Abstract
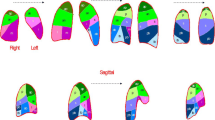
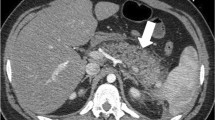
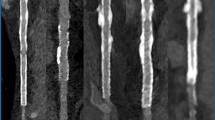
The purpose of the study was to compare the ability of dual energy CT (DECT) and perfusion scintigraphy (PS) to detect pulmonary embolism (PE) in a rabbit model. Gelfoam (n = 20) or saline (n = 4) was injected into the femoral vein of rabbits. After 2 h, DECT pulmonary angiography (CTPA) was used to create blood flow imaging (BFI) and fusion images. The rabbits then underwent PS. Pathological determination of locations and numbers of lung lobes with PE was recorded. The sensitivity and specificity for BFI, CTPA, fused images and PS were calculated using the pathological results as reference standards. Compared with pathological evaluation, CTPA correctly identified PE in 40 lobes and absence of emboli in 80 lobes, corresponding to a sensitivity and specificity of 100%. BFI and fused images correctly identified PE in 40 lobes and the absence of emboli in 78 lobes, corresponding to a sensitivity and specificity of 100% and 98%, respectively. PS correctly detected 27 lobes with PE and 65 lobes without PE, corresponding to a sensitivity and specificity of 68% and 81%, respectively. BFI, CTPA and fused images derived from a single contrast-enhanced DECT provide a higher diagnostic accuracy of detecting PE than PS in a rabbit model.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang LJ, Wang YZ, Huang W, Chen P, Zhou CS, Lu GM (2008) In vivo visualization of sinuatrial nodal artery using dual-source CT. Circ J 72:1615–1620
Lu GM, Zhang LJ, Guo H, Huang W, Merges RD (2008) Comparison of myocardial bridging by dual-source CT with conventional coronary angiography. Circ J 72:1079–1085
Brodoefel H, Burgstahler C, Tsiflikas I et al (2008) Dual-source CT: effect of heart rate, heart rate variability, and calcification on image quality and diagnostic accuracy. Radiology 247:346–355
Takahashi N, Hartman RP, Vrtiska TJ et al (2008) Dual-energy CT iodine-subtraction virtual unenhanced technique to detect urinary stones in an iodine-filled collecting system: a phantom study. Am J Roentgenol 190:1169–1173
Grosjean R, Sauer B, Guerra RM et al (2008) Characterization of human renal stones with MDCT: advantage of dual energy and limitations due to respiratory motion. AJR Am J Roentgenol 190:720–728
Boll DT, Merkle EM, Paulson EK, Fleiter TR (2008) Coronary stent patency: dual-energy multidetector CT assessment in a pilot study with anthropomorphic phantom. Radiology 247:687–695
Sun C, Miao F, Wang XM et al (2008) An initial qualitative study of dual-energy CT in the knee ligaments. Surg Radiol Anat 30:443–447
Stolzmann P, Frauenfelder T, Pfammatter T et al (2008) Endoleaks after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: detection with dual-energy dual-source CT. Radiology 249:682–691
Chandarana H, Godoy M, Vlahos I et al (2008) Abdominal aorta: evaluation with dual-source dual-energy multidetector CT after endovascular repair of aneurysms-initial observations. Radiology 249:692–700
Ruzsics B, Lee H, Zwerner PL, Gebregziabher M, Costello P, Schoepf UJ (2008) Dual-energy CT of the heart for diagnosing coronary artery stenosis and myocardial ischemia—initial experience. Eur Radiol 18:2414–2424
Chae EJ, Seo JB, Goo HW et al (2008) Xenon ventilation CT with a dual-energy technique of dual-source CT: initial experience. Radiology 248:615–624
Chae EJ, Song JW, Seo JB, Krauss B, Jang YM, Song KS (2008) Clinical utility of dual-energy CT in the evaluation of solitary pulmonary nodules: initial experience. Radiology 249:671–681
Johnson TR, Krauss B, Sedlmair M et al (2007) Material differentiation by dual energy CT: initial experience. Eur Radiol 17:1510–1517
Fink C, Johnson TR, Michaely HJ et al (2008) Dual-energy CT angiography of the lung in patients with suspected pulmonary embolism: initial results. Rofo 180:879–883
Thieme SF, Becker CR, Hacker M, Nikolaou K, Reiser MF, Johnson TR (2008) Dual energy CT for the assessment of lung perfusion—correlation to scintigraphy. Eur J Radiol 68:369–374
Pontana F, Faivre JB, Remy-Jardin M et al (2008) Lung perfusion with dual-energy multidetector-row CT (MDCT) feasibility for the evaluation of acute pulmonary embolism in 117 consecutive patients. Acad Radiol 15:1494–1504
Hoey ET, Gopalan D, Ganesh V et al (2009) Dual-energy CT pulmonary angiography: a novel technique for assessing acute and chronic pulmonary thromboembolism. Clin Radiol 64:414–419
Goldin JG, Yoon HC, Greaser LE 3rd, Nishimura EK (1998) Detection of pulmonary emboli at the segmental and subsegmental level with electron-beam CT: validation in a porcine model. Acad Radiol 5:503–508
Hurst DR, Kazerooni EA, Stafford-Johnson D et al (1999) Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: comparison of CT angiography and MR angiography in canines. J Vasc Interv Radiol 10:309–318
Stein PD, Gottschalk A (2000) Review of criteria appropriate for a very low probability of pulmonary embolism on ventilation-perfusion lung scans: a position paper. Radiographics 20:99–105
Goldhaber SZ (2004) Pulmonary embolism. Lancet 363:1295–1305
The PIOPED Investigators (1990) Value of the ventilation/perfusion scan in acute pulmonary embolism: results of the Prospective Investigation of Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosis (PIOPED). JAMA 263:2753–2759
Anderson DR, Kahn SR, Rodger MA et al (2007) Computed tomographic pulmonary angiography vs ventilation-perfusion lung scanning in patients with suspected pulmonary embolism: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 298:2743–2753
Sostman HD, Miniati M, Gottschalk A, Matta F, Stein PD, Pistolesi M (2008) Sensitivity and specificity of perfusion scintigraphy combined with chest radiography for acute pulmonary embolism in PIOPED II. J Nucl Med 49:1741–1748
Sostman HD, Stein PD, Gottschalk A, Matta F, Hull R, Goodman L (2008) Acute pulmonary embolism: sensitivity and specificity of ventilation-perfusion scintigraphy in PIOPED II study. Radiology 246:941–946
Remy-Jardin M, Pistolesi M, Goodman LR et al (2007) Management of suspected acute pulmonary embolism in the era of CT angiography: a statement from the Fleischner Society. Radiology 245:315–329
Ritchie G, McGurk S, McCreath C, Graham C, Murchison JT (2007) Prospective evaluation of unsuspected pulmonary embolism on contrast enhanced multidetector CT (MDCT) scanning. Thorax. 62:536–540
Wildberger JE, Schoepf UJ, Mahnken AH et al (2005) Approaches to CT perfusion imaging in pulmonary embolism. Semin Roentgenol 40:64–73
Zhang LJ, Zhao YE, Wu SY et al (2009) Pulmonary embolism detection with dual-energy CT: experimental study of dual-source CT in rabbits. Radiology 252:61–70
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, LJ., Chai, X., Wu, SY. et al. Detection of pulmonary embolism by dual energy CT: correlation with perfusion scintigraphy and histopathological findings in rabbits. Eur Radiol 19, 2844–2854 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-009-1518-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-009-1518-z