Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the effect of the choice of b values and prior use of contrast medium on apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs) of breast lesions derived from diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), and on the discrimination between benign and malignant lesions.
Methods
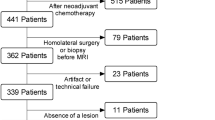
A literature search of relevant DWI studies was performed. The accuracy of DWI to characterize lesions by using b value ≤600 s/mm2 and b value >600 s/mm2 was presented as pooled sensitivity and specificity, and the ADC was calculated for both groups. Lesions were pooled as pre- or post-contrast DWI.
Results
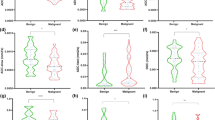
Of 198 articles, 26 met the inclusion criteria. Median ADCs were significantly higher (13.2–35.1 %, p < 0.001) for the group of b values ≤600 s/mm2 compared to >600 s/mm2. The sensitivity in both groups was similar (91 % and 89 %, p = 0.495) as well as the specificity (75 % and 84 %, p = 0.237). Contrast medium had no significant effects on the ADCs (p ≥ 0.08). The differentiation between benign and malignant lesions was optimal (58.4 %) for the combination of b = 0 and 1,000 s/mm2.
Conclusions
The wide variety of b value combinations applied in different studies significantly affects the ADC of breast lesions and confounds quantitative DWI. If only a couple of b values are used, those of b = 0 and 1,000 s/mm2 are recommended for the best improvement of differentiating between benign and malignant lesions.
Key Points
• The choice of b values significantly affects the ADC of breast lesions.
• Sensitivity and specificity are not affected by the choice of b values.
• b values 0 and 1,000 s/mm 2 are recommended for optimal differentiation between benign and malignant lesions.
• Contrast medium prior to DWI does not significantly affect the ADC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Orel SG, Schnall MD (2001) MR imaging of the breast for the detection, diagnosis, and staging of breast cancer. Radiology 220:13–30
Macura KJ, Ouwerkerk R, Jacobs MA, Bluemke DA (2006) Patterns of enhancement on breast MR images: interpretation and imaging pitfalls. Radiographics 26:1719–1734
Schnall MD, Blume J, Bluemke DA, DeAngelis GA, DeBruhl N, Harms S, Heywang-Kobrunner SH, Hylton N, Kuhl CK, Pisano ED, Causer P, Schnitt SJ, Thickman D, Stelling CB, Weatherall PT, Lehman C, Gatsonis CA (2006) Diagnostic architectural and dynamic features at breast MR imaging: multicenter study. Radiology 238:42–53
Szabo BK, Aspelin P, Wiberg MK, Bone B (2003) Dynamic MR imaging of the breast. Analysis of kinetic and morphologic diagnostic criteria. Acta Radiol 44:379–386
Bluemke DA, Gatsonis CA, Chen MH et al (2004) Magnetic resonance imaging of the breast prior to biopsy. JAMA 292:2735–2742
Hrung JM, Sonnad SS, Schwartz JS, Langlotz CP (1999) Accuracy of MR imaging in the work-up of suspicious breast lesions: a diagnostic meta-analysis. Acad Radiol 6:387–397
Peters NH, Borel Rinkes IH, Zuithoff NP, Mali WP, Moons KG, Peeters PH (2008) Meta-analysis of MR imaging in the diagnosis of breast lesions. Radiology 246:116–124
Martincich L, Faivre-Pierret M, Zechmann CM et al (2011) Multicenter, double-blind, randomized, intraindividual crossover comparison of gadobenate dimeglumine and gadopentetate dimeglumine for breast MR imaging (DETECT trial). Radiology 258:396–408
Pinker K, Bogner W, Baltzer P et al (2014) Clinical application of bilateral high temporal and spatial resolution dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of the breast at 7T. Eur Radiol 24:913–920
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Aubin ML, Vignaud J, Laval-Jeantet M (1988) Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 168:497–505
Gourtsoyianni S, Papanikolaou N, Yarmenitis S, Maris T, Karantanas A, Gourtsoyiannis N (2008) Respiratory gated diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver: value of apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in the differentiation between most commonly encountered benign and malignant focal liver lesions. Eur Radiol 18:486–492
Namimoto T, Yamashita Y, Sumi S, Tang Y, Takahashi M (1997) Focal liver masses: characterization with diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 204:739–744
Michielsen K, Vergote I, Op de Beeck K (2014) Whole-body MRI with diffusion-weighted sequence for staging of patients with suspected ovarian cancer: a clinical feasibility study in comparison to CT and FDG-PET/CT. Eur Radiol 24(4):889–901
