Abstract
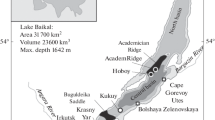
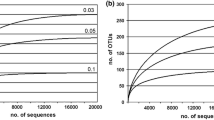
Detailed lithological, biogeochemical and molecular biological analyses of core sediments collected in 2002–2006 from the vicinity of the Malenky mud volcano, Lake Baikal, reveal considerable spatial variations in pore water chemical composition, with total concentrations of dissolved salts varying from 0.1 to 1.8‰. Values of methane δ13С in the sediments suggest a biogenic origin (δ13Сmin. −61.3‰, δ13Сmax. −72.9‰). Rates of sulphate reduction varied from 0.001 to 0.7 nmol cm−3 day−1, of autotrophic methanogenesis from 0.01 to 2.98 nmol CH4 cm−3 day−1, and of anaerobic oxidation of methane from 0 to 12.3 nmol cm−3 day−1. These results indicate that methanogenic processes dominate in gas hydrate-bearing sediments of Lake Baikal. Based on clone libraries of 16S rRNA genes amplified with Bacteria- and Archaea-specific primers, investigation of microbial diversity in gas hydrate-bearing sediments revealed bacterial 16S rRNA clones classified as Deltaproteobacteria, Gammaproteobacteria, Chloroflexi and OP11. Archaeal clone sequences are related to the Crenarchaeota and Euryarchaeota. Baikal sequences of Archaea form a distinct cluster occupying an intermediate position between the marine groups ANME-2 and ANME-3 of anaerobic methanotrophs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alperin MJ, Blair NE, Albert DB, Hoehler TM, Martens CS (1992) Factors that control the stable carbon isotopic composition of methane produced in an anoxic marine sediment. Global Biogeochem Cycles 6:271–291
Ashi J, Tokuyama H, Taira A (2002) Distribution of methane hydrate BSRs and its implication for the prism growth in the Nankai Trough. Mar Geol 187:177–191
Baram GI, Vereshchagin AL, Golobokova LP (1999) Micro-column high-performance liquid chromatography with UV-detection for anions identification in the environment. J Anal Chem 54:962–965
Belyaev SS (1979) Microbiological formation of СН4 in different ecosystems. In: The role of microorganisms in gases turnover under natural conditions. Nauka, Moscow, pp 125–137
Boetius A, Suess E (2004) Hydrate Ridge: a natural laboratory for the study of microbial life fueled by methane from near-surface gas hydrates. Chem Geol 205:291–310
Boetius A, Ravenschlag K, Schubert CJ, Rickert D, Widdel F, Gieseke A, Amann R, Jørgensen BB, Witte U, Pfannkuche O (2000) A marine microbial consortium apparently mediating anaerobic oxidation of methane. Nature 407:623–626
Bol’shakov AM, Egorov AV (1987) Using of phase-equilibrium degassing method for gasometrical studies. Oceanology 27:861–862
Bowman JP, McCuaig RD (2003) Biodiversity, community structural shifts, and biogeography of prokaryotes within Antarctic continental shelf sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:2463–2483
Bradbury JP, Bezrukova YV, Chernyaeva GP, Colman SM, Khursevich G, King JW, Likhoshway YV (1994) A synthesis of post-glacial diatom records from Lake Baikal. Paleolimnology 10:213–252
Callender E, Granina L (1997) Geochemical mass balances of major elements in Lake Baikal. Limnol Oceanogr 42(1):148–155
Cappenberg TE (1974) Interrelations between sulfate-reducing and methane-producing bacteria in bottom deposits of a fresh-water lake. I. Field observations. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 40:285–295
Collett TS, Kuuskraa VA (1998) Hydrates contain vast world gas resources. Oil Gas J 96:90–95
Cragg BA, Parkes RJ, Fry JC, Weightman AJ, Rochelle PA, Maxwell JR (1996) Bacterial populations and processes in sediments containing gas hydrates (ODP Leg 146, Cascadia Margin). Earth Planet Sci Lett 139:497–507
