Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate MRI using T1 and T2* mapping sequences in patients with suspected hepatic iron overload (HIO).
Methods
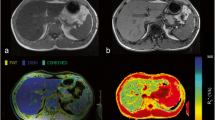
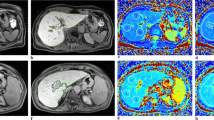
Twenty-five consecutive patients with clinically suspected HIO were retrospectively studied. All underwent MRI and liver biopsy. For the quantification of liver T2* values we used a fat-saturated multi-echo gradient echo sequence with 12 echoes (TR = 200 ms, TE = 0.99 ms + n × 1.41 ms, flip angle 20°). T1 values were obtained using a fast T1 mapping sequence based on an inversion recovery snapshot FLASH sequence. Parameter maps were analysed using regions of interest.
Results
ROC analysis calculated cut-off points at 10.07 ms and 15.47 ms for T2* in the determination of HIO with accuracy 88 %/88 %, sensitivity 84 %/89.5 % and specificity 100 %/83 %. MRI correctly classified 20 patients (80 %). All patients with HIO only had decreased T1 and T2* relaxation times. There was a significant difference in T1 between patients with HIO only and patients with HIO and steatohepatitis (P = 0.018).
Conclusions
MRI-based T2* relaxation diagnoses HIO very accurately, even at low iron concentrations. Important additional information may be obtained by the combination of T1 and T2* mapping. It is a rapid, non-invasive, accurate and reproducible technique for validating the evidence of even low hepatic iron concentrations.
Key Points
• Hepatic iron overload causes fibrosis, cirrhosis and increases hepatocellular carcinoma risk.
• MRI detects iron because of the field heterogeneity generated by haemosiderin.
• T2* relaxation is very accurate in diagnosing hepatic iron overload.
• Additional information may be obtained by T1 and T2* mapping.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HH:
-
hereditary haemochromatosis
- HII:
-
hepatic iron index
- HIC:
-
hepatic iron concentration
- HIO:
-
hepatic iron overload
- LIC:
-
liver iron concentration
- MRI:
-
magnetic resonance imaging
- SH:
-
steatohepatitis
References
Alustiza JM, Castiella A, De Juan MD, Emparanza JI, Artetxe J, Uranga M (2007) Iron overload in the liver diagnostic and quantification. Eur J Radiol 61:499–506
Siegelman ES, Mitchell DG, Semelka RC (1996) Abdominal iron deposition: metabolism, MR findings, and clinical importance. Radiology 199:13–22
Stevens RG, Jones DY, Micozzi MS, Taylor PR (1988) Body iron stores and the risk of cancer. N Engl J Med 319:1047–1052
Niederau C, Fischer R, Sonnenberg A, Stremmel W, Trampisch HJ, Strohmeyer G (1985) Survival and causes of death in cirrhotic and in noncirrhotic patients with primary hemochromatosis. N Engl J Med 313:1256–1262
Adams P, Brissot P, Powell LW (2000) EASL international consensus conference on haemochromatosis. J Hepatol 33:485–504
Gandon Y, Olivie D, Guyader D et al (2004) Non-invasive assessment of hepatic iron stores by MRI. Lancet 363:357–362
Bonkovsky HL, Rubin RB, Cable EE, Davidoff A, Rijcken TH, Stark DD (1999) Hepatic iron concentration: noninvasive estimation by means of MR imaging techniques. Radiology 212:227–234
Villeneuve JP, Bilodeau M, Lepage R, Cote J, Lefebvre M (1996) Variability in hepatic iron concentration measurement from needle-biopsy specimens. J Hepatol 25:172–177
Lim RP, Tuvia K, Hajdu CH et al (2010) Quantification of hepatic iron deposition in patients with liver disease: comparison of chemical shift imaging with single-echo T2*-weighted imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194:1288–1295
Gandon Y, Guyader D, Heautot JF et al (1994) Hemochromatosis: diagnosis and quantification of liver iron with gradient-echo MR imaging. Radiology 193:533–538
Chandarana H, Lim RP, Jensen JH et al (2009) Hepatic iron deposition in patients with liver disease: preliminary experience with breath-hold multiecho T2*-weighted sequence. AJR Am J Roentgenol 193:1261–1267
St Pierre TG, Clark PR, Chua-Anusorn W (2005) Measurement and mapping of liver iron concentrations using magnetic resonance imaging. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1054:379–385
St Pierre TG, Clark PR, Chua-anusorn W et al (2005) Noninvasive measurement and imaging of liver iron concentrations using proton magnetic resonance. Blood 105:855–861
