Abstract
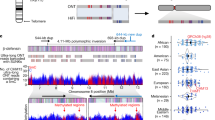
Comparative mapping and sequencing of the mouse and human genomes have defined large, conserved chromosomal segments in which gene content and order are highly conserved. These regions span megabase-sized intervals and together comprise the vast majority of both genomes. However, the evolutionary relationships among the small remaining portions of these genomes are not as well characterized. Here we describe the sequencing and annotation of a 341-kb region of mouse Chr 2 containing nine genes, including biliverdin reductase A (Blvra), and its comparison with the orthologous regions of the human and rat genomes. These analyses reveal that the known conserved synteny between mouse Chromosome (Chr) 2 and human Chr 7 reflects an interval containing one gene (Blvra/BLVRA) that is, at most, just 34 kb in the mouse genome. In the mouse, this segment is flanked proximally by genes orthologous to human chromosome 15q21 and distally by genes orthologous to human Chr 2q11. The observed differences between the human and mouse genomes likely resulted from one or more rearrangements in the rodent lineage. In addition to the resulting changes in gene order and location, these rearrangements also appear to have included genomic deletions that led to the loss of at least one gene in the rodent lineage. Finally, we also have identified a recent mouse-specific segmental duplication. These finding illustrate that small genomic regions outside the large mouse–human conserved segments can contain a single gene as well as sequences that are apparently unique to one genome.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
S Aparicio J Chapman E Stupka N Putnam JM Chia et al. (2002) ArticleTitleWhole-genome shotgun assembly and analysis of the genome of Fugu rubripes. Science 297 1301–1310 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1072104 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xms1ejtr8%3D Occurrence Handle12142439
JA Bailey Z Gu RA Clark K Reinert RV Samonte et al. (2002) ArticleTitleRecent segmental duplications in the human genome. Science 297 1003–1007 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1072047 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xmt1Cktr4%3D Occurrence Handle12169732
P Dehal P Predki AS Olsen A Kobayashi P Folta et al. (2001) ArticleTitleHuman chromosome 19 and related regions in mouse: conservative and lineage-specific evolution. Science 293 104–111 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1060310 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXltFCntbw%3D Occurrence Handle11441184
A Felsenfeld J Peterson J Schloss M Guyer (1999) ArticleTitleAssessing the quality of the DNA sequence from The Human Genome Project. Genome Res 9 1–4 Occurrence Handle9927479
SG Gregory M Sekhon J Schein S Zhao K Osoegawa et al. (2002) ArticleTitleA physical map of the mouse genome. Nature 418 743–750 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature00957 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XmtV2nsr8%3D Occurrence Handle12181558
TJ Hudson DM Church S Greenaway H Nguysn A Cook et al. (2001) ArticleTitleA radiation hybrid map of mouse genes. Nat Genet 29 201–205 Occurrence Handle10.1038/ng1001-201 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXnsFKgu7k%3D Occurrence Handle11586302
InstitutionalAuthorNameInternational Human Genome Sequencing Consortium (2001) ArticleTitleInitial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409 860–921 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXhsFCjtLc%3D Occurrence Handle11237011
J Lund F Chen A Hua B Roe M Budarf et al. (2000) ArticleTitleComparative sequence analysis of 634 kb of the mouse chromosome 16 region of conserved synteny with the human velocardiofacial syndrome region on chromosome 22q11.2. Genomics 63 374–383 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhsFShsb4%3D Occurrence Handle10704284
KP Meera LMM Wijnen JT Wijnen K-H Grzeschik (1983) ArticleTitleElectrophoretic characterization and genetics of human biliverdin reductase (BLVR; EC 1.3.2.24): assignment of BLVR to the p14→ cen region of human chromosome 7 in mouse-human somatic cell hybrids. Biochem Genet 21 123–133 Occurrence Handle6838484
InstitutionalAuthorNameInternational Human Genome Sequencing ConsortiumMouse Genome Sequencing Consortium (2002) ArticleTitleInitial sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome. Nature 420 520–562 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature01262 Occurrence Handle12466850
SJ O’Brien M Menotti-Raymond WJ Murphy WG Nash J Wienberg et al. (1999) ArticleTitleThe promise of comparative genomics in mammals. Science 286 458–481 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXmvVOht74%3D Occurrence Handle10521336
K Osoegawa M Tateno PY Woon E Frengen AG Mammoser et al. (2000) ArticleTitleBacterial artificial chromosome libraries for mouse sequencing and functional analysis. Genome Res 10 116–128 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXpsl2jtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10645956
J Peters ST Ball A von Deimling (1989) ArticleTitleLocalization of Blvr, biliverdin reductase, on mouse chromosome 2. Genomics 5 270–274 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BD3cjlsVM%3D Occurrence Handle2793182
P Pevzner G Tesler (2003) ArticleTitleGenome rearrangements in mammalian evolution: lessons from human and mouse genomes. Genome Res 13 37–45 Occurrence Handle10.1101/gr.757503 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXnvFGmsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle12529304
S Schwartz Z Zhang KA Frazer A Smit C Riemer et al. (2000) ArticleTitlePipMaker—a web server for aligning two genomic DNA sequences. Genome Res 10 577–586 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjtVKrsLg%3D Occurrence Handle10779500
MS Springer WJ Murphy E Eizirik SJ O’Brien (2003) ArticleTitlePlacental mammal diversification and the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100 1056–1061 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXhtF2gtrw%3D Occurrence Handle12552136
JW Thomas TJ Summers S-Q Lee-Lin VV Braden Maduro JR Idol et al. (2000) ArticleTitleComparative genome mapping in the sequence-based era: early experience with human chromosome 7. Genome Res 10 624–633 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjsFegtLo%3D Occurrence Handle10810084
JW Thomas MG Schueler TJ Summers RW Blakesley JC McDowell et al. (2003) ArticleTitlePericentromeric duplications in the laboratory mouse. Genome Res 13 55–63 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXnvFGmtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle12529306
SJ Wheelan DM Church JM Ostell (2001) ArticleTitleSpidey: a tool for mRNA-to-genomic alignments. Genome Res 11 1952–1957 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXotlaju7g%3D Occurrence Handle11691860
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the contributions of Jeff Touchman and Pamela Thomas as members of the NISC Comparative Sequencing Program for finishing the sequence of the reported BACs, and Mary Schueler for critical review of the manu- script.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, J.W., NISC Comparative Sequencing Program. & NISC Comparative Sequencing Program. Comparative sequence analysis of a single-gene conserved segment in mouse and human . Mamm Genome 14, 673–678 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-003-2300-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-003-2300-1