De Batist M, Klerkx J, Van Rensbergen PV, Vanneste M, Poort J, Golmshtok AY, Kremlev A, Khlystov OM, Krinitsky P (2002) Active hydrate destabilization in Lake Baikal, Siberia? Terra Nova 14(6):436–442
Edgington DN, Klump JV, Robbins JA, Kusner YS, Pampura VD, Sandimirov IV (1991) Sedimentation rates, residence times and radionuclide inventories in Lake Baikal from Cs-137 and Pb-210 in sediment cores. Nature 350:601–604
Elvert M, Suess E, Whiticar MJ (1999) Anaerobic methane oxidation associated with marine gas hydrates: super-light C-isotopes from saturated and unsaturated c-20 and c-25 irregular isoprenoids. Naturwissenschaften 86:295–300
EMEP CCC (1995) Manual for sampling and chemical analysis. EMEP Chemical Coordinating Centre, Norwegian Institute of Air Research, Kjeller, Report /95/0-7726/June 1995
Falkner KK, Measures CI, Herbelin SE, Edmond JM (1991) The major and minor element geochemistry of Lake Baikal. Limnol Oceanogr 36:413–423
Fisher CR, MacDonald IR, Sassen R, Young CM, Macko SA, Hourdez S, Carney RS, Joye S, McMullin E (2000) Methane ice worms: Hesiocaeca colonizing fossil fuel reserves. Naturwissenschaften 87:84–187
Fomin GS (2000) Water. Control of chemical, bacterial and radiation safety according to international standards. Protector, Moscow
Galchenko VF (1994) Sulfate reduction, methane formation and methane oxidation in different water bodies of Banger Hills oasis, Antarctica. Microbiology 63:388–396
Granina LZ, Kallender E, Lomonosov IS, Mats VD, Golobokova LP (2001) Anomalies in pore waters composition in Lake Baikal bottom sediments. Russ Geol Geophys 42:362–372
Hallam SJ, Girguis PR, Preston СM, Richardson PM, Delong EF (2003) Identification of methyl coenzyme M reductase A (mcrA) genes associated with methane-oxidizing archaea. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(9):5483–5491
Hallam SJ, Putnam N, Preston СM, Detter JC, Rokshar D, Richardson PM, Delong EF (2004) Reverse methanogenesis: testing the hypothesis with environmental genomics. Science 305:1457–1462
Han X, Suess E, Sahling H, Wallmann K (2004) Fluid venting activity on the Costa Rica margin: new results from authigenic carbonates. Int J Earth Sci 93:596–611
Hinrichs K-U, Boetius A (2002) The anaerobic oxidation of methane: new insights in microbial ecology and biogeochemistry. In: Wefer G, Billett D, Hebbeln D, Jørgensen BB, Schlueter M, van Weering TCE (eds) Ocean marine systems. Springer, Berlin, pp 457–477
Hinrichs K-U, Summons RE, Orphan VJ, Sylva SP, Hayes JM (2000) Molecular and isotopic analysis of anaerobic methane-oxidizing communities in marine sediments. Org Geochem 31:1651–1701
Hoehler TM, Alperin MJ, Albert DB, Martens CS (1994) Field and laboratory studies of methane oxidation in an anoxic marine sediment—evidence for a methanogen-sulfate reducer consortium. Global Biogeochem Cycles 8:451–463
Inagaki F, Nunoura T, Nakagawa S, Teske A, Lever M, Lauer A, Suzuki M, Takai K, Delwiche M, Colwell FS, Nealson KH, Horikoshi K, D’Hondt S, Jørgensen BB (2006) Biogeographical distribution and diversity of microbes in methane hydrate-bearing deep marine sediments on the Pacific Ocean Margin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(8):2815–2820
Jørgensen BB, Weber A, Zopfi J (2001) Sulfate reduction and anaerobic methane oxidation in Black Sea sediments. Deep-Sea Res 48:2097–2120
Joye SB, Orcutt BN, Boetius A, Montoya JP, Schulz H, Erickson MJ, Lugo SK (2004) The anaerobic oxidation of methane and sulfate reduction in sediments from Gulf of Mexico cold seeps. Chem Geol 205(3/4):219–238
Kalmychkov GV, Egorov AV, Kuzmin MI, Khlystov OM (2006) Genetic types of methane of Lake Baikal. Dokl Earth Sci 411(5):672–675
