Abstract
Pulsed laser ablation of reactively sintered MgO–NiO (9:1, 1:1, 1:9 molar ratio) disks was used to fabricate dense rocksalt-type Mg x Ni1−x O in the form of submicron-sized spherical particulate and nanocubes for X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopic characterizations. The rapidly solidified particulates and the condensed nanocubes have internal compressive stress increasing up to ca. 1 GPa with the increases in Ni content. The nanocubes were coalesced over well-developed polar surfaces, i.e., {100}, minor {110} and their vicinal surfaces with growth ledges, to form special grain boundaries, i.e., (100) 15° and 45° twist boundaries and [100] {001}/{011} asymmetric tilt boundaries. The Mg x Ni1−x O nanocubes also showed 3-D paracrystalline distribution of defect clusters with 2 nm and 1.5–2 nm interspacing for M1N9 and M1N1 compositions, respectively, but G.P. zone-like features for M9N1 composition. The Mg x Ni1−x O particulates and nanocondensates have UV–visible absorption edge in the range 4.0–3.3 eV, decreasing with increasing Ni content for potential engineering applications.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.G. Sockel, H. Schmalzries, Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 72, 745 (1968)
S.M. Tomlinson, C.R.A. Catlow, J.H. Harding, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 51, 477 (1990)
B.E.F. Fender, F.D. Riley, in The Chemistry of Extended Defects in Non-metallic Solids, eds. by L. Eyring, M. O’Keefe (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1970)
J. Chen, P. Shen, J. Solid State Chem. 140, 361 (1998)
S.R. Wang, P. Shen, J. Solid State Chem. 140, 38 (1998)
M.L. Jeng, P. Shen, J. Solid State Chem. 152, 421 (2000)
T.R. Welberry, A.G. Christy, J. Solid State Chem. 117, 398 (1995)
H.V. Wartenberg, E. Prophet, Z. Anorg. Chem. 208, 369 (1932)
E.M. Levin, C.R. Robbins, H.F. McMurdie, Phase Diagram for Ceramists, compiled at the Nation Bureau of Standard (edited and published by the American Ceramic Society Inc., 1964)
G. Pacchioni, C. Di Valentin, D. Dominguez-Ariza, F. Illas, T. Bredow, T. Klüner, V. Staemmler, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 16, S2497 (2004)
R. Valero, J.R.B. Gomes, D.G. Truhlar, F. Illas, J. Chem. Phys. 132, 104701 (2010)
S. Yagi, Y. Ichikawa, I. Yamada, T. Doi, T. Ichitsubo, E. Matsubara, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 52, 025501 (2013)
J. Srinakruang, K. Sato, T. Vitidsant, K. Fujimoto, Catal. Commun. 6, 437 (2005)
J. Srinakruang, K. Sato, T. Vitidsant, K. Fujimoto, Fuel 85, 2419 (2006)
C.M. Tsai, MS Thesis, National Sun Yat-sen University, Taiwan (2003)
D.A. Porter, K.E. Easterling, M.Y. Sherif, Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys, 3rd edn. (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2009)
S.Y. Chen, P. Shen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 096106 (2002)
S.Y. Chen, P. Shen, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 43, 1519 (2004)
M.H. Tsai, S.Y. Chen, P. Shen, J. Chem. Phys. 122, 204708 (2005)
M.H. Tsai, S.Y. Chen, R.P. Shen, P. Shen, J. Appl. Phys. 99, 054302 (2006)
W.J. Tseng, P. Shen, S.Y. Chen, J. Solid State Chem. 179, 1237 (2006)
C. Pan, S.Y. Chen, P. Shen, J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 24340 (2006)
C. Pan, S.Y. Chen, P. Shen, J. Cryst. Growth 310, 699 (2008)
C.H. Lin, S.Y. Chen, N.J. Ho, D. Gan, P. Shen, J. Phys. Chem. Solid 70, 1505 (2009)
G. Chryssolouris, Laser Machining-Theory and Practice (Springer, New York, 1991), p. 274
W.S. Lee, P. Shen, J. Cryst. Growth 205, 169 (1999)
M.H. Tsai, S.Y. Chen, P. Shen, Nano Lett. 4, 1179 (2004)
M.H. Tsai, P. Shen, S.Y. Chen, J. Appl. Phys. 100, 114313 (2006)
C.N. Huang, S.Y. Chen, M.H. Tsai, P. Shen, J. Cryst. Growth 305, 285 (2007)
P.J. Chen, C.H. Wu, P. Shen, S.Y. Chen, Appl. Phys. A 116, 823 (2014)
Y.T. Chan, C.H. Wu, P. Shen, S.Y. Chen, Appl. Phys. A 116, 1065 (2014)
S.W. Yeh, Y.J. Ji, H.L. Huang, D. Gan, P. Shen, J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 18886 (2010)
