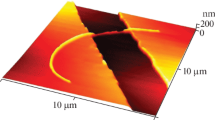
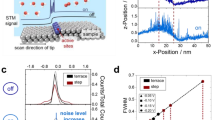
Abstract
Structural defects greatly affect the electronic properties of single wall carbon nanotubes (CNT’s), for instance by increasing the sensitivity to their environment; an effect which can be utilized for better performance of CNT based chemical sensors. Here we show that electrostatic force microscopy (EFM) can be used as a non-invasive technique for probing defects in individual CNT’s supported on insulating substrates. The technique is demonstrated by monitoring the change in EFM signal upon intentionally inducing defect by an oxygen plasma etch, and is applied to assess the quality of as-grown CNT samples and to study the effect of exposing CNT’s to the low energy electron irradiation of a scanning electron microscope (SEM).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Biercuk, S. Garaj, N. Mason, J. Chow, C. Marcus, Nano Lett. 5, 1267 (2005)
J. Park, Y. Yaish, M. Brink, S. Rosenblatt, P. Mceuen, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 4446 (2002)
J. Robinson, E. Snow, S. Badescu, T. Reinecke, F. Perkins, Nano Lett. 6, 1747 (2006)
Q. Wang, T. Corrigan, J. Dai, R. Chang, A. Krauss, Appl. Phys. Lett. 70, 3308 (1997)
C. Zhi, X. Bai, E. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 1690 (2002)
Y. Liu, L. Liu, P. Liu, L. Sheng, S. Fan, Diam. Relat. Mater. 13, 1609 (2004)
M. Zdrojek, T. Melin, C. Boyaval, D. Stievenard, B. Jouault, M. Wozniak, A. Huczko, W. Gebicki, L. Adamowicz, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 213114 (2005)
M. Bockrath, N. Markovic, A. Shepard, M. Tinkham, L. Gurevich, L. Kouwenhoven, M. Wu, L. Sohn, Nano Lett. 2, 187 (2002)
C. Staii, A. Johnson, N. Pinto, Nano Lett. 4, 859 (2004)
J. Heo, M. Bockrath, Nano Lett. 5, 853 (2005)
J. Hafner, C. Cheung, T. Oosterkamp, C. Lieber, J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 743 (2001)
S. Reich, C. Thomsen, J. Maultzsch, Carbon Nanotubes: Basic Concepts and Physical Properties (Wiley-VCH, New York, 2004)
B. Smith, D. Luzzi, J. Appl. Phys. 90, 3509 (2001)
S. Suzuki, K. Kanzaki, Y. Homma, S. Fukuba, Japan. J. Appl. Phys. 43, L1118 (2004)
S. Suzuki, Y. Kobayashi, Japan. J. Appl. Phys. 44, L1498 (2005)
A. Vijayaraghavan, K. Kanzaki, S. Suzuki, Y. Kobayashi, H. Inokawa, Y. Ono, S. Kar, P. Ajayan, Nano Lett. 5, 1575 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
PACS
68.37.-d; 68.37.Ps; 61.46.Fg; 68.35.Dv
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sand Jespersen, T., Nygård, J. Probing induced defects in individual carbon nanotubes using electrostatic force microscopy. Appl. Phys. A 88, 309–313 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-007-3927-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-007-3927-7