Abstract
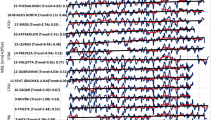
The impact of climate change on sea level has re]a great deal of attention by scientists worldwide. In this context, the problem of sea levels on global and regional scales have been analyzed in a number of studies based on tide gauges observations and satellite altimetry measurements. This study focuses on trend estimates from 18 high-quality tide gauge stations along the Mediterranean Sea coast. The seasonal Mann-Kendall test was run at a 5% significance level for each of the 18 stations for the period of 1993–2015 (satellite altimetry era). The results of this test indicate that the trends for 17 stations were statistically significant and showed an increase (no significant trend was observed only at one station). The rates of sea level change for the 17 stations that exhibit significant trends, estimated using seasonal Sen’s approach, range after correction for Vertical Land Motion (VLM) from 1.48 to 8.72 mm/a for the period 1993–2015. Furthermore, the magnitude of change at the location of each tide gauge station was estimated using the satellite altimetry measurements. Thus, the results obtained agree with those from the tide-gauge data analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argus D F, Peltier W R, Drummond R, Moore A W. 2014. The Antarctica component of postglacial rebound model ICE-6G_C (VM5a) based on GPS positioning, exposure age dating of ice thicknesses, and relative sea level histories. Geophysical Journal International, 198(1): 537–563.
Bindoff N L, Willebrand J, Artale V, Cazenave A, Gregory J, Gulev S, Hanawa K, Le Quéré C, Levitus S, Nojiri Y, Shum C K, Talley L D, Unnikrishnan A. 2007. Observations: oceanic climate change and sea level. In: Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Birol F, Delebecque C. 2014. Using high sampling rate (10/20 Hz) altimeter data for the observation of coastal surface currents: a case study over the northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Journal of Marine Systems, 129: 318–333.
Bonaduce A, Pinardi N, Oddo P, Spada G, Larnicol G. 2016. Sea-level variability in the Mediterranean Sea from altimetry and tide gauges. Climate Dynamics, 47(9–10): 2 851–2 866.
Church J A and White N J. 2011. Sea-level rise from the late 19th to the early 21st century. Surveys in Geophysics, 32(4–5): 585–602.
CLS. 2018. SSALTO/DUACS Experimental Product Handbook, SALP-MU-P-EA-23172-CLS, 49 pp. https://doi.org/www.aviso.altimetry.fr/fileadmin/documents/data/tools/hdbk_duacs_experimental.pdf. Accessed on 24 Sep. 2018.
Douglas B C, Peltier W R. 2002. The puzzle of global sea-level rise. Physics Today, 55(3): 35–40.
Fenoglio-Marc L, Braitenberg C, Tunini L. 2012. Sea level variability and trends in the Adriatic Sea in 1993–2008 from tide gauges and satellite altimetry. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part A/B/C, 40–41: 47–58.
Fenoglio-Marc L. 2002. Long-term sea level change in the Mediterranean Sea from multi-satellite altimetry and tide gauges. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part A/B/C, 27(32–34): 1 419–1 431.
Haddad M, Hassani H, Taibi H. 2013b. Sea level in the Mediterranean Sea: seasonal adjustment and trend extraction within the framework of SSA. Earth Science Informatics, 6(2): 99–111.
Haddad M, Taibi H, Mohammed Arezki S M. 2013a. On the recent global mean sea level changes: trend extraction and El Nino’s impact. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 345(4): 167–175.
Hipel K W, McLeod A I. 1994. Time Series Modelling of Water Resources and Environmental Systems. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Hirsch R M, Slack J R, Smith R A. 1982. Techniques of trend analysis for monthly water quality data. Water Resources Research, 18(1): 107–121.
Holgate S J, Matthews A, Woodworth P L, Rickards L J, Tamisiea M E, Bradshaw E, Foden P R, Gordon K M, Jevrejeva S, Pugh J. 2013. New data systems and products at the permanent service for mean sea level. Journal of Coastal Research, 29(3): 493–504.
IOC. 1992. Joint IAPSO-IOC Workshop on Sea Level Measurements and Quality Control. Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission, Workshop Report No. 81, IOC, Paris.
IPCC. 2013. The Physical Science Basis. https://doi.org/www.climatechange2013.org. Accessed on 17 July 2018.
Kendall M G. 1975. Rank Correlation Methods. 4th edn. Charles Griffin, London.
Mann H B. 1945. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica, 13(3): 245–259.
Motiee H, McBean E. 2009. An assessment of long term trends in hydrologic components and implications for water levels in lake superior. Hydrology Research, 40(6): 564–579.
Nicholls R J, Cazenave A. 2010. Sea-level changes and their impacts on coastal zones. Science, 328(5985): 1 517–1 520.
Pascual A, Pujol M I, Larnicol G, Traon P Y L, Rio M H. 2007. Mesoscale mapping capabilities of multisatellite altimeter missions: first results with real data in the Mediterranean Sea. Journal of Marine Systems, 65(1–4): 190–211.
Peltier W R, Argus D F, Drummond R. 2015. Space geodesy constrains ice age terminal deglaciation: the global ICE-6G_C (VM5a) model. Journal of Geophysical Research. Solid Earth, 120(1): 450–487.
Permanent Service for Mean Sea Level — PSMSL. 2018. https://doi.org/www.psmsl.org, Accessed on 2018-02-18.
Salmi T, Määttä A, Antilla P, Ruoho-Airola T, Amnell T. 2002. Detecting Trends of Annual Values of Atmospheric Pollutants by the Mann-Kendall Test and Sen’s Slope Estimates — the Excel Template Application Makesens. Finnish Meteor-ological Institute, Helsinki, Finland, 35p.
Sen P K. 1968. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’S tau. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 63(324): 1 379–1 389.
Tabari H, Marofi S, Ahmadi M. 2011. Long-term variations of water quality parameters in the Maroon River, Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 177(1–4): 273–287.
Taibi H, Kahlouche S, Haddad M, Rami A. 2013. Trends in global and regional sea level from satellite altimetry within the framework of Auto-SSA. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 6(12): 4 575–4 584.
Vignudelli S, Cipollini P, Roblou L, Lyard F, Gasparini G P, Manzella G, Astraldi M. 2005. Improved satellite altimetry in coastal systems: case study of the Corsica channel (Mediterranean Sea). Geophysical Research Letters, 32(7): L07608.
White N J, Church J A, Gregory J M. 2005. Coastal and global averaged sea level rise for 1950 to 2000. Geophysical Research Letters, 32(1): L01601.
Woodworth P L, Spencer N E, Alcock G A. 1990. On the availability of European mean sea level data. International Hydrographic Review, 67(1): 131–146.
Wöppelmann G. 1997. Rattachement géodésique des marégraphes dans un système de référence mondial par techniques de géodésie spatiale. Paris Observatory, France.
XLSTAT. 2017. Data Analysis and Statistical Solution for Microsoft Excel. Addinsoft, Paris, France.
Acknowledgement
The authors are enormously grateful to PSMSL for providing sea level time series and to AVISO for providing altimetry data. The authors greatly thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable and constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taibi, H., Haddad, M. Estimating trends of the Mediterranean Sea level changes from tide gauge and satellite altimetry data (1993–2015). J. Ocean. Limnol. 37, 1176–1185 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-019-8164-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-019-8164-3