Abstract
Background
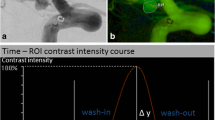
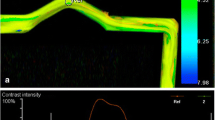
Quantifiable parameters to evaluate the effectiveness of flow diverters (FDs) are desirable. We measured time-density curves (TDCs) and calculated quantifiable parameters in the rabbit elastase-induced aneurysm model after stent (Neuroform [NF]) and FD (Pipeline embolisation device [PED]) treatment.
Methods
Sixteen rabbit elastase-induced aneurysms were treated with FD (n = 9) or NF (n = 5). Angiography was performed before and after treatment and TDCs were created. The time to peak (TTP), the full width at half maximum (FWHM) and the average slope of the curve which represent the inflow (IF) and outflow (OF) were calculated.
Results
Mean values before treatment were TTP = 0.8 s, FWHM = 1.2 s, IF = 153.5 and OF = −54.9. After PED treatment, the TTP of 1.8 s and FWHM of 47.8 s were extended. The IF was 31.2 and the OF was -11.5 and therefore delayed. The values after NF treatment (TTP = 1.1 s, FWHM = 1.8 s, IF = 152.9, OF = −33.2) changed only slightly.
Conclusion
It was feasible to create TDCs in the rabbit aneurysm model. Parameters describing the haemodynamic effect of PED and NF were calculated and were different according to the type of device used. These parameters could possibly serve as predictive markers for aneurysm occlusion.
Key Points
• Detachable coils are now widely used instead of surgery for intracranial aneurysms
• Time-density curves of aneurysms can indicate effectiveness in reducing intra-aneurysmal flow
• Time-density curves can now be measured by a prototype software
• Time-density curves after treatment with a flow diverter or a conventional stent are different
• Parameters of the time-density curves can be calculated and may serve as predictive parameters



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CFD:
-
Computational haemodynamic analysis
- DSA:
-
Digital subtraction angiography
- FD:
-
Flow diverter
- Fps:
-
Frames per second
- FWHM:
-
Full width at half maximum
- IF:
-
Inflow
- NF:
-
Neuroform
- OF:
-
Outflow
- PCC:
-
Parametric colour-coding
- PED:
-
Pipeline embolisation device
- TDC:
-
Time-density curve
- TTP:
-
Time to peak
References
Meyer FB, Morita A, Puumala MR, Nichols DA (1995) Medical and surgical management of intracranial aneurysms. Mayo Clin Proc 70:153–172
Guglielmi G, Viñuela F, Duckwiler G et al (1992) Endovascular treatment of posterior circulation aneurysms by electrothrombosis using electrically detachable coils. J Neurosurg 77:515–524
Molyneux A, Kerr R, Stratton I et al (2002) International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised trial. Lancet 360:1267–1274
Geremia G, Haklin M, Brennecke L (1994) Embolization of experimentally created aneurysms with intravascular stent devices. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15:1223–1231
Wakhloo AK, Schellhammer F, de Vries J, Haberstroh J, Schumacher M (1994) Self-expanding and balloon-expandable stents in the treatment of carotid aneurysms: an experimental study in a canine model. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15:493–502
Marks MP, Dake MD, Steinberg GK, Norbash AM, Lane B (1994) Stent placement for arterial and venous cerebrovascular disease: preliminary experience. Radiology 191:441–446
Lieber BB, Stancampiano AP, Wakhloo AK (1997) Alteration of hemodynamics in aneurysm models by stenting: influence of stent porosity. Ann Biomed Eng 25:460–469
Wakhloo AK, Lanzino G, Lieber BB, Hopkins LN (1998) Stents for intracranial aneurysms: the beginning of a new endovascular era? Neurosurgery 43:377–379
Fiorella D, Hsu D, Woo RW, Tarr HH, Nelson PK (2010) Very late thrombosis of a pipeline embolization device construct: case report. Neurosurgery 67:onsE313–onsE314
Lubicz B, Collignon L, Raphaeli G et al (2010) Flow-diverter stent for the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms: a prospective study in 29 patients with 34 aneurysms. Stroke 41:2247–2253
Kulcsár Z, Houdart E, Bonafé A et al (2011) Intra-aneurysmal thrombosis as a possible cause of delayed aneurysm rupture after flow-diversion treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:20–25
Turowski B, Macht S, Kulcsár Z, Hänggi D, Stummer W (2011) Early fatal haemorrhage after endovascular cerebral aneurysm treatment with a flow diverter (SILK-stent): do we need to rethink our concepts? Neuroradiology 53:37–41
O’kelly CJ, Krings T, Fiorella D, Marotta TR (2010) A novel grading scale for the angiographic assessment of intracranial aneurysms treated using flow diverting stents. Interv Neuroradiol 16:133–137
Kamran M, Yarnold J, Grunwald IQ, Byrne JV (2011) Assessment of angiographic outcomes after flow diversion treatment of intracranial aneurysms: a new grading schema. Neuroradiology 53:501–508