Kasai Y, Takahata Y, Hoaki T, Watanabe K (2005) Physiological and molecular characterization of a microbial community established in unsaturated, petroleum-contaminated soil. Environ Microbiol 7(6):806–818
Khlystov OM (2006) New findings of gas hydrates in Lake Baikal bottom sediments. Russ Geol Geophys 47:979–981
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Klerkx J, Zemskaya TI, Matveeva TV, Khlystov OM, Grachev MA, Namsaraev BB, Dagurova OP, Golobokova LP, Vorobyova SS, Pogodaeva TP, Granin NG, Kalmychkov GV, Ponomarchuk VA, Shoji H, Mazurenko LL, Kaulio VV, Solovyov VA (2003) Methane hydrates in surface layer of deep water sediments of Lake Baikal. Dokl Earth Sci 393:822–826
Knyazeva LM (1954) Sedimentation in the sediments in USSR wetlands zone. In: Southern Baikal. Nauka, Moscow, pp 232–236
Krylov A, Khlystov O, Zemskaya T, Minami H, Hachikubo A, Nunokawa Y, Kida M, Shoji H, Naudts L, Poort J, Pogodaeva T (2008a) First discovery and formation process of authigenic siderite from gas hydrate-bearing mud volcanoes in fresh water: Lake Baikal, Eastern Siberia. Geophys Res Lett 35:1–6
Krylov A, Khlystov O, Zemskaya T, Minami H, Hachikubo A, Shoji H, Kida M, Pogodaeva T, Naudts L, Poort J (2008b) Formation of authigenic carbonates in mud volcanoes of Lake Baikal. Int Geochem 10:1051–1062
Krylov AA, Khlystov OM, Hachikubo A, Minami H, Nunokawa Y, Shoji H, Zemskaya TI, Naudts L, Pogodaeva TV, Kida M, Kalmychkov GV, Poort J (2010) Isotopic composition of dissolved inorganic carbon in subsurface sediments of gas hydrate-bearing mud volcanoes, Lake Baikal: implications for methane and carbonate origin. In: Bohrmann G, Jørgensen BB (eds) Proc 9th Int Conf Gas in Marine Sediments, 15–19 September 2008, Bremen. Geo-Mar Lett SI 30 (in press). doi:10.1007/s00367-010-0190-2
Kulm LD, Suess E, Moore JC, Carson B, Lewis BT, Ritger SD, Kadko DC, Thonburg TM, Embley RW, Rugh WD, Massoth GJ, Langseth MG, Cochrane GR, Camman RL (1986) Oregon subduction zone-venting, fauna, and carbonates. Science 231:561–566
Kuzmin MI, Kalmychkov GV, Gelety VA, Gnilusha VA, Goreglyad AV, Khakhaev BN, Pevzner LA, Kawai T, Yoshida N, Duchkov AD, Ponomarchuk VA, Kontorovich AE, Bazhin NM, Makhov GA, Dyadin YA, Kuznetsov FA, Larionov EG, Manakov AY, Smolyakov BS, Mandelbaum MM, Zheleznyakov NK (1998) First GH finding in Lake Baikal sedimentary bed. Dokl Earth Sci 362(4):541–543
Lanoil BD, Sassen R, La Duc MT, Sweet ST (2001) Bacteria and Archaea physically associated with Gulf of Mexico gas hydrates. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5143–5153
Lanoil BD, La Duc MT, Wright M, Kastner M, Nealson KH, Bartlett D (2005) Archaeal diversity in ODP legacy borehole 892b and associated seawater and sediments of the Cascadia Margin. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 54:167–177
Lin B, Braster M, van Breukelen BM, van Verseveld HW, Westerhoff HV, Roling WF (2005) Geobacteraceae community composition is related to hydrochemistry and biodegradation in an iron-reducing aquifer polluted by a neighboring landfill. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(10):5983–5991
MacDonald IR, Sager WW, Peccini MB (2003) Gas hydrate and chemosynthetic biota in mounded bathymetry at mid-slope hydrocarbon seeps: Northern Gulf of Mexico. Mar Geol 198:133–158
MacDonald IR, Bohrmann G, Escobar E, Abegg F, Blanchon P, Blinova V, Brückmann W, Drews M, Eisenhauer A, Han X, Heeschen K, Meier F, Mortera C, Naehr T, Orcutt B, Bernard B, Brooks J, de Farago M (2004) Asphalt volcanism and chemosynthetic life in the Campeche Knolls, Gulf of Mexico. Science 304:999–1002
