Abstract
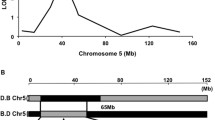
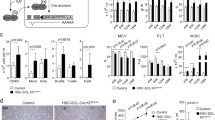
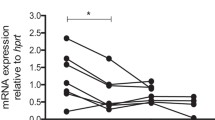
Kit ligand (Kitl), which is a member of the helical cytokine superfamily, is encoded by the Steel (Sl) locus of mice and is essential for the development of hematopoietic cells, germ cells, and melanocytes. A large series of Kitl Sl alleles has been described, including some that arose spontaneously and others that were induced by either chemical or radiation mutagenesis. Here we describe the nucleotide sequence alterations in two spontaneous Kitl Sl alleles. The Kitl Sl-18R allele has a point mutation that introduces a premature termination codon, and the encoded protein is expected to be null functionally. The Kitl Sl-5R allele has an in-frame deletion that results in deletion of amino acids at position 31 and 32 of Kitl. While both mutations exert severe effects on blood cells and survival of homozygous mice, these effects are slightly milder than those of a previously characterized spontaneous deletion allele, Kitl Sl-gb. Examination of the survival of compound heterozygotes provided strong genetic evidence that the Kitl Sl-18R and Kitl Sl-5R mutants are null functionally for mouse survival.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajaraman, S., Wood, L., Willhite, D. et al. Effects of spontaneous Kitl Steel mutations on survival and red blood cells of mice . Mamm Genome 14, 168–174 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-002-2193-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-002-2193-4