Cha J, Kim ST, Kim HJ et al (2013) Analysis of the layering pattern of the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) for differentiation of radiation necrosis from tumour progression. Eur Radiol 23:879–886
Kartalis N, Lindholm TL, Aspelin P, Permert J, Albiin N (2009) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of pancreas tumours. Eur Radiol 19:1981–1990
Yamashita Y, Namimoto T, Mitsuzaki K, Urata J, Tsuchigame T, Takahashi M, Ogawa M (1998) Mucin-producing tumor of the pancreas: diagnostic value of diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 208:605–609
Ueno Y, Takahashi S, Kitajima K et al (2013) Computed diffusion-weighted imaging using 3-T magnetic resonance imaging for prostate cancer diagnosis. Eur Radiol 23:3509–3516
Ochi M, Kuroiwa T, Sunami S et al (2013) Diffusion weighted imaging (b-value = 1500 s/mm2) is useful to decrease false-positive breast cancer cases due to fibrocystic changes. Breast Cancer 20:137–144
Sonmez G, Cuce F, Mutlu H et al (2011) Value of diffusion-weighted MRI in the differentiation of benign and malignant lesions. Wien Klin Wochenschr 123:655–661
Inoue K, Kozawa E, Mizukoshi W et al (2011) Usefulness of diffusion-weighted imaging of breast tumors: quantitative and visual assessment. Jpn J Radiol 29:429–436
Imamura T, Isomoto I, Sueyoshi E et al (2010) Diagnostic performance of ADC for non-mass-like breast lesions on MR imaging. Magn Reson Med Sci 9:217–225
Kul S, Cansu A, Alhan E, Dinc H, Gunes G, Reis A (2011) Contribution of diffusion-weighted imaging to dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in the characterization of breast tumors. AJR Am J Roentgenol 196:210–217
Fornasa F, Pinali L, Gasparini A, Toniolli E, Montemezzi S (2011) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in focal breast lesions: analysis of 78 cases with pathological correlation. Radiol Med 116:264–275
Baltzer PA, Schäfer A, Dietzel M, Grässel D, Gajda M, Camara O, Kaiser WA (2011) Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging of the breast: a pilot study. Eur Radiol 21:1–10
Partridge SC, Mullins CD, Kurland BF, Allain MD, DeMartini WB, Eby PR, Lehman CD (2010) Apparent diffusion coefficient values for discriminating benign and malignant breast MRI lesions: effects of lesion type and size. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194:1664–1673
Xie CM, Yin SH, Li H et al (2010) Diagnostic value of ADC and rADC of diffusion weighted imaging in malignant breast lesions. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 32:217–220
Jin G, An N, Jacobs MA, Li K (2010) The role of parallel diffusion-weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map values for evaluating breast lesions: preliminary results. Acad Radiol 17:456–463
Partridge SC, Demartini WB, Kurland BF, Eby PR, White SW, Lehman CD (2010) Differential diagnosis of mammographically and clinically occult breast lesions on diffusion-weighted MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 31:562–570
Baltzer PA, Benndorf M, Dietzel M, Gajda M, Camara O, Kaiser WA (2010) Sensitivity and specificity of unenhanced MR mammography (DWI combined with T2-weighted TSE imaging, ueMRM) for the differentiation of mass lesions. Eur Radiol 20:1101–1110
Partridge SC, DeMartini WB, Kurland BF, Eby PR, White SW, Lehman CD (2009) Quantitative diffusion-weighted imaging as an adjunct to conventional breast MRI for improved positive predictive value. AJR Am J Roentgenol 193:1716–1722
Belli P, Costantini M, Bufi E, Magistrelli A, La Torre G, Bonomo L (2010) Diffusion-weighted imaging in breast lesion evaluation. Radiol Med 115:51–69
Pereira FP, Martins G, Figueiredo E, Domingues MN, Domingues RC, da Fonseca LM, Gasparetto EL (2009) Assessment of breast lesions with diffusion-weighted MRI: comparing the use of different b values. AJR Am J Roentgenol 193:1030–1035
Tozaki M, Fukuma E (2009) 1H MR spectroscopy and diffusion-weighted imaging of the breast: are they useful tools for characterizing breast lesions before biopsy? AJR Am J Roentgenol 193:840–849
Barceló J, Vilanova JC, Albanell J et al (2009) Breast MRI: the usefulness of diffusion-weighted sequences for differentiating between benign and malignant lesions. Radiologia 51:469–476
Stadlbauer A, Bernt R, Gruber S et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS) for the diagnosis of malignant and benign breast lesions. Eur Radiol 19:2349–2356
Baltzer PA, Renz DM, Herrmann KH et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in MR mammography (MRM): clinical comparison of echo planar imaging (EPI) and half-Fourier single-shot turbo spin echo (HASTE) diffusion techniques. Eur Radiol 19:1612–1620
