666
Brown CJ, Mitchell A, Limpenny DS, Robertson MR, Service M, Golding N (2005) Mapping seabed habitats in the Firth of Lorn off the west coast of Scotland: evaluation and comparison of habitat maps produced using the acoustic ground-discrimination system RoxAnn, and sidescan sonar. ICES J Mar Sci 62:790–802
Chen C, Liu H, Beardsley RC (2003) An unstructured grid, finite-volume, three-dimensional, primitive equations ocean model: application to coastal ocean and estuaries. J Atmos Ocean Tech 20(1):159–186
Chivers RC, Emerson NC, Burns D (1990) New acoustic processing for underway surveying. Hydrogr J 56:9–17
Cook AJ, Fox AJ, Vaughan DG, Ferrigno JG (2005) Retreating glacier fronts on the Antarctic Peninsula over the past half-century. Science 308:541–544
Domack EW, Ishman SE (1993) Oceanographic and physiographic controls on modern sedimentation within Antarctic fjords. Geol Soc Am Bull 105:1175–1189
Dumke I, Klaucke I, Berndt C, Bialas J (2014) Sidescan backscatter variations of cold seeps on the Hikurangi Margin (New Zealand): indications for different stages in seep development. Geo-Mar Lett 34:169–184. doi:10.1007/s00367-014-0361-7
Folk RL, Ward WC (1957) Brazos River bar: a study in the significance of grain-size parameters. J Sediment Petrol 27(1):3–26
Foster-Smith RL, Sotheran IS (2003) Mapping marine benthic biotopes using acoustic ground-discrimination systems. Int J Remote Sens 24(13):2761–2784
Greenstreet SPR, Tuck ID, Grewar GN, Armstrong E, Reid DG, Wright PJ (1997) An assessment of the acoustic survey technique, RoxAnn, as a means of mapping seabed habitat. ICES J Mar Sci 54:939–959
Greenstreet SPR, Holland GJ, Guirey EJ, Armstrong E, Fraser HM, Gibb IM (2010) Combining hydroacoustic seabed survey and grab sampling techniques to assess “local” sandeel population abundance. ICES J Mar Sci 67(5):971–984
Griffith TW, Anderson JB (1989) Climatic controls of sedimentation in bays and fjords of the northern Antarctic Peninsula. Mar Geol 85(2/4):181–204
Hair JF, Anderson RE, Tatham RL, Black WC (1995) Multivariate data analysis. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Hamilton LJ, Mulhearn PJ, Poeckert R (1999) Comparison of RoxAnn and QTC-View acoustic bottom classification system performance for the Cairns area, Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Cont Shelf Res 19(12):1577–1597
Hemer MA (2006) The magnitude and frequency of combined flow bed shear stress as a measure of exposure on the Australian continental shelf. Cont Shelf Res 26(11):1258–1280
Hobbs CA (1985) Side-scan sonar as a tool for mapping spatial variations in sediment type. Geo-Mar Lett 5:241–245. doi:10.1007/BF02233809
Humborstad O-B, Nøttestad L, Løkkeborg S, Rapp HT (2004) RoxAnn bottom classification system, side-scan sonar and video-sledge: spatial resolution and their use in assessing trawling impacts. ICES J Mar Sci 61:53–63
Ierodiaconou D, Monk J, Rattray A, Laurenson L, Versace VL (2011) Comparison of automated classification techniques for predicting biological communities using hydroacoutics and video observations. Cont Shelf Res 31:28–38
Iken K, Quartino ML, Barrera-Oro E, Palermo J, Wiencke C, Brey T (1998) Trophic relations between macroalgae and herbivores in Potter Cove (King George Island, Antarctica). In: Wiencke C, Ferreyra GA, Arntz W, Rinaldi C (eds) The Potter Cove Coastal Ecosystem, Antarctica. Reports on Polar Research 299. Karl Kamloth, Bremen, pp 258–262
Jerosch K, Schlüter M, Foucher J-P, Allais A-G, Klages M, Edy C (2007) Spatial distribution of mud flows, chemoautotrophic communities and biogeochemical habitats at Håkon Mosby Mud Volcano. Mar Geol 243:1–17
Kenny AJ, Cato I, Desprez M, Fader G, Schüttenhelm RTE, Side J (2003) An overview of seabed-mapping technologies in the context of marine habitat classification. ICES J Mar Sci 60(2):411–418
Khim BK, Yoon HI (2003) Postglacial marine environmental changes in Maxwell Bay, King George Island, West Antarctica. Polar Res 22(2):341–353
Khim BK, Shim J, Yoon HI, Kang YC, Jang YH (2007) Lithogenic and biogenic particle deposition in an Antarctic coastal environment (Marian Cove, King George Island): seasonal patterns from a sediment trap study. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 73(1/2):111–122
