Abstract
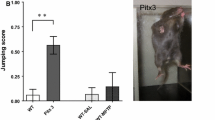
A new spontaneous mouse mutant was characterized by closed eyelids at weaning and without apparent eyes (provisional gene name, eyeless; provisional gene symbol, eyl). The mutation follows a recessive pattern of inheritance and was mapped to the region of chromosome 19 containing Pitx3. Genetic complementation tests using Pitx3 ak/+ mice confirmed eyl as a new allele of Pitx3 (Pitx3 eyl). Sequencing of the Pitx3 gene in eyl mutants identified an inserted G after cDNA position 416 (416insG; exon 4). The shifted open reading frame is predicted to result in a hybrid protein still containing the Pitx3 homeobox, but followed by 121 new amino acids. The novel Pitx3 eyl/eyl mutants expressed ophthalmological and brain defects similar to Pitx3 ak/ak mice: microphthalmia or anophthalmia and loss of dopamine neurons of the substantia nigra. In addition, we observed in the homozygous eyeless mutants increased extramedullary hematopoiesis in the spleen, frequently liver steatosis, and reduced body weight. There were also several behavioral changes in the homozygous mutants, including reduced forelimb grip strength and increased nociception. In addition to these alterations in both sexes, we observed in female Pitx3 eyl/eyl mice increased anxiety-related behavior, reduced locomotor activity, reduced object exploration, and increased social contacts; however, we observed decreased anxiety-related behavior and increased arousal in males. Most of these defects identified in the new Pitx3 mutation are observed in Parkinson patients, making the Pitx3 eyl mutant a valuable new model. It is the first mouse mutant carrying a point mutation within the coding region of Pitx3.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alessandrini F, Jakob T, Wolf A, Wolf E, Balling R et al (2001) ENU mouse mutagenesis: generation of mouse mutants with aberrant plasma IgE levels. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 124:25–28
Ardayfio P, Moon J, Leung KK, Youn-Hwang D, Kim KS (2008) Impaired learning and memory in Pitx3 deficient aphakia mice: a genetic model for striatum-dependent cognitive symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 31:406–412
Baba Y, Kuroiwa A, Uitti RJ, Wszolek ZK, Yamada T (2005) Alterations of T-lymphocyte populations in Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 11:493–498
Barrantes IB, Montero-Pedrazuela A, Guadaño-Ferraz A, Obregon MJ, Martinez de Mena R et al (2006) Generation and characterization of dickkopf3 mutant mice. Mol Cell Biol 26:2317–2326
Beeler JA, Cao ZF, Kheirbek MA, Zhuang X (2009) Loss of cocaine locomotor response in Pitx3-deficient mice lacking a nigrostriatal pathway. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:1149–1161
Bergman O, Håkansson A, Westberg L, Nordenström K, Belin AC (2010) PITX3 polymorphism is associated with early onset Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 31:114–117
Berry V, Yang Z, Addison PKF, Francis PJ, Ionides A et al (2004) Recurrent 17 bp supplication in PITX3 is primarily associated with posterior polar cataract (CPP4). J Med Genet 41:e109
Bi S, Chen J, Behles RR, Hyun J, Kopin AS et al (2007) Differential body weight and feeding responses to high-fat diets in rats and mice lacking cholecystokinin 1 receptors. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 293:R55–R63
Bidinost C, Matsumoto M, Chung D, Salem N, Zhang K et al (2006) Heterozygous and homozygous mutations in PITX3 in a large Lebanese family with posterior polar cataracts and neurodevelopmental abnormalities. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:1274–1280
Bowes C, Li T, Frankel WN, Danciger M, Coffin JM et al (1993) Localization of a retroviral element within the rd gene coding for the beta subunit of cGMP phosphodiesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:2955–2959
