Abstract
Objectives
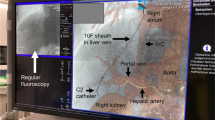
Establishment of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts (TIPS) constitutes a standard procedure in patients suffering from portal hypertension. The most difficult step in TIPS placement is blind puncture of the portal vein. This study aimed to evaluate three-dimensional mapping of portal vein branches and targeted puncture of the portal vein.
Methods
Twelve consecutive patients suffering from refractory ascites by liver cirrhosis were included in this retrospective study to evaluate feasibility, technical success and procedural time of C-arm CT-targeted puncture of the portal vein. As a control, 22 patients receiving TIPS placement with fluoroscopy-guided blind puncture were included to compare procedural time.
Results
Technical success could be obtained in 100 % of the study group (targeted puncture) and in 95.5 % of the control group (blind puncture). Appropriate, three-dimensional C-arm CT-guided mapping of the portal vein branches could be achieved in all patients. The median number of punctures in the C-arm CT-guided study group was 2 ± 1.3 punctures. Procedural time was significantly lower in the study group (14.8 ± 8.2 min) compared to the control group (32.6 ± 22.7 min) (p = 0.02).
Conclusions
C-arm CT-guided portal vein mapping is technically feasible and a promising tool for TIPS placement resulting in a significant reduction of procedural time.
Key Points
• C-arm CT-mapping of the portal vein for 3D TIPS guidance is feasible.
• Targeted punctures of the portal vein by C-arm CT reduce procedural time.
• A decreased number of punctures could improve patient safety.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rossle M, Haag K et al (1994) The transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt procedure for variceal bleeding. N Engl J Med 330:165–171
Fidelman N, Kwan SW et al (2012) The transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: an update. AJR Am J Roentgenol 199:746–755
Boyer TD, Haskal ZJ (2005) American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Practice Guidelines: the role of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation in the management of portal hypertension. J Vasc Interv Radiol 16:615–629
Raza SA, Walser E et al (2006) Transhepatic puncture of portal and hepatic veins for TIPS using a single-needle pass under sonographic guidance. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187:W87–W91
Kwan SW, Fidelman N et al (2011) Rex shunt preoperative imaging: Diagnostic capability of imaging modalities. PLoS ONE 6, e22222
Marquardt S, Rodt T et al (2015) Impact of anatomical, procedural, and operator skill factors on the success and duration of fluoroscopy-guided transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 38:903–912
Tsauo J, Luo X et al (2015) Three-dimensional path planning software-assisted transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: a technical modification. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 38:742–746
Farsad K, Fuss C et al (2012) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation using intravascular ultrasound guidance. J Vasc Interv Radiol 23:1594–1602
Longo JM, Bilbao JI et al (1992) Color Doppler-US guidance in transjugular placement of intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Radiology 184:281–284
Adamus R, Pfister M et al (2009) Enhancing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt puncture by using three-dimensional path planning based on the back projection of two two-dimensional portographs. Radiology 251:543–547
Kim H, Park CM et al (2015) C-arm cone-beam CT virtual navigation-guided percutaneous mediastinal mass biopsy: Diagnostic accuracy and complications. Eur Radiol 25:3508–3517
Krajina A, Hulek P et al (2012) Quality improvement guidelines for Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS). Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 35:1295–1300
Casado M, Bosch J et al (1998) Clinical events after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: correlation with hemodynamic findings. Gastroenterology 114:1296–1303
Sorensen HT, Thulstrup AM et al (2003) Long-term survival and cause-specific mortality in patients with cirrhosis of the liver: a nationwide cohort study in Denmark. J Clin Epidemiol 56:88–93
Kew J, Davies RP (2004) Intravascular ultrasound guidance for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt procedure in a swine model. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 27:38–41
Petersen B (2003) Intravascular ultrasound-guided direct intrahepatic portacaval shunt: description of technique and technical refinements. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:21–32
Bloch R, Fontaine A et al (2001) CT-guided transfemoral portocaval shunt creation. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 24:106–110
Kee ST, Rhee JS et al (1999) 1999 Gary J. Becker Young Investigator Award. MR-guided transjugular portosystemic shunt placement in a swine model. J Vasc Interv Radiol 10:529–535
Sze DY, Strobel N et al (2006) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation in a polycystic liver facilitated by hybrid cross-sectional/angiographic imaging. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17:711–715
Wallace MJ, Kuo MD et al (2008) Three-dimensional C-arm cone-beam CT: applications in the interventional suite. J Vasc Interv Radiol 19:799–813
Luo X, Ye L et al (2015) C-arm cone-beam volume CT in transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: initial clinical experience. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 38:1627–1631
Kapoor BS, Esparaz A et al (2013) Nonvascular and portal vein applications of cone-beam computed tomography: current status. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol 16:150–160
Schernthaner RE, Duran R et al (2015) A new angiographic imaging platform reduces radiation exposure for patients with liver cancer treated with transarterial chemoembolization. Eur Radiol 25:3255–3262
Miraglia R, Maruzzelli L et al (2016) Radiation exposure in transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 39:210–217
Miller DL, Kwon D et al (2009) Reference levels for patient radiation doses in interventional radiology: proposed initial values for U.S. practice. Radiology 253:753–764
Acknowledgments
The scientific guarantor of this publication is PD Dr. Dominik Ketelsen, MD. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper. Institutional Review Board approval was not required due to retrospective study design. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study. Methodology: retrospective, observational study, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ketelsen, D., Groezinger, G., Maurer, M. et al. Three-dimensional C-arm CT-guided transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt placement: Feasibility, technical success and procedural time. Eur Radiol 26, 4277–4283 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-016-4340-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-016-4340-4