Matveeva TV, Mazurenko LL, Soloviev VA, Klerkx J, Kaulio VV, Prasolov EM (2003) Gas hydrate accumulation in the subsurface sediments of Lake Baikal (Eastern Siberia). In: Woodside JM, Garrison RE, Moore JC, Kvenvolden KA (eds) Proc 7th Int Conf Gas in Marine Sediments, 7–11 October 2002, Baku, Azerbaijan. Geo-Mar Lett 23(3/4):289–299. doi:10.1007/s00367-003-0144-z
Michaelis W, Seifert R, Nauhaus K, Treude T, Thiel V, Blumenberg M, Knittel K, Gieseke A, Peterknecht K, Pape T, Boetius A, Amann R, Jørgenson BB, Widdel F, Peckmann J, Pimenkov N, Gulin MB (2002) Microbial reefs in the Black Sea fueled by anaerobic methane oxidation. Science 297:1013–1015
Milkov AV (2004) Global estimates of hydrate-bound gas in marine sediments: how much is really out there? Earth-Sci Rev 66:183–197
Milkov AV, Vogt PR, Crane K, Lein AY, Sassen R, Cherkashev GA (2004) Geological, geochemical and microbial processes at the hydrate-bearing Håkon Mosby mud volcano: a review. Chem Geol 205:347–366
Mizandrontsev IB (1975) On geochemistry of ground solutions. In: Baikal Depression dynamics. Nauka, Siberian Branch, Novosibirsk, pp 203–231
Namsaraev BB, Zemskaya TI (2000) Microbial processes of carbon circulation in bottom sediment of Lake Baikal (in Russian). RAS, Siberian Branch, Novosibirsk
Namsaraev BB, Dulov LY, Dubinina GA, Zemskaya TI, Granina LZ, Karabanov YB (1994) Participation of bacteria in the processes of organic matter synthesis and destruction in Lake Baikal microbial mats. Microbiology 63:345–351
Namsaraev BB, Dulov LY, Zemskaya TI, Karabanov YB (1995) Geochemical activity of sulfate reducing bacteria in Lake Baikal bottom sediments. Microbiology 64:405–410
Nauhaus K, Boetius A, Kruger M, Widdel F (2002) In vitro demonstration of anaerobic oxidation of methane coupled to sulphate reduction in sediment from a marine gas hydrate area. Environ Microbiol 4(5):296–305
Orcutt BN, Boetius A, Lugo SK, MacDonald IR, Samarkin VA, Joye SB (2004) Life at the edge of methane ice: microbial cycling of carbon and sulfur in Gulf of Mexico gas hydrates. Chem Geol 205:239–251
Orcutt B, Boetius A, Elvert M, Samarkin V, Joye S (2005) Molecular biogeochemistry of sulfate reduction, methanogenesis and the anaerobic oxidation of methane at Gulf of Mexico cold seeps. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69(17):4267–4281
Orphan VJ, Hinrichs K-U, Ussler W, Paull CK, Taylor LT, Sylva SP, Hayes JM, Delong EF (2001) Comparative analysis of methane-oxidizing archaea and sulfate-reducing bacteria in anoxic marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1922–1934
Orphan VJ, House CH, Hinrichs K-U, McKeegan KD, Delong EF (2002) Multiple archaeal groups mediate methane oxidation in anoxic cold deep sediments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:7663–7668
Peckmann J, Reiner A, Luth U, Luth C, Hansen BT, Heinicke C, Hoefs J, Reiner J (2001) Methane-denied carbonates and authigenic pyrite from the northwestern Black Sea. Mar Geol 177:129–150
Pimenov NV, Savvichev AS, Rusanov II, Lein AY, Ivanov MV (2000) Microbiological processes of carbon and sulfur cycles at cold methane seeps of the North Atlantic. Microbiology 69(6):709–720
Pimenov NV, Ul’yanova MO, Kanapatskii TA, Sivkov VV, Ivanov MV (2008) Microbiological and biogeochemical processes in a pockmark of the Gdansk Depression, Baltic Sea. Russian Microbiol 77(5):651–659
Pogodaeva TV, Zemskaya TI, Golobokova LP, Khlystov OM, Minami H, Sakagami H (2007) Chemical composition of pore waters of bottom sediments in Baikal basins. Russ Geol Geophys 48(11):886–900
Purdy KJ, Nedwell DB, Embley TM, Purdy KJ (2003) Analysis of the sulfate-reducing bacterial and methanogenic archaeal populations in contrasting Antarctic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3181–3191
