Abstract
Purpose
There is an unmet need to develop prognostic biomarkers in post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) patients. We examine whether Ki-67 and PD-L1 expression can be used to guide adjuvant therapy.
Methods
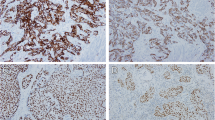
Tissue microarrays were constructed from 130 post-NAC radical cystectomy samples. Up to 5 cores per sample were included. Expressions of Ki-67 and PD-L1 were evaluated using immunohistochemistry (IHC).
Results
Using a Cox regression model, positive Ki-67 expression in post-NAC radical cystectomy samples was associated with poorer overall survival (OS) (HR = 2.412, 95% CI, 1.076–5.408), independent of the pathological lymph node/N-stage. Positive Ki-67 expression was also associated with lack of tumor downstaging in a multivariable logistic regression model analysis (OR = 0.081, 95% CI, 0.014–0.464). PD-L1− and PD-L1+ expression was associated with a median OS of 49.8 months and 26.9 months, respectively, which did not reach statistical significance. Patients with Ki-67/PD-L1 double-negative tumors had a significantly longer median OS of 98.2 months versus 29.9 and 26.9 months in PD-L1−/Ki-67+ and PD-L1+/Ki-67+ tumors, respectively. Lack of tumor downstaging was significantly associated with positive Ki-67 and positive PD-L1 expression.
Conclusion
Positive Ki-67 and PD-L1 expression in post-NAC radical cystectomy samples was associated with inferior OS and absence of tumor downstaging. IHC on Ki-67 and PD-L1 would help to select patients for adjuvant therapy in post-NAC muscle-invasive bladder cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MIBC:
-
Muscle-invasive bladder cancer
- MVAC:
-
Methotrexate, Vinblastine, Doxorubicin/Adriamycin, Cisplatin
- NAC:
-
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- TMA:
-
Tissue microarray
References
Urinary Bladder (Invasive & In Situ) Cancer Recent Trends in U.S. Mortality Rates, 2000–2016 By Sex (2000–2016) National Cancer Institute.
Rosenberg J, Sridhar SS, Zhang J, Smith D, Ruether D, Flaig TW, Baranda J, Lang J, Plimack ER, Sangha R, Heath EI, Merchan J, Quinn DI, Srinivas S, Milowsky M, Wu C, Gartner EM, Zuo P, Melhem-Bertrandt A, Petrylak DP (2020) EV-101: a phase I study of single-agent enfortumab vedotin in patients with nectin-4-positive solid tumors, including metastatic urothelial carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 38(10):1041–1049. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.19.02044
Rosenberg JE, O'Donnell PH, Balar AV, McGregor BA, Heath EI, Yu EY, Galsky MD, Hahn NM, Gartner EM, Pinelli JM, Liang SY, Melhem-Bertrandt A, Petrylak DP (2019) Pivotal trial of enfortumab vedotin in urothelial carcinoma after platinum and anti-programmed death 1/programmed death ligand 1 therapy. J Clin Oncol 37(29):2592–2600. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.19.01140
Grossman HB, Natale RB, Tangen CM, Speights VO, Vogelzang NJ, Trump DL, deVere White RW, Sarosdy MF, Wood DP, Raghavan D, Crawford ED (2003) Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus cystectomy compared with cystectomy alone for locally advanced bladder cancer. N Engl J Med 349(9):859–866. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa022148
Martinez Chanza N, Werner L, Plimack E, Yu EY, Alva AS, Crabb SJ, Powles T, Rosenberg JE, Baniel J, Vaishampayan UN, Berthold DR, Ladoire S, Hussain SA, Milowsky MI, Agarwal N, Necchi A, Pal SK, Sternberg CN, Bellmunt J, Galsky MD, Harshman LC, Investigators R (2019) Incidence, patterns, and outcomes with adjuvant chemotherapy for residual disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in muscle-invasive urinary tract cancers. Eur Urol Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euo.2018.12.013
Shariat SF, Bolenz C, Godoy G, Fradet Y, Ashfaq R, Karakiewicz PI, Isbarn H, Jeldres C, Rigaud J, Sagalowsky AI, Lotan Y (2009) Predictive value of combined immunohistochemical markers in patients with pT1 urothelial carcinoma at radical cystectomy. J Urol 182(1):78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2009.02.125(discussion 84)
Shariat SF, Tokunaga H, Zhou J, Kim J, Ayala GE, Benedict WF, Lerner SP (2004) p53, p21, pRB, and p16 expression predict clinical outcome in cystectomy with bladder cancer. J Clin Oncol 22(6):1014–1024. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2004.03.118
Vetterlein MW, Roschinski J, Gild P, Marks P, Soave A, Doh O, Isbarn H, Höppner W, Wagner W, Shariat SF, Brausi M, Büscheck F, Sauter G, Fisch M, Rink M (2017) Impact of the Ki-67 labeling index and p53 expression status on disease-free survival in pT1 urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Transl Androl Urol 6(6):1018–1026. https://doi.org/10.21037/tau.2017.11.10
Sweis RF, Galsky MD (2016) Emerging role of immunotherapy in urothelial carcinoma-Immunobiology/biomarkers. Urol Oncol 34(12):556–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.10.006
Bellmunt J, Mullane SA, Werner L, Fay AP, Callea M, Leow JJ, Taplin ME, Choueiri TK, Hodi FS, Freeman GJ, Signoretti S (2015) Association of PD-L1 expression on tumor-infiltrating mononuclear cells and overall survival in patients with urothelial carcinoma. Ann Oncol 26(4):812–817. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdv009