Klöser H, Ferreyra G, Schloss I, Mercuri G, Laturnus F, Curtosi A (1994) Hydrography of Potter Cove, a small fjord-like inlet on King George Island (South Shetlands). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 38(5):523–537
Klöser H, Quartino ML, Wiencke C (1996) Distribution of macroalgae and macroalgal communities in gradients of physical conditions in Potter Cove, King George Island, Antarctica. Hydrobiologia 333(1):1–17
Kostylev VE, Todd BJ, Fader GBJ, Courtney RC, Cameron GDM, Pickrill RA (2001) Benthic habitat mapping on the Scotian Shelf based on multibeam bathymetry, surficial geology and seafloor photographs. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 219:121–137
Kraus S, del Valle R (2008) Geological map of Potter Peninsula (King George Island, South Shetland Islands, Antarctic Peninsula). Instituto Antártico Chileno, Punta Arenas & Instituto Antártico Argentino, Buenos Aires. doi:10.1594/PANGAEA.667386
Kruss A, Tęgowski J, Wiktor J, Tatarek A (2006) Acoustic estimation of macrophytes in the Hornsund fjord (the Svalbard Archipelago). Hydroacoustics 9:89–96
Kruss A, Blondel P, Tęgowski J, Wiktor J, Tatarek A (2008) Estimation of macrophytes using single-beam and multibeam echosounding for environmental monitoring of Arctic fjords (Kongsfjord, West Svalbard Island). J Acoust Soc Am 123:3213. doi:10.1121/1.2933397
Lim CH (2014) Modelling waves and currents in Potter Cove, King George Island, Antarctica. PhD thesis, Carl von Ossietzky University, Oldenburg, Germany
Lim CH, Lettmann K, Wolff J-O (2013) Numerical study on wave dynamics and wave-induced bed erosion characteristics in Potter Cove, Antarctica. Ocean Dyn 63(11/12):1151–1174. doi:10.1007/s10236-013-0651-z
Lucieer V (2005) Applying discriminate analysis to characterise shallow rocky reef habitat. In: Chinese Bureau of Surveying and Mapping, Proc Symp Spatial-temporal Modeling, Spatial Reasoning, Analysis, Data Mining and Data Fusion (STM’05), 27–29 August 2005, Peking University, Beijing, pp 215–219
Lucieer V, Lucieer A (2009) Fuzzy clustering for seafloor classification. Mar Geol 264(3/4):230–241
Magorrian BH, Service M, Clarke W (1995) An acoustic bottom-classification survey of Strangford Lough, Northern Ireland. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 75:987–992
McRea JE Jr, Greene HG, O’Connell VM, Wakefield WW (1999) Mapping marine habitats with high resolution sidescan sonar. Oceanol Acta 22:679–686
Mielck F, Bartsch I, Hass HC, Wölfl A-C, Bürk D, Betzler C (2014) Predicting spatial kelp abundance in shallow coastal waters using the acoustic ground discrimination system RoxAnn. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 143:1–11
Monien P, Schnetger B, Brumsack H-J, Hass HC, Kuhn G (2011) A geochemical record of late Holocene palaeoenvironmental changes at King George Island (maritime Antarctica). Antarctic Sci 23(3):255–267
Montes-Hugo M, Doney SC, Ducklow HW, Fraser W, Martinson D, Stammerjohn SE, Schofield O (2009) Recent changes in phytoplankton communities associated with rapid regional climate change along the western Antarctic Peninsula. Science 323(5920):1470–1473. doi:10.1126/science.1164533
Penrose JD, Siwabessy PJW, Gavrilov A, Parnum I, Hamilton LJ, Bickers A, Brooke B, Ryan DA, Kennedy P (2005) Acoustic Techniques for Seabed Classification. Cooperative Research Centre for Coastal Zone, Estuary and Waterway Management, Indooroopilly, Queensland, Australia, Technical Report 32
Qi J, Chen C, Beardsley RC, Perrie W, Cowles GW, Lai Z (2009) An unstructured-grid finite-volume surface wave model (FVCOM-SWAVE): implementation, validations and applications. Ocean Model 28:153–166
Quartino ML, Boraso de Zaixso AL (2008) Summer macroalgal biomass in Potter Cove, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica: its production and flux to the ecosystem. Polar Biol 31(3):281–294
Quartino ML, Deregibus D, Campana GL, Latorre GEJ, Momo FR (2013) Evidence of macroalgal colonization on newly ice-free areas following glacial retreat in Potter Cove (South Shetland Islands), Antarctica. PLOS ONE 8(3):e58223
Roese M, Drabble M (1998) Wind driven circulation in Potter Cove. In: Wiencke C, Ferreyra GA, Arntz W, Rinaldi C (eds) The Potter Cove Coastal Ecosystem, Antarctica. Reports on Polar Research 299. Karl Kamloth, Bremen, pp 40–46
