Abstract
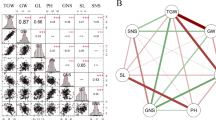
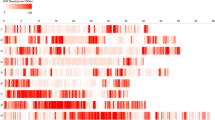
RAD-seq method is a recently developed, cost-effective, and high-throughput approach for detecting genetic variability based on single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and high-density genetic map. This study aimed to construct the quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping for yield-associated agronomic traits in rice using a BC2F6 population which was derived from japonica hybrid rice Liaoyou 5218. Liaoyou 5218 were firstly crossed to female parent 5216A, and the subsequent self-crossed BC1F6 population was backcrossed to 5216A. The 167 BC2F6 breeding lines showed different agronomic traits from parental Liaoyou 5218 and C418. RAD-seq and bioinformatics methods were used to identify high-quality SNPs in the 167 BC2F6 breeding lines, which generated 40968 SNP markers on 12 chromosomes in rice. Linkage and QTL mapping was constructed, and 14 QTLs related to 6 agronomic traits were identified, including 4, 3, and 4 QTLs on chr03, 09, and 10, respectively. Among the yield-associated QTLs mapping genes, ITPK3 and EGY3 were related to plant height; CYP724B1, GAPC2, TRS120, BADH1, AOX1a, AOX1b, and COLD1 were associated with average panicle length; ACT2 and BAMY1 were associated with 1000-grain weight and tiller number per plant, respectively. We suggested that the 14 QTLs in the BC2F6 breeding lines derived from Liaoyou 5218 might be of important values for the identification and marker-assisted selection of candidate genes in rice breeding.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki Y, Okamura Y, Tadaka S, Kinoshita K, Obayashi T (2016) ATTED-II in 2016: a plant coexpression database towards lineage-specific coexpression. Plant Cell Physiol 57:e5. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcv165
Baicharoen A, Vijayan R, Pongprayoon P (2018) Structural insights into betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase (BADH2) from Oryza sativa explored by modeling and simulations. Sci Rep 8:12892. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31204-z
Baird NA, Etter PD, Atwood TS, Currey MC, Shiver AL, Lewis ZA, Selker EU, Cresko WA, Johnson AE (2008) Rapid SNP discovery and genetic mapping using sequenced RAD markers. PLoS ONE 3:e3376. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0003376
Begum H, Spindel JE, Lalusin A, Borromeo T, Gregorio G, Hernandez J, Virk P, Collard B, Mccouch SR (2015) Genome-wide association mapping for yield and other agronomic traits in an elite breeding population of tropical rice (Oryza sativa). PLoS ONE 10:e0119873. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119873
Bodénès C, Chancerel E, Ehrenmann F, Kremer A, Plomion C (2016) High-density linkage mapping and distribution of segregation distortion regions in the oak genome. DNA Res 23:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsw001
Brar DS, Khush GS (2018) Wild relatives of rice: a valuable genetic resource for genomics and breeding research. Springer, Cham, pp 1–25
Brondani C, Rangel N, Brondani V, Ferreira E (2002) QTL mapping and introgression of yield-related traits from Oryza glumaepatula to cultivated rice (Oryza sativa) using microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 104:1192–1203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-0869-5
Chemaly ER, Kang S, Zhang S, Mccollum LT, Chen J, Bénard L, Purushothaman KR, Hajjar RJ, Lebeche D (2015) Genetic gains in grain yield through genomic selection in eight bi-parental maize populations under drought stress. J Physiol 591:5337–5355. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2014.07.0460
Chen X, Yuan L, Ludewig U (2016) Natural genetic variation of seed micronutrients of Arabidopsis thaliana grown in zinc-deficient and zinc-amended soil. Front Plant Sci 7:1070. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01070
Dong Z, Yu Y, Li S, Wang J, Tang S, Huang R (2016) Abscisic acid antagonizes ethylene production through the ABI4-mediated transcriptional repression of ACS4 and ACS8 in arabidopsis. Mol Plant 9:126–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2015.09.007
Duitama J, Silva A, Sanabria Y, Cruz DF, Quintero C, Ballen C, Lorieux M, Scheffler B, Farmer A, Torres E (2015) Whole genome sequencing of elite rice cultivars as a comprehensive information resource for marker assisted selection. PLoS ONE 10:e0124617. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0124617
Fan W, Zong J, Luo Z, Chen M, Zhao X, Zhang D, Qi Y, Yuan Z (2016) Development of a RAD-Seq based DNA polymorphism identification software, AgroMarker finder, and its application in rice marker-assisted breeding. PLoS ONE 11:e0147187. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0147187
Geber A, Hitchcock CA, Swartz JE, Pullen FS, Marsden KE, Kwonchung KJ, Bennett JE (1995) Deletion of the Candida glabrata ERG3 and ERG11 genes: effect on cell viability, cell growth, sterol composition, and antifungal susceptibility. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 39:2708–2717
