Abstract
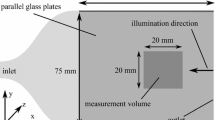
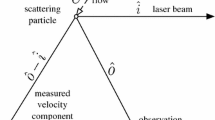
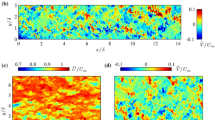
Non-intrusive Planar Doppler Velocimetry (PDV) has been extended to two-component measurements in a Mach 3, flat plate turbulent boundary layer and the distorted boundary layers downstream of 7° and 14° expansions. PDV results were compared to redundant Laser Doppler Velocimetry (LDV) measurements. Mean velocity results obtained with the two techniques agree to within ±5%. PDV measurements were obtained within 0.4 mm of the surface while LDV could be employed only to within approximately 2.0 mm, highlighting a near-wall resolution advantage for PDV. Effects including those associated with separate filtered and reference cameras led to PDV uncertainties of the same order as the encountered moderate turbulence intensities, precluding an investigation of instantaneous turbulence fields. Despite these difficulties, the current multi-component measurements in distorted, compressible boundary layers highlight the potential of PDV and represent progress in its ongoing evolution. Sources of error and improvements required for quantitative turbulence measurements are discussed. Further advances can be expected from ongoing development efforts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 14 February 1997 / Accepted: 26 August 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arnette, S., Samimy, M. & Elliott, G. Two-component planar Doppler velocimetry in the compressible turbulent boundary layer. Experiments in Fluids 24, 323–332 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480050179
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480050179