Yili Z, Xiaoyan H, Hongwen D, Yun Z, Xin C, Peng W, Youmin G (2009) The value of diffusion-weighted imaging in assessing the ADC changes of tissues adjacent to breast carcinoma. BMC Cancer 9:18
Marini C, Iacconi C, Giannelli M, Cilotti A, Moretti M, Bartolozzi C (2007) Quantitative diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the differential diagnosis of breast lesion. Eur Radiol 17(10):2646–2655
Luo JD, Liu YY, Zhang XL, Shi LC (2007) Application of diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging to differential diagnosis of breast diseases. Ai Aizheng 26:168–171
Rubesova E, Grell AS, De Maertelaer V, Metens T, Chao SL, Lemort M (2006) Quantitative diffusion imaging in breast cancer: a clinical prospective study. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:319–324
Woodhams R, Matsunaga K, Kan S, Hata H, Ozaki M, Iwabuchi K, Kuranami M, Watanabe M, Hayakawa K (2005) ADC mapping of benign and malignant breast tumors. Magn Reson Med Sci 4:35–42
Tang JH, Yan FH, Zhou ML, Ye F, Xu PJ (2008) Comparative study of diffusion weighted imaging and dynamic contrast enhanced MRI for the detection of small breast cancers. Zhonghua Fang She Yi Xue Yu Fang Hu Za Zhi 42:152–156
Gu YJ, Feng XY, Tang F, Peng WJ, Mao J, Yang WT (2007) Diffusion-weighted MRI of the breast: Lesion characterization and parameter selection. Zhonghua Fang She Yi Xue Yu Fang Hu Za Zhi 41:451–456
Baron P, Dorrius MD, Kappert P et al (2010) Diffusion-weighted imaging of normal fibroglandular breast tissue: influence of microperfusion and fat suppression technique on the apparent diffusion coefficient. NMR 23:399–405
Yuen S, Yamada K, Goto M, Nishida K, Takahata A, Nishimura T (2009) Microperfusion-induced elevation of ADC is suppressed after contrast in breast carcinoma. J Magn Reson Imaging 29:1080–1084
Janka R, Hammon M, Geppert C, Nothhelfer A, Uder M, Wenkel E (2014) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of benign and malignant breast lesions before and after contrast-enhancement. Röfo 186:130–135
Matsuoka A, Manito M, Harada M, Kubo H, Bandou Y, Tangoku A, Nakano K, Nishitani H (2008) Comparison of 3.0- and 1.5-tesla diffusion-weighted imaging in the visibility of breast cancer. Radiat Med 26:15–20
Whiting P, Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PM, Kleijnen J (2003) The development of QUADAS: a tool for the quality assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy included in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol 3:25
Whiting PF, Weswood ME, Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PN, Kleijnen J (2006) Evaluation of QUADAS, a tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. BMC Med Res Methodol 6:9
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Br Med J 2327:557–560
Tsushima Y, Takahashi-Taketomi A, Endo K (2009) Magnetic resonance (MR) differential diagnosis of breast tumors using apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) on 1.5-T. J Magn Reson Imaging 30:249–255
Chen X, Li WL, Zhang YL, Wu Q, Guo YM, Bai ZL (2010) Meta-analysis of quantitative diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the differential diagnosis of breast lesions. BMC Cancer 10:693
Bogner W, Gruber S, Pinker K et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted MR for differentiation of breast lesions at 3.0T: how does selection of diffusion protocols affect diagnosis? Radiology 253:341–351
Firat AK, Sanli B, Karakas HM, Erdem G (2006) The effect of intravenous gadolinium-DTPA on diffusion-weighted imaging. Neuroradiol 48:465–470
Chen L, Zhang J, Bao J et al (2013) Meta-analysis of diffusion-weighted MRI in differential diagnosis of lung lesions. J Magn Reson Imaging 37:1351–1358
Acknowledgements
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Prof. M. Oudkerk. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. One of the authors has significant statistical expertise. No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper. Institutional review board approval was not required because this study was a meta-analysis. Written informed consent was not required for this study because this study was a meta-analysis. No study subjects or cohorts have been previously reported. Methodology: meta-analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Monique D. Dorrius and Hildebrand Dijkstra contributed equally
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dorrius, M.D., Dijkstra, H., Oudkerk, M. et al. Effect of b value and pre-admission of contrast on diagnostic accuracy of 1.5-T breast DWI: a systematic review and meta-analysis . Eur Radiol 24, 2835–2847 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3338-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3338-z