Brefel-Courbon C, Payoux P, Thalamas C, Ory F, Quelven I et al (2005) Effect of Levadopa on pain threshold in Parkinson’s disease: a clinical and positron emission tomography study. Movement Dis 20:1557–1563
Chudler EH, Dong WK (1995) The role of the basal ganglia in nociception and pain. Pain 60:3–38
Corteling R, Trifilieff A (2004) Gender comparison in a murine model of allergen-driven airway inflammation and the response to budesonide treatment. BMC Pharmacol 4:4
Coulon V, L’Honoré A, Ouimette JF, Dumontier É, van den Munckhof P et al (2007) A muscle-specific promoter directs Pitxc3 gene expression in skeletal muscle cells. J Biol Chem 282:33192–33200
Drorbaugh JE, Fenn WO (1955) A barometric method for measuring ventilation in newborn infants. Pediatrics 16:81–87
Fahn S (2003) Description of Parkinson’s disease as a clinical syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci 991:1–14
Favor J, Grimes P, Neuhäuser-Klaus A, Pretsch W, Stambolian D (1997) The mouse Cat4 locus maps to chromosome 8 and mutants express lens-corneal adhesion. Mamm Genome 8:403–406
Fleming SM, Fernagut PO, Chesselet MF (2005) Genetic mouse models of Parkinsonism: strengths and limitations. NeuroRx 2:495–503
Fuchs J, Mueller JC, Lichtner P, Schulte C, Munz M et al (2009) The transcription factor PITX3 is associated with sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 30:731–738
Furukawa T, Kozak CA, Cepko CL (1997) rax, a novel paired-type homeobox gene, shows expression in the anterior neural fold and developing retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:3088–3093
Gage PJ, Suh H, Camper SA (1999) The bicoid-related Pitx family in development. Mamm Genome 10:197–200
Gailus-Durner V, Fuchs H, Becker L, Bolle I, Brielmeier M et al (2005) Introducing the German Mouse Clinic: open access platform for standardized phenotyping. Nat Methods 2:403–404
Glerup S, Kloverpris S, Laursen LS, Dagnaes-Hansen F, Thiel S et al (2007) Cell surface detachment of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A requires the formation of intermolecular proteinase-inhibitor disulfide bonds and glycosaminoglycan covalently bound to the inhibitor. J Biol Chem 282:1769–1778
Graw J, Jung M, Löster J, Klopp N, Soewarto D et al (1999) Mutation in the βA3/A1-crystallin encoding gene Cryba1 causes a dominant cataract in the mouse. Genomics 62:67–73
Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C, Joris J (1988) A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 32:77–88
Haubenberger D, Reinthaler E, Mueller JC, Pirker W, Katzenschlager R et al (2009) Association of transcription factor polymorphisms PITX3 and EN1 with Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2009.02.015
Hofmann HA, De Vry J, Siegling A, Spreyer P, Denzer D (2003) Pharmacological sensitivity and gene expression analysis of the tibial nerve injury model of neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 470:17–25
Horsch M, Schädler S, Gailus-Durner V, Fuchs H, Meyer H et al (2008) Systematic gene expression profiling of mouse model series reveals coexpressed genes. Proteomics 8:1248–1256
Jacobs FM, van Erp S, van der Linden AJ, von Oerthel L, Burbach JP et al (2009) Pitx3 potentiates Nurr1 in dopamine neuron terminal differentiation through release of SMRT-mediated repression. Development 136:531–540
Kas MJH, van der Linden AJA, Oppelaar H, von Oerthel L, Ramakers GMJ et al (2008) Phenotypic segregation of aphakia and Pitx3-null mutants reveals that Pitx3 deficiency increases consolidation of specific movement components. Behav Brain Res 186:208–214
Kim HJ, Paek SH, Kim JY, Lee JY, Lim YH et al (2008) Chronic subthalamic deep brain stimulation improves pain in Parkinson disease. J Neurol 255:1889–1894