Gichuhi E, Himi E, Takahashi H, Zhu S, Doi K, Tsugane K, Maekawa M (2016) Identification of QTLs for yield-related traits in RILs derived from the cross between pLIA-1 carrying Oryza longistaminata chromosome segments and Norin 18 in rice. Breed Sci 66:720–733. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.16083
Guo M, Yang YH, Liu M, Meng QC, Zeng XH, Dong LX, Tang SZ, Gu MH, Yan CJ (2014a) Clustered spikelets 4, encoding a putative cytochrome P450 protein CYP724B1, is essential for rice panicle development. Chin Sci Bull 59:4050–4059. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0568-z
Guo Y, Yuan H, Fang D, Song L, Liu Y, Liu Y, Wu L, Yu J, Li Z, Xu X (2014b) An improved 2b-RAD approach (I2b-RAD) offering genotyping tested by a rice (Oryza sativa L.) F2 population. BMC Genom 15:956. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-956
He Q, Yu J, Kim TS, Cho YH, Lee YS, Park YJ (2015) Resequencing reveals different domestication rate for BADH1 and BADH2 in rice (Oryza sativa). PLoS ONE 10:e0134801. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0134801
Hu WW, Gong H, Pua EC (2010) Modulation of SAMDC expression in Arabidopsis thaliana alters in vitro shoot organogenesis. Physiol Plant 128:740–750. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2006.00799.x
Hyejeong C, Hyekyoung K, Wang MH (2010) Expression of Kip-related protein 4 gene (KRP4) in response to auxin and cytokinin during growth of Arabidopsis thaliana. BMB Rep 43:273–278. https://doi.org/10.5483/BMBRep.2010.43.4.273
Ito Y, Saisho D, Nakazono M, Tsutsumi N, Hirai A (1997) Transcript levels of tandem-arranged alternative oxidase genes in rice are increased by low temperature. Gene 203:121. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00502-7
Khush GS (2013) Strategies for increasing the yield potential of cereals: case of rice as an example. Plant Breed 132:433–436. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.1991
Kurata N, Nagamura Y, Yamamoto K, Harushima Y, Sue N, Wu J, Antonio BA, Shomura A, Shimizu T, Lin SY (1994) A 300 kilobase interval genetic map of rice including 883 expressed sequences. Nat Genet 8:365–372
Lee T, Yang S, Kim E, Ko Y, Hwang S, Shin J, Shim JE, Shim H, Kim H, Kim C (2015) AraNet v2: an improved database of co-functional gene networks for the study of Arabidopsis thaliana and 27 other nonmodel plant species. Nucleic Acids Res 43:996–1002. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1053
Li C, Bai G, Carver BF, Chao S, Wang Z (2015) Single nucleotide polymorphism markers linked to QTL for wheat yield traits. Euphytica 206:89–101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1475-3
Liu S, Li Y, Qin Z, Geng X, Bao L, Kaltenboeck L, Kucuktas H, Dunham R, Liu Z (2016) High-density interspecific genetic linkage mapping provides insights into genomic incompatibility between channel catfish and blue catfish. Anim Genet 47:81–90. https://doi.org/10.1111/age.12372
Ma Y, Dai X, Xu Y, Luo W, Zheng X, Zeng D, Pan Y, Lin X, Liu H, Zhang D (2015) COLD1 confers chilling tolerance in rice. Cell 160:1209–1221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.046
Mcdowell JM, Huang S, Mckinney EC, Chambliss S, Meagher RB (2010) Strong, constitutive expression of the Arabidopsis ACT2/ACT8 actin subclass in vegetative tissues. Plant J Cell Mol Biol 10:107–121. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1996.10010107.x
Naramoto S, Nodzyński T, Dainobu T, Takatsuka H, Okada T, Friml J, Fukuda H (2014) VAN4 encodes a putative TRS120 that is required for normal cell growth and vein development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 55:750. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcu012
Niu N, Liang W, Yang X, Jin W, Wilson ZA, Hu J, Zhang D (2013) EAT1 promotes tapetal cell death by regulating aspartic proteases during male reproductive development in rice. Nat Commun 4:1445. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2396
Nunes JDRDS, Liu S, Pértille F, Perazza CA, Villela PMS, Almeidaval VMFD, Hilsdorf AWS, Liu Z, Coutinho LL (2017) Large-scale SNP discovery and construction of a high-density genetic map of Colossoma macropomum through genotyping-by-sequencing. Sci Rep 7:46112. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46112
Pan L, Yin Z, Huang Y, Chen J, Zhu L, Zhao Y, Guo J (2017) QTL for maize grain yield identified by QTL mapping in six environments and consensus loci for grain weight detected by meta-analysis. Plant Breed 136:820–833. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12524
Pegadaraju V, Nipper R, Hulke B, Qi L, Schultz Q (2013) De novo sequencing of sunflower genome for SNP discovery using RAD (Restriction site Associated DNA) approach. BMC Genom 14:556–556. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-556
Peng Y, Hu Y, Mao B, Xiang H, Shao Y, Pan Y, Sheng X, Li Y, Ni X, Xia Y (2015) Genetic analysis for rice grain quality traits in the YVB stable variant line using RAD-seq. Mol Genet Genom 291:297–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-015-1104-9
