Abstract
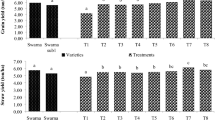
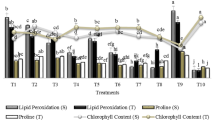
The aim of this work was to evaluate the effects of co-inoculation with phosphate-solubilizing and nitrogen-fixing rhizobacteria on growth promotion, yield, and nutrient uptake by wheat. Out of twenty-five bacteria isolated from the rhizosphere soils of cereal, vegetable, and agro-forestry plants in eastern Uttar Pradesh, three superior most plant growth-promoting (PGP) isolates were characterized as Serratia marcescens, Microbacterium arborescens, and Enterobacter sp. based on their biochemical and 16S rDNA gene sequencing data and selected them for evaluating their PGP effects on growth and yield of wheat. Among them, Enterobacter sp. and M. arborescens fixed significantly higher amounts (9.32 ± 0.57 and 8.89 ± 0.58 mg Ng−1 carbon oxidized, respectively) of atmospheric nitrogen and produced higher amounts (27.06 ± 1.70 and 26.82 ± 1.63 TP 100 µg mL−1, respectively) of IAA in vitro compared to S. marcescens (8.32 ± 0.39 mg Ng−1 carbon oxidized and 21.29 ± 0.99 TP 100 µg mL−1). Although both M. arborescens and S. marcescens solubilized remarkable amounts of phosphate from tricalcium phosphate likely through production of organic acids, however, Enterobacter sp. was inactive. The effects of these three rhizobacteria were evaluated on wheat in alluvial soils of the Indo-Gangetic Plain by inoculation of plants with bacterial isolates either alone or in combinations in both pot and field conditions for two successive years. Rhizobacterial inoculation either alone or in consortium of varying combinations significantly (P ≤ 0.05) increased growth and yield of wheat compared to mock inoculated controls. A consortium of two or three rhizobacterial isolates also significantly increased plant height, straw yield, grain yield, and test weight of wheat in both pot and field trials compared to single application of any of these isolates. Among the rhizobacterial treatment, co-inoculation of three rhizobacteria (Enterobacter, M. arborescens and S. marcescens) performed best in promotion of growth, yield, and nutrient (N, P, Cu, Zn, Mn, and Fe) uptake by wheat. Taken together, our results suggest that co-inoculation of Enterobacter with S. marcescens and M. arborescens could be used for preparation of an effective formulation of PGP consortium for eco-friendly and sustainable production of wheat.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi MK, Sharif S, Kazmi M, Sultan T, Aslam M (2011) Isolation of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria from wheat rhizosphere and their effect on improving growth, yield and nutrient uptake of plants. Plant Bios 145:159–168
Abdel-Wahab AFM, Mekhemar GAA, Badawi FSHF, Shehata HSH (2008) Enhancement of nitrogen fixation, growth and productivity of Bradyrhizobium-lupin symbiosis via co-inoculation with rhizobacteria in different soil types. J Agric Sci Mansoura Univ 33:469–484
Ahmad M, Nadeem SM, Naveed M, Zahir ZA (2016) Potassium-solubilizing bacteria and their application in agriculture. In: Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS (eds) Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer, India, pp 293–313
Akhtar MS, Siddiqui ZA (2009) Effects of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms and Rhizobium sp. on the growth, nodulation, yield and root-rot disease complex of chickpea under field condition. Afr J Biotechnol 8: 3489–3496
Asghar HN, Zahir ZA, Arshad M (2004) Screening rhizobacteria for improving the growth, yield and oil content of canola (Brassica napus L.) Aust J Agric Res 5: 187–194
Ashrafuzzaman M, Hossen FA, Ismail MR, Hoque MA, Islam MZ, Shahidullah SM, Meon S (2009) Efficiency of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) for the enhancement of rice growth. Afr J Biotechnol 8:1247–1252
Askary MA, Mostajeran R, Amooaghaei MM (2009) Influence of co-inoculation Azospirillum brasilense andRhizobium meliloti plus 2, 4-D on grain yield and N, P, K content of Triticumaestivum(Cv. Baccros and Mahdavi). Am-Eur J Agric Env Sci 5: 296–307
Bahadur I, Meena VS, Kumar S (2014) Importance and application of potassic biofertilizer in Indian agriculture. Int Res J Biol Sci 3:80–85