Wood JC, Enriquez C, Ghugre N et al (2005) MRI R2 and R2* mapping accurately estimates hepatic iron concentration in transfusion-dependent thalassemia and sickle cell disease patients. Blood 106:1460–1465
Reeder SB, Sirlin CB (2010) Quantification of liver fat with magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Imag Clin N Am 18:337–357, ix
Castiella A, Alustiza JM, Emparanza JI, Zapata EM, Costero B, Diez MI (2011) Liver iron concentration quantification by MRI: are recommended protocols accurate enough for clinical practice? Eur Radiol 21:137–141
Guyader D, Gandon Y (2000) Quantification of iron overload. Bull Acad Natl Med 184:337–347, discussion 347–338
Tavill AS (2001) Diagnosis and management of hemochromatosis. Hepatology 33:1321–1328
Chevallier P (2005) What can we expect from non invasive imaging methods to detect and grade liver fatty infiltration? Gastroenterol Clin Biol 29:1133–1135
Kremser C, Trieb TR, Judmaier W, DeVries AF (2006) Assessing tumor perfusion and treatment response in rectal cancer. Radiology 238:756–757, author reply 757–758
Haase A, Matthaei D, Bartkowski R, Duhmke E, Leibfritz D (1989) Inversion recovery snapshot FLASH MR imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr 13:1036–1040
Anderson LJ, Holden S, Davis B et al (2001) Cardiovascular T2-star (T2*) magnetic resonance for the early diagnosis of myocardial iron overload. Eur Heart J 22:2171–2179
Bluml S, Schad LR, Stepanow B, Lorenz WJ (1993) Spin-lattice relaxation time measurement by means of a TurboFLASH technique. Magn Reson Med 30:289–295
rde Bazelaire CM, Duhamel GD, Rofsky NM, Alsop DC (2004) MR imaging relaxation times of abdominal and pelvic tissues measured in vivo at 3.0 T: preliminary results. Radiology 230:652–659
Pepe A, Lombardi M, Positano V et al (2006) Evaluation of the efficacy of oral deferiprone in beta-thalassemia major by multislice multiecho T2*. Eur J Haematol 76:183–192
St Pierre TG, Clark PR, Chua-Anusorn W (2004) Single spin-echo proton transverse relaxometry of iron-loaded liver. NMR Biomed 17:446–458
Kreeftenberg HG Jr, Mooyaart EL, Huizenga JR, Sluiter WJ (2000) Quantification of liver iron concentration with magnetic resonance imaging by combining T1-, T2-weighted spin echo sequences and a gradient echo sequence. Neth J Med 56:133–137
Alustiza JM, Artetxe J, Castiella A et al (2004) MR quantification of hepatic iron concentration. Radiology 230:479–484
Westwood M, Anderson LJ, Firmin DN et al (2003) A single breath-hold multiecho T2* cardiovascular magnetic resonance technique for diagnosis of myocardial iron overload. J Magn Reson Imaging 18:33–39
Storey P, Thompson AA, Carqueville CL, Wood JC, de Freitas RA, Rigsby CK (2007) R2* imaging of transfusional iron burden at 3 T and comparison with 1.5 T. J Magn Reson Imaging 25:540–547
Chai JW, Lin YC, Chen JH et al (2001) In vivo magnetic resonance (MR) study of fatty liver: importance of intracellular ultrastructural alteration for MR tissue parameters change. J Magn Reson Imaging 14:35–41
Ludwig J, Hashimoto E, Porayko MK, Moyer TP, Baldus WP (1997) Hemosiderosis in cirrhosis: a study of 447 native livers. Gastroenterology 112:882–888
Emond MJ, Bronner MP, Carlson TH, Lin M, Labbe RF, Kowdley KV (1999) Quantitative study of the variability of hepatic iron concentrations. Clin Chem 45:340–346
Adams PC (2001) Is there a threshold of hepatic iron concentration that leads to cirrhosis in C282Y hemochromatosis? Am J Gastroenterol 96:567–569
Moyer TP, Highsmith WE, Smyrk TC, Gross JB Jr (2011) Hereditary hemochromatosis: laboratory evaluation. Clin Chim Acta 412:1485–1492
Moirand R, Mortaji AM, Loreal O, Paillard F, Brissot P, Deugnier Y (1997) A new syndrome of liver iron overload with normal transferrin saturation. Lancet 349:95–97
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henninger, B., Kremser, C., Rauch, S. et al. Evaluation of MR imaging with T1 and T2* mapping for the determination of hepatic iron overload. Eur Radiol 22, 2478–2486 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2506-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2506-2