Pujol V, Forrest KL, Zhang P, Rouse MN, Hayden MJ, Huang L, Tabe L, Lagudah E (2015) Identification of a stem rust resistance locus effective against Ug99 on wheat chromosome 7AL using a RAD-Seq approach. Theor Appl Genet 128:1397–1405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2514-0
Reineke LC (2014) Reassessment of QTLs for Late Blight Resistance in the Tomato Accession L3708 using a Restriction Site Associated DNA (RAD) linkage map and highly aggressive isolates of Phytophthora infestans. PLoS ONE 9:e96417. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0096417
Schwacke R, Fischer K, Ketelsen B, Krupinska K, Krause K (2007) Comparative survey of plastid and mitochondrial targeting properties of transcription factors in Arabidopsis and rice. Mol Genet Genom 277:631–646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-007-0214-4
Sheng WT, Jun WU, Bai B, Rao YS (2017) Research progress on utilization of wild rice germplasm in rice high-yield breeding. J South Agric 48:222–230
Shi Y, Yang S (2015) COLD1: a cold sensor in rice. Sci China Life Sci 58:409–410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-015-4831-6
Shu K, Chen Q, Wu Y, Liu R, Zhang H, Wang S, Tang S, Yang W, Xie Q (2016) ABSCISIC ACID-INSENSITIVE 4 negatively regulates flowering through directly promoting Arabidopsis FLOWERING LOCUS C transcription. J Exp Bot 67:195–205. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv459
Stratula OR, Kalendar RN, Sivolap YM (2015) Allelic variants of the gene bamy1 barley in Eastern European and Central Asian areas. Cytol Genet 49:80–89. https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452715020103
Su Z, Jin S, Lu Y, Zhang G, Chao S, Bai G (2016) Single nucleotide polymorphism tightly linked to a major QTL on chromosome 7A for both kernel length and kernel weight in wheat. Mol Breed 36:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-016-0436-4
Tang W, Wu T, Ye J, Sun J, Jiang Y, Yu J, Tang J, Chen G, Wang C, Wan J (2016) Erratum to: SNP-based analysis of genetic diversity reveals important alleles associated with seed size in rice. BMC Plant Biol 16:93. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0801-9
Terziyska N, Lutz T, Kozany C, Mokranjac D, Mesecke N, Neupert W, Herrmann J, Hell K (2005) Mia40, a novel factor for protein import into the intermembrane space of mitochondria is able to bind metal ions. FEBS Lett 579:179–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2004.11.072
Thakur A, Bhatla SC (2015) Proteomic analysis of oil body membrane proteins accompanying the onset of desiccation phase during sunflower seed development. Plant Signal Behav 10:e1030100. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2015.1030100
Vishwakarma A, Bashyam L, Senthilkumaran B, Scheibe R, Padmasree K (2014) Physiological role of aox1a in photosynthesis and maintenance of cellular redox homeostasis under high light in arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol Biochem 81:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.01.019
Wang J, Wang Z, Du X, Yang H, Han F, Han Y, Yuan F, Zhang L, Peng S, Guo E (2017) A high-density genetic map and QTL analysis of agronomic traits in foxtail millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.] using RAD-seq. PLoS ONE 12:717. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179717
Winter D, Vinegar B, Nahal H, Ammar R, Wilson GV, Provart NJ (2007) An “Electronic Fluorescent Pictograph” browser for exploring and analyzing large-scale biological data sets. PLoS ONE 2:e718. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0000718
Wu K, Liu H, Yang M, Tao Y, Ma H, Wu W, Zuo Y, Zhao Y (2014) High-density genetic map construction and QTLs analysis of grain yield-related traits in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) based on RAD-Seq techonology. BMC Plant Biol 14:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-014-0274-7
Zhou L, Wang SB, Jian J, Geng QC, Wen J, Song Q, Wu Z, Li GJ, Liu YQ, Dunwell JM (2015) Identification of domestication-related loci associated with flowering time and seed size in soybean with the RAD-seq genotyping method. Sci Rep 5:9350. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09350
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (31271676), National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFD0101106), Tianjin Key R&D Program (18YFZCNC01250), and Tianjin Modern Agricultural Industry Technology System Innovation Team (ITTRRS2018010 and ITTRRS2018008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declared there were no conflicts of interests involved.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Hua, Z., Dong, L. et al. Quantitative Trait Locus Mapping for Yield-Associated Agronomic Traits in a BC2F6 Population of Japonica Hybrid Rice Liaoyou 5218. J Plant Growth Regul 39, 60–71 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-019-09963-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-019-09963-4