Bahadur I, Maurya BR, Kumar A, Meena VS, Raghuwanshi R (2016) Towards the soil sustainability and potassium-solubilizing microorganisms. In: Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS (eds) Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer, India, pp 225–266
Bashan Y, De-Bashan LE (2010) Chapter two-How the plant growth-promoting bacterium Azospirillum promotes plant growth—a critical assessment. Adv Agron 108: 77–136
Bremner JM (1965) Total nitrogen. In: Black CA, Evans DD, White JL, Ensminger LE, Clark FE (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties, ASA, Madison, Wisconsin, pp. 1149–1176
Chen YP, Rekha PD, Arun AB, Shen FT, Lai WA, Young CC (2006) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria from subtropical soil and their tricalcium phosphate solubilizing abilities. Appl Soil Ecol 34:33–41
Das I, Pradhan M (2016) Potassium-solubilizing microorganisms and their role in enhancing soil fertility and health. In: Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS (eds) Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer, India, pp 281–291
Dominguez-Nunez JA, Benito B, Berrocal-Lobo M, Albanesi A (2016) Mycorrhizal fungi: role in the solubilization of potassium. In: Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS (eds) Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer, India, pp 77–98
Dotaniya ML, Meena VD, Basak BB, Meena RS (2016) Potassium uptake by crops as well as microorganisms. In: Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS (eds) Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer, India, pp 267–280
Elkoca E, Turan M, Donmez MF (2010) Effects of single, dual and triple inoculation with Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus megaterium and Rhizobium leguminosarumbv. phaseoil on nodulation, nutrient uptake, yield and yield parameters of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L. cv. ‘Elkoca-05’). J Plant Nutr 33:2104–2119
Fayez M (1990) Untraditional N2-fixing bacteria as biofertilizers for wheat and barley. Folia Microbiol 35:218–226
Fernandez LA, Zalba P, Gomez MA, Sagarday MA (2007) Phosphate solubilization activity of bacterial strains in soil and their effect on soybean growth under greenhouse conditions. Biol Fertil Soils 43: 805–809
Gaur AC (1990) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria as biofertilizer. Omega Scientific Publishers, New Delhi
Hameeda B, Rupela OP, Reddy G, Satyavani K (2006) Application of plant growth-promoting bacteria associated with composts and macrofauna for growth promotion of Pearl millet (Pennisetumglaucum L.). Biol Fertil Soils 43: 221–227
Hameeda B, Harini G, Rupela OP, Wani SP, Reddy G (2008) Growth promotion of maize by phosphate solubilizing bacteria isolated from composts and Macrofauna. Microbiol Res 163:234–242
Hayat R, Safdar AS, Amara U, Khalid R, Ahmed I (2010) Soil beneficial bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion: a review. Ann Microbiol 60: 579–598
Islam MT, Hossain MM (2013) Biological control of peronosporomycete phytopathogen by bacterial antagonist. In: Maheshwari DK (ed) Bacteria in agrobiology: disease management, Springer, Heidelberg, pp 167–218
Iswaran V, Marwah TS (1980) A modified rapid Kjeldahl method for determination of total nitrogen in agricultural and biological materials. Geobios 7:281–282
Jackson ML (1973) Soil Chemical Analysis. Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi
Jaiswal DK, Verma JP, Prakash S, Meena VS, Meena RS (2016) Potassium as an important plant nutrient in sustainable agriculture: a state of the art. In: Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS (eds) Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer, India, pp 21–29
Jia Y, Huang H, Zhong M, Wang FH, Zhang LM, Zhu YG (2013) Microbial arsenic methylation in soil and rice rhizosphere. Environ Sci Technol 47:3141–3148
Kaymak HC (2011) Potential of PGPR in Agricultural Innovations. In: Maheshwari DK (ed) Plant growth and health promoting bacteria, 18. Springer, Berlin, pp 45–79
Khalid A, Arshad M, Zahir ZA (2004) Screening plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for improving growth and yield of wheat. J Appl Microbiol 46:473–480
Kumar A, Maurya BR, Raghuwanshi R (2014) Isolation and Characterization of PGPR and their effect on growth, yield and nutrient content in wheat (Triticumaestivum L.). Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 3:121–128