Reeburgh WS (1980) Anaerobic methane oxidation: rate depth distributions in Skan Bay sediments. Earth Planet Sci Lett 47:345–352
Reed DW, Fujita Y, Delwiche ME, Blackwelder DB, Sheridan PP, Uchida T, Colwell FS (2002) Microbial communities from methane hydrate-bearing deep marine sediments in a forearc basin. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(8):3759–3770
Sassen R, MacDonald IR (1994) Evidence of structure H hydrate, Gulf of Mexico continental slope. Org Geochem 23:1029–1032
Shubenkova OV, Zemskaya TI, Chernitsyna SM, Khlystov OM, Triboy TI (2005) First results of investigation of phylogenetic diversity of Southern Baikal sediments microorganisms in the area of methane hydrates near-surface bedding. Microbiology 74:370–377
Stein LY, Jones G, Alexander B, Elmund K, Wright-Jones С, Nealson KH (2002) Intriguing microbial diversity associated with metal-rich particles from a freshwater reservoir. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 42:431–440
Suess E, Torres ME, Bohrmann G, Collier RW, Greinert J, Linke P, Rehder G, Tréhu A, Wallmann K, Winckler G, Zuelger E (1999) Gas hydrate destabilization: enhanced dewatering, benthic material turnover and large methane plumes at the Cascadia convergent margin. Earth Planet Sci Lett 170:1–15
Teske A, Hinrichs KU, Edgcomb V, Gomez AD, Kysela D, Sylva SP, Sogin ML, Jannasch HW (2002) Microbial diversity of hydrothermal sediments in the Guaymas Basin: evidence for anaerobic methanotrophic communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(4):1994–2007
Treude T, Boetius A, Knittel K, Wallmann K, Jørgensen BB (2003) Anaerobic oxidation of methane above gas hydrates at Hydrate Ridge, NE Pacific Ocean. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 264:1–14
Valentine DL, Reeburgh WS (2000) New perspectives on anaerobic methane oxidation. Environ Microbiol 2(5):477–484
Valentine DL, Blanton DC, Reeburgh WS, Kastner M (2001) Water column methane oxidation adjacent to an area of active hydrate dissociation, Eel river Basin. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65:2633–2640
Van Rensbergen P, De Batist M, Klerkx J, Hus R, Poort J, Vanneste M, Granin N, Khlystov O, Krinitsky P (2002) Sublacustrine mud volcanoes and methane seeps caused by dissociation of gas hydrates in Lake Baikal. Geology 30(7):631–634
Winfrey MR, Zeikus JG (1979) Anaerobic metabolism of immediate methane precursors in Lake Mendota. Appl Environ Microbiol 37:244–253
Zemskaya TI, Khlystov OM, Yegorov AV, Pogodaeva TV, Kalmychkov GV, Shubenkova OV, Chernitsyna SM, Vorobyova SS, Grachev MA (2008) Integrated studies of gas hydrates ingresses in Lake Baikal bottom sediments. In: Zavarzin GA, Kudeyarov VN (eds) Climatic and environmental changes, Processes in biosphere: changes in soil and vegetation cover and in RF territorial waters, matter turnover influenced by global climate changes and by catastrophic processes, vol. 4. IFKh & BPP RAN, Moscow, pp 125–152
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Presidium of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Program 17 (Project 17.9), and the Russian Foundation for Basic Research Projects Nos. 08-05-00709-а, Integration Project No. 27.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zemskaya, T.I., Pogodaeva, T.V., Shubenkova, O.V. et al. Geochemical and microbiological characteristics of sediments near the Malenky mud volcano (Lake Baikal, Russia), with evidence of Archaea intermediate between the marine anaerobic methanotrophs ANME-2 and ANME-3. Geo-Mar Lett 30, 411–425 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-010-0199-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-010-0199-6