Rückamp M, Braun M, Suckro S, Blindow N (2011) Observed glacial changes on the King George Island ice cap, Antarctica, in the last decade. Global Planet Change 79:99–109
Sahade R, Tatián M, Kowalke J, Kuehne S, Esnal G (1998) Benthic faunal associations on soft substrates at Potter Cove, King George Island, Antarctica. Polar Biol 19(2):85–91
Schloss IR, Ferreyra GA (2002) Primary production, light and vertical mixing in Potter Cove, a shallow bay in the maritime Antarctic. Polar Biol 25(1):41–48
Schloss IR, Ferreyra GA, Ruiz-Pino D (2002) Phytoplankton biomass in Antarctic Shelf Zones: a conceptual model based on Potter Cove, King George Island. J Mar Syst 36:129–143
Schloss IR, Abele D, Moreau S, Demers S, Bers AV, González O, Ferreyra GA (2012) Response of phytoplankton dynamics to 19-year (1991-2009) climate trends in Potter Cove (Antarctica). J Mar Syst 92(1):53–66
Schöne T, Pohl M, Zakrajsek A, Schenke H (1998) Tide gauge measurements, a contribution for the long term monitoring of sea level. In: Wiencke C, Ferreyra GA, Arntz W, Rinaldi C (eds) The Potter Cove Coastal Ecosystem, Antarctica. Reports on Polar Research 299. Karl Kamloth, Bremen, pp 12–14
Simões JC, Bremer UF, Aquino FE, Ferron FE (1999) Morphology and variations of glacial drainage basins in the King George Island ice field, Antarctica. Ann Glaciol 29:220–224
Sotheran IS, Foster-Smith RL, Davies J (1997) Mapping of marine benthic habitats using image processing techniques within a raster based Geographic Information System. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 44(A):25–31
Soulsby R (1997) Dynamics of marine sands. Thomas Telford Publications, London
Tanner WF (1969) The particle size scale. J Sediment Petrol 39:809–812
Thompson DWJ, Solomon S (2002) Interpretation of recent southern hemisphere climate change. Science 296:895–899. doi:10.1126/science.1069270
Varela L (1998) Hydrology of Matias and Potter Creeks. In: Wiencke C, Ferreyra GA, Arntz W, Rinaldi C (eds) The Potter Cove Coastal Ecosystem, Antarctica. Reports on Polar Research 299. Karl Kamloth, Bremen, pp 33–39
Vaughan DG, Marshall GJ, Connolley WM, King JC, Mulvaney R (2001) Devil in the detail. Science 293:1777–1779
Veit-Köhler G (1998) Meiofauna study in the Potter Cove. Sediment situation and resource availability for small crustaceans (Copepoda and Peracarida). In: Wiencke C, Ferreyra GA, Arntz W, Rinaldi C (eds) The Potter Cove Coastal Ecosystem, Antarctica. Reports on Polar Research 299. Karl Kamloth, Bremen, pp 132–136
Venables WN, Ripley BD (2002) Modern applied statistics with S, 4th edn. Springer, New York
Warwick RM, Uncles RJ (1980) Distribution of benthic macrofaunal associations in the Bristol Channel in relation to tidal stress. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 3:97–103
Wentworth CK (1922) A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments. J Geol 30:377–392
Yoon HI, Han MW, Park BK, Han SJ, Oh JK (1992) Distribution, provenance, and dispersal pattern of clay minerals in surface sediments, Bransfield Strait, Antarctica. Geo-Mar Lett 12(4):223–227. doi:10.1007/BF02091842
Acknowledgements
This study is part of the ESF IMCOAST project (grant no. 03F0617A) and the EU project IMCONet (FP7 IRSES, action no. 319718). The authors acknowledge the IAA (Instituto Antártico Argentino, Buenos Aires, Argentina) for providing bathymetric data. Many thanks go to Prof. Changsheng Chen, Dr. Jianhua Qi and the MEDM research group in SMAST, University of Massachusetts, Dartmouth, for providing the FVCOM source codes and advisory help. We would also like to express our gratitude to the crews of Carlini (formerly Jubany) Station from 2010/2011 and 2011/2012, with special thanks to Gastón Rihedel, Alejandro Ulrich, Verónica Fuentes, Alejandro Olariaga, Dolores Deregibus, Nina Wittenberg, Eduardo Ruiz Barlett and Marta Sierra for their unfailing support during field campaigns. Two anonymous reviewers are thanked for their constructive comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wölfl, AC., Lim, C.H., Hass, H.C. et al. Distribution and characteristics of marine habitats in a subpolar bay based on hydroacoustics and bed shear stress estimates—Potter Cove, King George Island, Antarctica. Geo-Mar Lett 34, 435–446 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-014-0375-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-014-0375-1