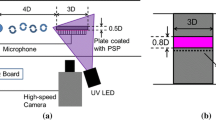
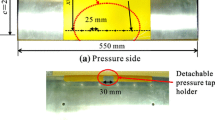
Abstract
Pressure-sensitive-paint (PSP) measurement was conducted for unsteady phenomena at various frequencies up to the order of kHz in low-speed flow to evaluate measurement accuracy of PSP. Pressure fluctuations on the floor surface induced by the Karman vortex were measured by PSP and unsteady pressure transducer. The dominant frequency of the pressure fluctuations is varied from 0.15 to 1.7 kHz by changing the size of the square cylinder. While regions with large pressure fluctuations could be visualized by calculating root mean square of pressure fluctuations from PSP images, the values significantly differed from those measured by pressure transducer. By applying Fast Fourier Transform (FFT), the power spectral density (PSD) at peak frequencies could be obtained within an error of 20%. Singular-value decomposition (SVD) yields a remarkable improvement in signal-to-noise ratio. However, amplitude of pressure fluctuations is changed depending on the way how to select modes. Three mode-selection methods for SVD filtering/reconstruction analysis are proposed in this study which show good improvement compared with convection method and are proved capable of extracting characteristic behaviors of the flow phenomena even below the noise floor.
Graphic abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
m × n matrix
- A, B :
-
Stern–Volmer coefficient
- D :
-
Width and depth of square cylinder model
- f :
-
Frequency
- f s :
-
Frame rate of camera
- Δf :
-
Frequency resolution
- I :
-
Intensity of PSP luminescence
- L :
-
Length
- N :
-
Number of images
- N FFT :
-
Number of images for FFT
- P :
-
Pressure
- ΔP :
-
Measurement error of PSP
- PtTFPP:
-
Platinum(II)-5,10,15,20-tetrakis-(2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorphenyl)-porphyrin
- POD:
-
Proper orthogonal decomposition
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- St :
-
Strouhal number
- S XX :
-
Auto spectral obtained by FFT
- s(ω):
-
Spectral density function
- T :
-
Temperature
- U :
-
Eigenvector matrix of AAT
- U :
-
Velocity
- U ∞ :
-
Free stream velocity
- u :
-
Left singular vectors
- V :
-
Eigenvector matrix of ATA
- v :
-
Right singular vectors
- w :
-
Frequency
- x :
-
x-direction
- y :
-
y-direction
- Σ :
-
Non-zero singular values of matrix A
- σ :
-
Singular values
- ave:
-
Average
- fps:
-
Frame per second
- Kulite:
-
Pressure transducer
- MS:
-
Mode spectral
- PC-PSP:
-
Polymer/Ceramic PSP
- PSP:
-
Pressure-sensitive paint
- PSD:
-
Power spectral density
- ref:
-
Reference condition
- reconst:
-
Reconstructed value/mode
- rms/RMS:
-
Root mean square of pressure fluctuations
- SNR:
-
Signal-to-noise ratio
- SVD:
-
Singular-value decomposition
- TS:
-
Time series
- Σ:
-
Sum
References
Anyoji M, Numata D, Nagai H, Asai K (2015) Pressure-sensitive paint technique for surface pressure measurement in a low density wind tunnel. J Vis 18(2):297–309
Asai K, Yorita D (2011) Unsteady PSP measurement in low-speed flow—overview of recent advancement at Tohoku University. AIAA paper 2011, 2011-0847
Bell JH, Schairer ET, Lawrence A, Hand LA, Mehta RD (2001) Surface pressure measurements using luminescent coatings. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 33:155–206
Davis T, Edstrand A, Alvi FS, Cattaffesta L, Yorita D, Asai K (2015) Investigation of impinging jet resonant modes using unsteady pressure-sensitive paint measurements. Exp Fluids 56(5):1–13
Fujii S, Numata D, Nagai H, Asai K (2013) Development of ultrafast response anodized aluminum pressure-sensitive paints. In: Proceedings of the 51st AIAA aerospace sciences meeting including the new horizons forum and aerospace exposition, grapevine, Texas, USA, AIAA-2013-0485
Gordeyev S, De Lucca N, Jumper EJ, Hird K, Juliano TJ, Gregory JW, Thordahl J, Wittich DJ (2014) Comparison of unsteady pressure fields on turrets with different surface features using pressure-sensitive paint. Exp Fluids 55:1–20
Gregory JW, Sakaue H, Sullivan JP, Raghu S (2001) Characterization of miniature fluidic oscillator flowfields using porous pressure sensitive paint. In: Proceedings of the ASME fluid engineering division-summer meeting, New Orleans, LA, FEDSM-2001-18058