Klempt M, Rathkolb B, Aigner B, Wolf E (2006) Clinical chemical screen. In: Hrabé de Angelis M, Chambon P, Brown S (eds) Standards of Mouse Model Phenotyping. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, pp 87–107
Lau P, Fitzsimmons RL, Raichur S, Wang SC, Lechtken A et al (2008) The orphan nuclear receptor, RORalpha, regulates gene expression that controls lipid metabolism: staggerer (SG/SG) mice are resistant to diet-induced obesity. J Biol Chem 283:18411–18421
L’Honoré A, Coulon V, Marcil A, Lebel M, Lafrance-Vanasse J et al (2007) Sequential expression and redundancy of Pitx2 and Pitx3 genes during muscle development. Dev Biol 307:421–433
MacKenzie PI, Messer M (1976) Studies on the origin and excretion of serum alpha-amylase in the mouse. Comp Biochem Physiol B 54:103–106
Moss DW (1982) Alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes. Clin Chem 28:2007–2016
Moss DW (1987) Diagnostic aspects of alkaline phosphatase and its isoenzymes. Clin Biochem 20:225–230
Nunes I, Tovmasian LT, Silva RM, Burke RE, Goff SP (2003) Pitx3 is required for development of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:4245–4250
Ohl F, Sillaber I, Binder E, Keck ME, Holsboer F (2001) Differential analysis of behavior and diazepam-induced alterations in C57BL/6 N and BALB/c mice using the modified hole board test. J Psychiatr Res 35:147–154
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW, Dempfle L (2002) Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e36
Pittler SJ, Baehr W (1991) Identification of a nonsense mutation in the rod photoreceptor cGMP phosphodiesterase beta-subunit gene of the rd mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:8322–8326
Pogorelov VM, Rodriguiz RM, Insco ML, Caron MG, Wetsel WC (2005) Novelty seeking and stereotypic activation behavior in mice with disruption of the Dat1 gene. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:1818–1831
Racz I, Schütz B, Abo-Salem OM, Zimmer A (2005) Visceral, inflammatory and neuropathic pain in glycine receptor alpha 3-deficient mice. Neuroreport 16:2025–2028
Racz I, Nadal X, Alferink J, Baños JE, Rehnelt J et al (2008) Crucial role of CB2 cannabinoid receptor in the regulation of central immune responses during neuropathic pain. J Neurosci 25:12152-12135
Rieger DK, Reichenberger E, McLean W, Sidow A, Olsen BR (2001) A double-deletion mutation in the Pitx3 gene causes arrested lens development in aphakia mice. Genomics 72:61–72
Rogers DC, Fisher EMC, Brown SDM, Peters J, Hunter AJ et al (1997) Behavioral and functional analysis of mouse phenotype: SHIRPA, a proposed protocol for comprehensive phenotype assessment. Mamm Genome 8:711–713
Rosemann M, Lintrop M, Favor J, Atkinson MJ (2002) Bone tumorigenesis induced by alpha-particle radiation: mapping of genetic loci influencing predisposition in mice. Radiat Res 157:426–434
Sakazume S, Sorokina E, Iwamoto Y, Semina EV (2007) Functional analysis of human mutations in homeodomain transcription factor PITX3. BMC Mol Biol 8:84
Schibler U, Hagenbüchle O, Young RA, Tosi M, Wellauer PK (1982) Tissue specific expression of mouse α-amylase genes. Adv Exp Med Biol 158:381–385
Schneider I, Tirsch WS, Faus-Kessler T, Becker L, Kling E et al (2006) Systematic, standardized and comprehensive neurological phenotyping of inbred mice strains in the German Mouse Clinic. J Neurosci Methods 157:82–90
Semina EV, Ferrell RE, Mintz-Hittner HA, Bitoun P, Alward WLM et al (1998) A novel homeobox gene PITX3 is mutated in families with autosomal-dominant cataracts and ASMD. Nat Genet 19:167–170
Semina E, Murray JC, Reiter R, Hrstka RF, Graw J (2000) Deletion in the promotor region and altered expression of Pitx3 homeobox gene in aphakia mice. Hum Mol Genet 9:1575–1585