Kumar A, Bahadur I, Maurya BR, Raghuwanshi R, Meena VS, Singh DK, Dixit J (2015) Does a plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria enhance agricultural sustainability? J Pure Appl Microbiol 9:715–724
Kumar A, Patel JS, Bahadur I, Meena VS (2016a) The molecular mechanisms of KSMs for enhancement of crop production under organic farming. In: Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS (eds) Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer, India, pp 61–75
Kumar A, Meena R, Meena VS, Bisht JK, Pattanayak A (2016b) Towards the stress management and environmental sustainability. J Clean Prod 137:821–822
Lugtenberg B, Kamilova F (2009) Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 63:541–556
Masood S, Bano A (2016) Mechanism of potassium solubilization in the agricultural soils by the help of soil microorganisms. In: Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS (eds) Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer, India, pp 137–147
Maurya BR, Meena VS, Meena OP (2014) Influence of Inceptisol and Alfisol’s potassium solubilizing bacteria (KSB) isolates on release of K from waste mica. Vegetos 27:181–187
Meena OP, Maurya BR, Meena VS (2013) Influence of K-solubilizing bacteria on release of potassium from waste mica. Agric Sust Dev 1:53–56
Meena RS, Meena VS, Meena SK, Verma JP (2015a) The needs of healthy soils for a healthy world. J Clean Prod 102:560–561
Meena RS, Meena VS, Meena SK, Verma JP (2015b) Towards the plant stress mitigate the agricultural productivity: a book review. J Clean Prod 102:552–553
Meena RS, Bohra JS, Singh SP, Meena VS, Verma JP, Verma SK, Sihag SK (2016a) Towards the prime response of manure to enhance nutrient use efficiency and soil sustainability a current need: a book review. J Clean Prod 112(1):1258–1260
Meena VS, Bahadur I, Maurya BR, Kumar A, Meena RK, Meena SK, Verma JP (2016b) Potassium-solubilizing microorganism in evergreen agriculture: an overview. In: Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS (eds) Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer, India, pp 1–20
Meena VS, Meena SK, Bisht JK, Pattanayak A (2016c) Conservation agricultural practices in sustainable food production. J Clean Prod 137:690–691
Mukerji KG, Manoharachary C, Singh J (2006) Microbial activity in the rhizopshere. Springer, New York
Narde G, Kapley A, Purohit HJ (2004) Isolation and characterization of Citrobacterstrain HPC255 for broad range substrate specificity for chlorophenol. Curr Microbiol 48: 419–423
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. National Agricultural Society, Victoria, pp 939
Renato de Freitas J (2000) Yield and N assimilation of winter wheat (Triticumaestivum L., var. Norstar) inoculated with rhizobacteria. Pedobiol 44: 97–104
Saha M, Maurya BR, Bahadur I, Kumar A, Meena VS (2016a) Can potassium-solubilising bacteria mitigate the potassium problems in India? In: Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS (eds) Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer, India, pp 127–136
Saha M, Maurya BR, Meena VS, Bahadur I, Kumar A (2016b) Identification and characterization of potassium solubilizing bacteria (KSB) from Indo-Gangetic Plains of India. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 7:202–209
Schmidt EL, Belser LW (1982) Nitrifying bacteriain. In: Page AL (eds) Methods of Soil analysis Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Processes. ASA, Wisconsin, pp 1027–1042
Selvakumar G, Mohan M, Kundu S, Gupta AD, Joshi P, Nazim S, Gupta HS (2008) Cold tolerance and plant growth promotion potential of Serratiamarcescens strain SRM (MTCC 8708) isolated from flowers of summer squash (Cucurbitapepo). Lett Appl Microbiol 46: 171–175
Shankar T, Sivakumar T, Asha G, Sankaralingam S, Sundaram VM (2013) Effect of PSB on growth and development of Chilli and Maize plants. World J Appl Sci 26:610–617
Sharma A, Shankhdhar D, Shankhdhar SC (2016) Potassium-solubilizing microorganisms: mechanism and their role in potassium solubilization and uptake. In: Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS (eds) Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer, India, pp 203–219