Sobecki M, Mrouj K, Camasses A, Parisis N, Nicolas E, Llères D, Gerbe F, Prieto S, Krasinska L, David A, Eguren M, Birling MC, Urbach S, Hem S, Déjardin J, Malumbres M, Jay P, Dulic V, Lafontaine DLJ, Feil R, Fisher D (2016) The cell proliferation antigen Ki-67 organises heterochromatin. Elife 5:e13722. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.13722
Sun X, Bizhanova A, Matheson TD, Yu J, Zhu LJ, Kaufman PD (2017) Ki-67 contributes to normal cell cycle progression and inactive X heterochromatin in p21 checkpoint-proficient human cells. Mol Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00569-16
Peyton CC, Tang D, Reich RR, Azizi M, Chipollini J, Pow-Sang JM, Manley B, Spiess PE, Poch MA, Sexton WJ, Fishman M, Zhang J, Gilbert SM (2018) Downstaging and survival outcomes associated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy regimens among patients treated with cystectomy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. JAMA Oncol 4(11):1535–1542. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.3542
Margulis V, Lotan Y, Karakiewicz PI, Fradet Y, Ashfaq R, Capitanio U, Montorsi F, Bastian PJ, Nielsen ME, Müller SC, Rigaud J, Heukamp LC, Netto G, Lerner SP, Sagalowsky AI, Shariat SF (2009) Multi-institutional validation of the predictive value of Ki-67 labeling index in patients with urinary bladder cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 101(2):114–119. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djn451
Wang L, Zhou M, Feng C, Gao P, Ding G, Zhou Z, Jiang H, Wu Z, Ding Q (2016) Prognostic value of Ki67 and p63 expressions in bladder cancer patients who underwent radical cystectomy. Int Urol Nephrol 48(4):495–501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-1197-4
Shariat SF, Passoni N, Bagrodia A, Rachakonda V, Xylinas E, Robinson B, Kapur P, Sagalowsky AI, Lotan Y (2014) Prospective evaluation of a preoperative biomarker panel for prediction of upstaging at radical cystectomy. BJU Int 113(1):70–76. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.12343
Xylinas E, Robinson BD, Kluth LA, Volkmer BG, Hautmann R, Küfer R, Zerbib M, Kwon E, Thompson RH, Boorjian SA, Shariat SF (2014) Association of T-cell co-regulatory protein expression with clinical outcomes following radical cystectomy for urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Eur J Surg Oncol 40(1):121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2013.08.023
Boorjian SA, Sheinin Y, Crispen PL, Farmer SA, Lohse CM, Kuntz SM, Leibovich BC, Kwon ED, Frank I (2008) T-cell coregulatory molecule expression in urothelial cell carcinoma: clinicopathologic correlations and association with survival. Clin Cancer Res 14(15):4800–4808. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0731
Powles T, Kockx M, Rodriguez-Vida A, Duran I, Crabb SJ, Van Der Heijden MS, Szabados B, Pous AF, Gravis G, Herranz UA, Protheroe A, Ravaud A, Maillet D, Mendez MJ, Suarez C, Linch M, Prendergast A, van Dam PJ, Stanoeva D, Daelemans S, Mariathasan S, Tea JS, Mousa K, Banchereau R, Castellano D (2019) Clinical efficacy and biomarker analysis of neoadjuvant atezolizumab in operable urothelial carcinoma in the ABACUS trial. Nat Med 25(11):1706–1714. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0628-7
Necchi A, Raggi D, Gallina A, Madison R, Colecchia M, Lucianò R, Montironi R, Giannatempo P, Farè E, Pederzoli F, Bandini M, Bianchi M, Colombo R, Gandaglia G, Fossati N, Marandino L, Capitanio U, Dehò F, Ali SM, Chung JH, Ross JS, Salonia A, Briganti A, Montorsi F (2020) Updated results of PURE-01 with preliminary activity of neoadjuvant pembrolizumab in patients with muscle-invasive bladder carcinoma with variant histologies. Eur Urol 77(4):439–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2019.10.026
Acknowledgements
Dr. Alex Lopez performed pathological scoring of immunohistochemistry on AR and Ki-67. This work is supported in part by the Moffitt’s Tissue Core performed fixing and IHC staining, and Biostatistics and Bioinformatics Shared Resources at the H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center & Research Institute, an NCI-designated Comprehensive Cancer Center (P30-CA076292). We thank them for their help. Editorial assistance was provided by the Moffitt Cancer Center’s Scientific Editing Department by Dr. Paul Fletcher & Daley Drucker. No compensation was given beyond their regular salaries.
Funding
This study is funded by Moffitt’s internal research support to Jingsong Zhang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SR: data collection and manuscript writing; YK and JZ: data analysis and manuscript writing; JD: data collection; RL, PS, MP, BJM, JP, SG, and WS: data collection and manuscript editing; JZ: project development, data management, data analysis and manuscript writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Zhang has received honoraria for advisory board or speaker program from AstraZeneca, Merck and Seattle Genetics.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study qualified for expedited approval under the federal regulations at 45CFR46.116(d) per the USF Institutional Review Board, IRB #Pro00015860.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubino, S., Kim, Y., Zhou, J. et al. Positive Ki-67 and PD-L1 expression in post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy muscle-invasive bladder cancer is associated with shorter overall survival: a retrospective study. World J Urol 39, 1539–1547 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-020-03342-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-020-03342-5