Seymour BWP, Friebertshauser KE, Peake JL, Pinkerton KE, Coffmann RL et al (2002) Gender differences in the allergic response of mice neonatally exposed to environmental tobacco smoke. Dev Immunol 9:47–54
Sidman RL, Green MC (1965) Retinal degeneration in the mouse: location of the rd locus in linkage group XVII. J Hered 56:23–29
Silva AL, Romão L (2009) The mammalian nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway: to decay or not to decay! Which players make the decision? FEBS Lett 583:499–505
Singh B, Wilson JH, Vasavada HH, Guo Z, Allore HG et al (2007) Motor deficits and altered striatal gene expression in aphakia (ak) mice. Brain Res 1185:283–292
Smidt MP, Smits SM, Burbach JPH (2003) Molecular mechanisms underlying midbrain dopamine neuron development and function. Eur J Pharmacol 480:75–88
Smidt MP, Smits SM, Bouwmeester H, Hamers FPT, van der Linden AJA et al (2004) Early developmental failure of substantia nigra dopamine neurons in mice lacking the homeodomain gene Pitx3. Development 131:1145–1155
Van den Munckhof P, Luk KC, Ste-Marie L, Montgomery J, Blanchet PJ et al (2003) Pitx3 is required for motor activity and for survival of a subset of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Development 130:2535–2542
Van den Munckhof P, Gilbert F, Chamberland M, Lévesque D, Drouin J (2006) Striatal neuroadaptation and rescue of locomotor deficit by L-dopa in aphakia mice, a model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 96:160–170
VanderWende C, Margolin S (1956) Analgesic tests based upon experimentally induced acute abdominal pain in rats. Fed Proc 15:494
Vauti F, Goller T, Beine R, Becker L, Klopstock T et al (2007) The mouse Trm1-like gene is expressed in neural tissues and plays a role in motor coordination and exploratory behaviour. Gene 389:174–185
Vives J, Sasajala P, Chang KH, Zhao S, Li M (2008) A mouse model for tracking nigrostriatal dopamine neuron axon growth. Genesis 46:125–131
Zhao S, Maxwell S, Jimenez-Beristain A, Vives J, Kuehner E et al (2004) Generation of embryonic stem cells and transgenic mice expressing green fluorescence protein in midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Eur J Neurosci 19:1133–1140
Acknowledgments
This work was supported at least in part by the German National Genome Research Network (NGFN; grants 01GS0850, 01GS0851, 01GS0852, 01GS0854, 01GS0869, 01GS0853, 01GS08156, 01GR0430, 01GR0434, 01GR0438, 01KW9948, and R0313435B), the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (FOR926), and the European Union (FP6, EUMODIC, LSHG-CT-2006-037188). The expert technical assistance of Miriam Backs, Erika Bürkle, Christine Führmann, Anita Hellemons, Elfi Holupirek, Regina Kneuttinger, Maria Kugler, Astrid Markert, Jacqueline Müller, Eleonore Samson, Bahar Sanli-Bonazzi, Sandra Schädler, Florian Schleicher, Daniela Schmid, Ann-Elisabeth Schwarz, Reinhard Seeliger, Monika Stadler, Susanne Wittich, and Claudia Zeller is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. Rosemann and A. Ivashkevich contributed equally to this work.
A broad phenotypical analysis of wild-type controls and eyl3 -/- mice was done at the German Mouse Clinic. The complete set of data will be published at www.europhenome.org. The expression data obtained from livers of eyl mutant mice have been submitted to the GEO database (GSE15336), including a full description of our microarray platform (GPL3697).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosemann, M., Ivashkevich, A., Favor, J. et al. Microphthalmia, parkinsonism, and enhanced nociception in Pitx3 416insG mice. Mamm Genome 21, 13–27 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-009-9235-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-009-9235-0