Shrivastava M, Srivastava PC, D’Souza SF (2016) KSM soil diversity and mineral solubilization, in relation to crop production and molecular mechanism. In: Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS (eds) Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer, India, pp 221–234
Sindhu SS, Parmar P, Phour M, Sehrawat A (2016) Potassium-solubilizing microorganisms (KSMs) and its effect on plant growth improvement. In: Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS (eds) Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer, India, pp 171–185
Subbiah BV, Asija GL (1956) A rapid procedure for estimation of available N in soils. Curr Sci 25: 259–260
Teotia P, Kumar V, Kumar M, Shrivastava N, Varma A (2016) Rhizosphere microbes: potassium solubilization and crop productivity-present and future aspects. In: Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS (eds) Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer, India, pp 315–325
Tripura C, Sashidhar B, Podile AR (2007) Ethyl methanesulphonate mutagenesis-enhanced mineral phosphate solubilization by groundnut-associated Serratiamarcescens GPS-5. Curr Microbiol 54: 79–84.
Turan M, Gulluce M, Wirén NV, Sahin F (2012) Yield promotion and phosphorus solubilization by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in extensive wheat production in Turkey. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 175:818–826
Velazquez E, Silva LR, Ramírez-Bahena MH, Peix A (2016) Diversity of potassium-solubilizing microorganisms and their interactions with plants. In: Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS (eds) Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer, India, pp 99–110
Verma JP, Yadav J, Tiwari KN, Singh V (2010) Impact of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on crop production. Int J Agric Res 5:954–983
Verma JP, Jaiswa DK, Meena VS, Meena RS (2015a) Current need of organic farming for enhancing sustainable agriculture. J Clean Prod 102:545–547
Verma JP, Jaiswal DK, Meena VS, Kumar A, Meena RS (2015b) Issues and challenges about sustainable agriculture production for management of natural resources to sustain soil fertility and health. J Clean Prod 107:793–794
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Yadav BK, Sidhu AS (2016) Dynamics of potassium and their bioavailability for plant nutrition. In: Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS (eds) Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer, India, pp 187–201
Yasin M, Munir I, Faisal M (2016) Can Bacillus spp. enhance K+ uptake in crop species. In: Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS (eds) Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer, India, pp 163–170
Zahedi H (2016) Growth-promoting effect of potassium-solubilizing microorganisms on some crop species. In: Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS (eds) Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer, India, pp 31–42
Zahir AZ, Ghani U, Naveed M, Nadeem SM, Asghar HN (2009) Comparative effectiveness of Pseudomonas and Serratia sp. containing ACC-deaminase for improving growth and yield of wheat (Triticumaestivum L.) under salt-stressed conditions. Arch Microbiol 191:415–424
Zinniel DK, Lambrecht P, Harris NB, Feng Z, Kuczmarski D, Higley P, Ishimaru CA, Arunakumari A, Barletta RG, Vidaver AK (2002) Isolation and characterization of endophytic colonizing bacteria from agronomic crops and prairie plants. Appl Env Microbiol 68: 2198–2208.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Uttar Pradesh Council of Agricultural Research for funding the research work. Thanks are also due to the Head, Department of Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry, Institute of Agricultural Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India, for providing the necessary facilities required for conducting the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Maurya, B.R., Raghuwanshi, R. et al. Co-inoculation with Enterobacter and Rhizobacteria on Yield and Nutrient Uptake by Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in the Alluvial Soil Under Indo-Gangetic Plain of India. J Plant Growth Regul 36, 608–617 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-016-9663-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-016-9663-5