Abstract
Objective
To investigate the utility of acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) imaging, with the determination of shear wave velocity (SWV), to differentiate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) from non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in patients with morbid obesity before bariatric surgery.
Methods
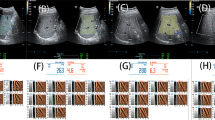
Thirty-two patients with morbid obesity were evaluated with ARFI and conventional ultrasound before bariatric surgery. The ARFI and ultrasound results were compared with liver biopsy findings, which is the reference standard. The patients were classed according to their histological findings into three groups: group A, simple steatosis; group B, inflammation; and group C, fibrosis.
Results
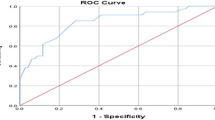
The median SWV was 1.57 ± 0.79 m/s. Hepatic alterations were observed in the histopathological findings for all the patients in the study (100 %), with the results of the laboratory tests proving normal. Differences in SWV were also observed between groups A, B and C: 1.34 ± 0.90 m/s, 1.55 ± 0.79 m/s and 1.86 ± 0.75 m/s (P < 0.001), respectively. The Az for differentiating NAFLD from NASH or fibrosis was 0.899 (optimal cut-off value 1.3 m/s; sensitivity 85 %; specificity 83.3 %).
Conclusion
The ARFI technique is a useful diagnostic tool for differentiating NAFLD from NASH in asymptomatic patients with morbid obesity.
Key Points
• Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging provides ultrasonic shear wave velocity measurements.
• SWV measurements were higher in patients with inflammation or fibrosis than NAFLD.
• ARFI differentiates NAFLD from NASH in patients with morbid obesity.
• Results suggest that ARFI can detect NASH in asymptomatic morbidly obese patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E et al (2004) Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 292:1724–1737
World Health Organization (2002) World health report 2002. Available via http://www.iotf.org. Accessed 1 Mar 2011
Must A, Spadano J, Coakley EH, Field AE, Colditz G, Dietz WH (2000) The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity. JAMA 282:1523–1529
National Task Force on the Prevention and Treatment of Obesity (2000) Overweight, obesity, and health risk. Arch Intern Med 160:898–904
McCullogh AJ et al (2005) The epidemiology and risk factors of NASH. In: Farrel GC, George J, de la PM Hall (eds) Fatty liver disease, NASH and related disorders. Blackwell, Malden, pp 23–37
Angulo P (2002) Non alcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med 346:1221–1231
Nguyen NT, Masoomi H, Laugenour K et al (2011) Predictive factors of mortality in bariatric surgery: data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample. Surgery 150:347–351
McHutchinson J, Poynard T, Afdhal N (2006) Fibrosis as an end point for clinical trials in liver disease: a report of the international fibrosis group. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 4:1214–1220
Guzmán-Aroca F, Reus M, Berná-Serna JD et al (2011) Reproducibility of shear-wave velocity measurements by acoustic radiation force impulse imaging in liver: a study in healthy volunteers. J Ultrasound Med 30:975–979
Sirli R, Sporea I, Tudora A, Deleanu A, Popescu A (2009) Transient elastographic evaluation of subjects without known hepatic pathology: does age change the liver stiffness? J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 18:57–60
Conference NIH (1991) Gastrointestinal surgery for severe obesity. Consensus development conference panel. Ann Intern Med 115:956–961
Babor TF, Higgins-Biddle JC, Saunders JB, Monteiro MG (2001) AUDIT. The alcohol use disorders identification test: guidelines for use in primary care, 2nd edn. WHO, Geneva
Zwiebel WJ (1995) Sonographic diagnosis of diffuse liver disease. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 16:8–15
Charatcharoenwitthaya P, Lindor KD (2007) Role of radiologic modalities in the management of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin Liver Dis 11:37–54
Mazhar SM, Shiehmorteza M, Sirlin CB (2009) Noninvasive assessment of hepatic steatosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:135–140
Frutos MD, Luján J, Hernández Q, Valero G, Parrilla P (2007) Clinical pathway for laparoscopic gastric bypass. Obes Surg 17:1584–1587
Brunt EM, Janney CG, Di Bisceglie AM, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Bacon BR (1999) Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am J Gastroenterol 94:2467–2474
Matteoni CA, Younosi ZM, Gramlich T, Bopari N, Liu YC, McCullough AJ (1999) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a spectrum of clinical and pathological severity. Gastroenterology 116:1413–1419
Cassidy FH, Yokoo T, Aganovic L et al (2009) Fatty liver disease: MR imaging techniques for the detection and quantification of liver steatosis. Radiographics 29:231–260
Vizzutti F, Arena U, Nobili V et al (2009) Non-invasive assessment of fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann Hepatol 8:89–94
Boursier J, Isselin G, Fouchard-Hubert I et al (2010) Acoustic radiation force impulse: a new ultrasonographic technology for the widespread noninvasive diagnosis of liver fibrosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22:1074–1084
Chen J, Talwalkar JA, Yin M, Glaser KJ, Sanderson SO, Ehman RL (2011) Early detection of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by using MR elastography. Radiology 259:749–756
Salameh N, Larrat B, Abarca-Quinones J et al (2009) Early detection of steatohepatitis in fatty rat liver by using MR elastography. Radiology 253:90–97
Georges PC, Hui JJ, Gombos Z et al (2007) Increased stiffness of the rat liver precedes matrix deposition: implications for fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 293:G1147–G1154
Guzmán-Aroca F, Ayala I, Serrano L et al (2010) Assessment of liver steatosis in chicken by using acoustic radiation force impulse imaging: preliminary results. Eur Radiol 10:2367–2371
Yoneda M, Suzuki K, Kato S et al (2010) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: US-based acoustic radiation force impulse elastography. Radiology 256:640–647
Regev A, Berho M, Jeffers LJ et al (2002) Sampling error and intraobserver variation in liver biopsy in patients with chronic HCV infection. Am J Gastroenterol 97:2614–2618
Castéra L, Vergniol J, Foucher J et al (2005) Prospective comparison of transient elastography, Fibrotest, APRI, and liver biopsy for the assessment of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 128:343–350
Bohte AE, van Werven JR, Bipat S, Stoker J (2011) The diagnostic accuracy of US, CT, MRI and 1H-MRS for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis compared with liver biopsy: a meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 21:87–97
van Werven JR, Marsman HA, Nederveen AJ et al (2010) Assessment of hepatic steatosis in patients undergoing liver resection: comparison of US, CT, T1-weighted dual-echo MR imaging, and point-resolved 1H MR spectroscopy. Radiology 256:159–168
van Werven JR, Schreuder TC, Aarts EO et al (2011) Hepatic steatosis in morbidly obese patients undergoing gastric bypass surgery: assessment with open-system 1H-MR spectroscopy. Am J Roentgenol 196:W736–W742
Palmeri ML, Wang MH, Rouze NC et al (2011) Noninvasive evaluation of hepatic fibrosis using acoustic radiation force-based shear stiffness in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol 55:666–672
Osaki A, Kubota T, Suda T et al (2010) Shear wave velocity is a useful marker for managing nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J Gastroenterol 16:2918–2925
Weingarten TN, Swain JM, Kendrick ML et al (2011) Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) does not increase complications after laparoscopic bariatric surgery. Obes Surg 21:1714–2170
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guzmán-Aroca, F., Frutos-Bernal, M.D., Bas, A. et al. Detection of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with morbid obesity before bariatric surgery: preliminary evaluation with acoustic radiation force impulse imaging. Eur Radiol 22, 2525–2532 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2505-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2505-3