P. Kofstad, Nonstoichiometry, Difusion and Electrical Conductivity in Binary Metal Oxides (Wiley Interscience, New York, 1972)
A. Atkinson, A.E. Hughes, A. Hammou, Phil. Mag. A 43, 1071 (1981)
F.A. Kröger, H.J. Vink, Solid State Phys. 3, 307 (1956)
R.D. Shannon, Acta Cryst. A 32, 751 (1976)
T.R. Welberry, A.G. Christy, Phys. Chem. Miner. 24, 24 (1997)
N.N. Greenwood, A. Earnshaw, Chemistry of the Elements (Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1984), pp. 1336–1337
P. Vallet, P. Raccah, Mem. Sci. Rev. Metall. 62, 1 (1965)
B. Anderson, J.O. Sletnes, Acta Cryst. A 33, 268 (1977)
W.S. Lee, P. Shen, J. Solid State Chem. 177, 101 (2004)
E. Huang, High Pressure Res. 13, 307 (1995)
Y.W. Fei, Am. Mineral. 84, 272 (1999)
S. Rekhi, S.K. Saxena, Z.D. Atlasa, J. Hub, Solid State Comm. 117, 33 (2001)
P. Shen, W.A. Bassett, L. Liu, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 47, 773 (1983)
S.C. Parker, E.T. Kelsey, P.M. Oliver, J.O. Titiloye, Faraday Discuss. 95, 75 (1993)
P.M. Oliver, S.C. Parker, W.C. Mackrodt, Model. Simul. Mat. Sci. Eng. 1, 755 (1993)
D. Cappus, M. Habel, E. Neuhaus, M. Heber, F. Rohr, H.J. Freund, Surf. Sci. 337, 268 (1995)
A. Wander, I.J. Bush, N.M. Harrison, Phys. Rev. B 68, 233405 (2003)
R.H. Wu, MS thesis, National Sun Yat-sen University, Taiwan (2014)
G. Hermann, H. Gleiter, G. Baro, Acta Metall. 24, 353 (1976)
S.W. Chan, R.W. Balluffi, Acta Metall. 33, 1113 (1985)
S.W. Chan, R.W. Balluffi, Acta Metall. 34, 2191 (1986)
R. Maurer, Acta Metall. 35, 2557 (1987)
Y. Gao, S.A. Dregia, P.G. Shewmon, Acta Mater. 37, 1627 (1989)
J.T.M. De Hosson, V. Vitec, Phil. Mag. 61, 305 (1990)
S.M. Allameh, S.A. Dregia, P.G. Shewmon, Acta Mater. 42, 3569 (1994)
M. Kohyama, R. Yamamoto, Phys. Rev. B 49, 17102 (1994)
K.L. Merkle, L.J. Thompson, Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 556 (1999)
J.M. Zhang, H. Xin, X.M. Wei, Appl. Surf. Sci. 246, 14 (2005)
J.M. Zhang, X.M. Wei, H. Xin, Appl. Surf. Sci. 243, 1 (2005)
H. Xin, J.M. Zhang, X.M. Wei, K.W. Xu, Surf. Interface Anal. 37, 608 (2005)
X.M. Wei, J.M. Zhang, K.W. Xu, Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 854 (2006)
M.L. Jeng, P. Shen, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 287, 1 (2000)
M.Y. Li, P. Shen, S.L. Hwang, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 343, 227 (2003)
J.Y. Wang, P. Shen, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 359, 192 (2003)
C.N. Huang, P. Shen, K.Y. Hsieh, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 27, 4685 (2007)
C. Dobe, E. González, P.L.W. Tregenna-Piggott, C. Reber, Dalton Trans. 43, 17864 (2014)
A. Singh, S.L.Y. Chang, R.K. Hocking, U. Bach, L. Spiccia, Energy Environ. Sci. 6, 579 (2013)
L.G. Ferguson, F. Dogan, J. Mater. Sci. 37, 1301 (2002)
M. Huang, F. Li, J.Y. Ji, Y. Zhang, X.L. Zhao, X. Gao, CrystEngComm (2014). doi:10.1039/C3CE42335B
J.J. Papike, Planetary materials, in Reviews in Mineralogy vol. 36, series Editor: Ribbe P.H. (Mineral. Soc. Am. 1998)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Center for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology at NSYSU and partly by the Ministry of Science and Technology, ROC. We thank anonymous referees and editor for constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
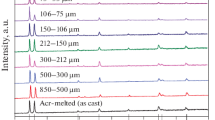
See Fig. 13.
SEM a SEI of the greenish M1N1 disk target subjected to PLA under free run mode in air for 10 min to form a ablated trough with dark color under naked eye (inset), b, c enlarged from intact and ablated area, respectively, showing that the former has the solid-state sintered grains ca. 10–20 μm in size with inter- and intragranular pores, whereas the latter has finer recrystallized grains and solidified molten flow
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, RH., Lin, SS., Shen, P. et al. Dense Mg x Ni1−x O nanocubes with special grain boundaries and paracrystalline distribution of defect clusters by pulsed laser ablation. Appl. Phys. A 120, 1121–1132 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-015-9287-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-015-9287-9