Sadasivan C, Lieber BB, Gounis MJ, Lopes DK, Hopkins LN (2002) Angiographic quantification of contrast medium washout from cerebral aneurysms after stent placement. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1214–1221
Sadasivan C, Cesar L, Seong J, Wakhloo AK, Lieber BB (2009) Treatment of rabbit elastase-induced aneurysm models by flow diverters: development of quantifiable indexes of device performance using digital subtraction angiography. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28:1117–1125
Ahmed AS, Deuerling-Zheng Y, Strother CM et al (2009) Impact of intra-arterial injection parameters on arterial, capillary, and venous time-concentration curves in a canine model. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1337–1341
Strother CM, Bender F, Deuerling-Zheng Y et al (2010) Parametric color coding of digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:919–924
Cloft HJ, Altes TA, Marx WF et al (1999) Endovascular creation of an in vivo bifurcation aneurysm model in rabbits. Radiology 213:223–228
Kallmes DF, Helm GA, Hudson SB et al (1999) Histologic evaluation of platinum coil embolization in an aneurysm model in rabbits. Radiology 213:217–222
Roth C, Struffert T, Grunwald IQ et al (2008) Long-term results with Matrix coils vs GDC: an angiographic and histopathological comparison. Neuroradiology 50:693–699
Struffert T, Roth C, Romeike B et al (2008) Onyx in an experimental aneurysm model: histological and angiographic results. J Neurosurg 109:77–82
Grunwald IQ, Romeike BF, Roth C et al (2005) Anticoagulation regimes and their influence on the occlusion rate of aneurysms: an experimental study in rabbits. Neurosurgery 57:1048–1055
Zeng Z, Kallmes DF, Durka MJ et al (2011) Hemodynamics and anatomy of elastase-induced rabbit aneurysm models: similarity to human cerebral aneurysms? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:595–601
Kallmes DF, Ding YH, Dai D, Kadirvel R, Lewis DA, Cloft HJ (2007) A new endoluminal, flow-disrupting device for treatment of saccular aneurysms. Stroke 38:2346–2352
Kallmes DF, Ding YH, Dai D, Kadirvel R, Lewis DA, Cloft HJ (2009) A second-generation, endoluminal, flow-disrupting device for treatment of saccular aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1153–1158
Ding Y, Dai D, Kadirvel R, Lewis DA, Kallmes DF (2010) Five-year follow-up in elastase-induced aneurysms in rabbits. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1236–1239
Grunwald IQ, Romeike B, Eymann R, Roth C, Struffert T, Reith W (2006) An experimental aneurysm model: a training model for neurointerventionalists. Interv Neuroradiol 12:17–24
Bouzeghrane F, Naggara O, Kallmes DF, Berenstein A, Raymond J (2010) International consortium of neuroendovascular centres. In vivo experimental intracranial aneurysm models: a systematic review. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:418–23
Dohatcu A, Ionita CN, Paciorek A, Bednarek DR, Hoffmann KR, Rudin S (2008) Endovascular image-guided treatment of in-vivo model aneurysms with asymmetric vascular stents (AVS): evaluation with time-density curve angiographic analysis and histology. Proc Soc Photo Opt Instrum Eng 6916:6916OP
Cantón G, Levy DI, Lasheras JC, Nelson PK (2005) Flow changes caused by the sequential placement of stents across the neck of sidewall cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg 103:891–902
Cebral JR, Mut F, Raschi M et al (2011) Aneurysm rupture following treatment with flow-diverting stents: computational haemodynamics analysis of treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:27–33
Fiorella D, Albuquerque FC, Deshmukh VR et al (2006) Endovascular reconstruction with the Neuroform stent as monotherapy for the treatment of uncoilable intradural pseudoaneurysms. Neurosurgery 59:291–300
Ediriwickrema A, Williamson T, Hebert R, Matouk C, Johnson MH, Bulsara KR (2012) Intracranial stenting as monotherapy in subarachnoid hemorrhage and sickle cell disease. J Neurointerv Surg. doi:10.1136/neurintsurg-2011-010224
Krings T, Hans FJ, Möller-Hartmann W et al (2005) Treatment of experimentally induced aneurysms with stents. Neurosurgery 56:1347–1359
Wang ZJ, Hoffmann KR, Wang Z, Rudin S, Guterman LR, Meng H (2005) Contrast settling in cerebral aneurysm angiography. Phys Med Biol 50:3171–3181
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Struffert, T., Ott, S., Kowarschik, M. et al. Measurement of quantifiable parameters by time-density curves in the elastase-induced aneurysm model: first results in the comparison of a flow diverter and a conventional aneurysm stent. Eur Radiol 23, 521–527 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2611-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2611-2