Gregory JW, Sakaue H, Liu T, Sullivan JP (2014) Fast pressure-sensitive paint for flow and acoustic diagnostics. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 46:303–330
Kameda M, Seki H, Makoshi T, Amao Y, Nakakita K (2008) Unsteady measurement of a transonic delta wing flow by a novel PSP. In: Proceedings of the 26th AIAA applied aerodynamics conference, AIAA-2008-6418
Kitashima S, Numata D, Asai K (2014) Characterization of pressure-sensitive paint containing ceramic particles. In: Proceedings of the 16th international symposium on flow visualization, Okinawa, Japan, ISFV16-1286
Liu T (2003) Pressure-correction method for low-speed pressure-sensitive paint measurements. AISS J 41:906–911
Liu T, Sullivan JP (2005) Pressure and temperature sensitive paints. Springer, Berlin
Lumley JL (1967) The structure of inhomogeneous turbulence. In: Yaglom AM, Tatarski VL (eds) Atmospheric turbulence and wave propagation. Nauka, Moscow, pp 166–178
Nakakita K (2011) Unsteady pressure measurement on NACA0012 model using global low-speed unsteady PSP technique. In: Proceedings of the 41st AIAA fluid dynamics conference and exhibit, 2011, Honolulu, Hawaii, AIAA 2011-3901
Nakakita K (2013) Detection of phase and coherence of unsteady pressure field using unsteady PSP measurement. In: Proceedings of the AIAA ground testing conference fluid dynamics and co-located conferences, San Duego, CA, AIAA-2013-3124
Nakakita K, Takama Y, Imagawa K, Kato H (2012) Unsteady PSP measurement of transonic unsteady flow field around a rocket fairing model. In: Proceedings of the 28th aerodynamic measurement technology, ground testing, and flight testing conference, Orleans, Louisiana, AIAA-2012-2578
Pandey A, Gregory JW (2015) Dynamic response characteristics of polymer/ceramic pressure-sensitive paint. In: Proceedings of the 53rd aerospace sciences meeting, Kissimmee, Florida, AIAA-2015-0021
Pastuhoff M, Yorita D, Asai K, Alfredsson PH (2013) Enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio of pressure sensitive paint data by singular value decomposition. Meas Sci Technol 24:075301
Peng D, Wang S, Liu Y (2016) Fast PSP measurements of wall-pressure fluctuation in low-speed flows: improvements using proper orthogonal decomposition. Exp Fluids 57:1–17
Sakaue H, Kakisako T, Ishikawa H (2011) Characterization and optimization of polymer-ceramic pressure-sensitive paint by controlling polymer content. Sensors 11(7):6967–6977
Scroggin AM, Slamovich EB, Crafton JW, Lachendo N, Sullivan JP (1999) Porous polymer/ceramic composites for luminescent-based temperature and pressure measurement. Mater Res Soc Proc 560:347–352
Sugimoto T, Kitashima S, Numata D, Nagai H, Asai K (2012) Characterization of frequency response of pressure-sensitive paints. In: Proceedings of the 50th AIAA aerospace sciences meeting including the new horizons forum and aerospace exposition, AIAA-2012-1185
Sugioka Y, Numata D, Asai K, Nakakita K, Koike S, Koga S (2015) Unsteady PSP measurement of transonic buffet on a wing. In: Proceedings of the 53rd AIAA aerospace sciences meeting, kissimmee, Florida, 5–9 January, 2015, AIAA-2015-0025
Sugioka Y, Numata D, Asai K, Koike S, Nakkita K, Nakajima T (2018) Polymer/ceramic pressure-sensitive paint with reduced roughness for unsteady measurement in transonic flow. AIAA J 56(6):2145–2156
Yorita D, Numata D, Nagai H, Asai K (2010) Measuring unsteady low-speed flow phenomena by using a time-series analysis of pressure-sensitive paint images. In: Proceedings of the international symposium on flow visualization, EXCO Daegu, Korea
Acknowledgements
This work and the experiments were conducted in the Lab of Experimental Aerodynamics, Tohoku University, Japan. The support from the Talents Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (China), the JSPS KAKENHI (No. 16H04582), and the JST-PREST (No. JPMJPR1678) are gratefully acknowledged by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugioka, Y., Hiura, K., Chen, L. et al. Unsteady pressure-sensitive-paint (PSP) measurement in low-speed flow: characteristic mode decomposition and noise floor analysis. Exp Fluids 60, 108 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-019-2755-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-019-2755-9