Abstract
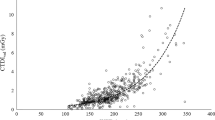
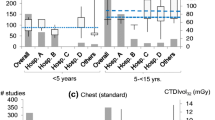
This work aimed at assessing the doses delivered in Switzerland to paediatric patients during computed tomography (CT) examinations of the brain, chest and abdomen, and at establishing diagnostic reference levels (DRLs) for various age groups. Forms were sent to the ten centres performing CT on children, addressing the demographics, the indication and the scanning parameters: number of series, kilovoltage, tube current, rotation time, reconstruction slice thickness and pitch, volume CT dose index (CTDIvol) and dose length product (DLP). Per age group, the proposed DRLs for brain, chest and abdomen are, respectively, in terms of CTDIvol: 20, 30, 40, 60 mGy; 5, 8, 10, 12 mGy; 7, 9, 13, 16 mGy; and in terms of DLP: 270, 420, 560, 1,000 mGy cm; 110, 200, 220, 460 mGy cm; 130, 300, 380, 500 mGy cm. An optimisation process should be initiated to reduce the spread in dose recorded in this study. A major element of this process should be the use of DRLs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (2000) Report to the general assembly, annex D: Medical radiation exposures. United Nations, New York
Aroua A, Vader JP, Valley JF, Verdun FR (2007) Exposure of the Swiss population by radiodiagnostics : 2003 Review. Health Phys 92:442–448
Børretzen I, Lysdahl KB, Olerud HM (2007) Diagnostic radiology in Norway—trends in examination frequency and collective effective dose. Radiat Prot Dosim 124:339–347
Aroua A, Burnand B, Decka I, Vader JP, Valley JF (2002) Nation-wide survey on radiation doses in diagnostic and interventional radiology in Switzerland in 1998. Health Phys 83:46–55
Aroua A, Decka I, Burnand B, Vader JP, Valley JF (2002) Dosimetric aspects of a national survey of diagnostic and interventional radiology in Switzerland. Medical Phys 29:2247–2259
Galanski M, Nagel HD, Stamm G (2007) Paediatric CT exposure practice in the federal republic of Germany: results of a nationwide survey in 2005-2006. Medizinische Hochschule, Hannover
Kanae N, Masaki M, Kazuo I, Takashi M (2004) Survey of CT practice in Japan and collective effective dose estimation. Nippon Acta Radiologica 64:151–158
Nationwide Evaluation of X-Ray Trends (NEXT): 2000 Survey of Computed Tomography (2006), CRCPD publication NEXT_2000CT-T
Donnelly LF, Emery KH, Brody AS, Laor T, Gylys-Morin VM, Anton CG, Thomas SR, Frush DP (2001) Minimizing radiation dose for paediatric body applications of single-detector helical CT: strategies at a large children’s hospital. AJR Am J Roentgenol 176:303–306
Cody DD, Moxley DM, Krugh KT, O’Daniel JC, Wagner LK, Eftekhari F (2004) Strategies for formulating appropriate MDCT techniques when imaging the chest, abdomen, and pelvis in pediatric patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 182:849–859
Hollingsworth C, Frush DP, Cross M, Lucaya J (2003) Helical CT of the body: a survey of techniques used for pediatric patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180:401–406
Vock P (2005) CT dose reduction in children. Eur Radiol 15:2330–2340
Boone JM, Geraghty EM, Sielbert JA, Wootton-George SL (2003) Dose reduction in pediatric CT: a rational approach. Radiology 228:352–360
Paterson A, Frush DP, Donnelly LF (2001) Helical CT of the body: are settings adjusted for pediatric patients? AJR Am J Roentgenol 176:297–301
Huda W, Lieberman KA, Chang J, Roskopf ML (2004) Patient size and x-ray technique factors in head computed tomography examinations. II. Image quality. Med Phys 31:595–601
Siegel MJ, Schmidt B, Bradley D, Suess C, Hildebolt C (2004) Radiation dose and image quality in pediatric CT: effect of technical factors and phantom size and shape. Radiology 233:515–522
Verdun FR, Lepori D, Monnin P, Valley JF, Schnyder P, Gudinchet F (2004) Management of patient dose and image noise in routine pediatric CT abdominal examinations. Eur Radiol 14:835–841
Wilting JE, Zwartkruis A, van Leeuwen MS, Timmer J, Kamphuis AG, Feldberg M (2001) A rational approach to dose reduction in CT: individualized scan protocols. Eur Radiol 11:2627–2632
Pages J, Buls N, Osteuax M (2003) CT doses in children: a multicentre study. Br J Radiol 76:803–811
Linton OA, Mettler FA (2003) National conference on dose reduction in CT with an emphasis on pediatric patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 181:321–329
Hall EJ (2002) Lessons we have learned from our children: cancer risks from diagnostic radiology. Pediatr Radiol 32:700–706
Ron E (2002) Let’s not relive the past: a review of cancer risk after diagnostic or therapeutic irradiation. Pediatric Radiology 32:739–744 discussion 751–754
Brenner DJ, Elliston CD, Hall EJ, Berdon WE (2001) Estimated risks of radiation-induced fatal cancer from paediatric CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 176:289–296
Frush DP, Donnelly LF, Rosen NS (2003) Computed tomography and radiation risks: what pediatric health care providers should know. Pediatrics 112:951–957
International Commission on Radiological Protection (1997) Radiological protection and safety in medicine. ICRP Publication 73, Pergamon, Oxford New York
Schrimpton PC, Hillier MC, Lewis MA, Dunn M (2005) Dose from CT examination in the UK–2003 review. NRPB–W67 Report. National Radiological Protection Board, Chilton
International Electrotechnical Committee (2002) Medical diagnostic X-ray equipment-Particular requirements for the safety of X-ray equipment for CT; Standard IEC #60601-2-44
Neofotistou V (2001) Review of patient dosimetry in cardiology. Radiat Prot Dosim 94:177–182
Aroua A, Besançon A, Buchillier-Decka I, Trueb P, Valley JF, Verdun FR, Zeller W (2004) Adult reference levels in diagnostic and interventional radiology for temporary use in Switzerland. Radiat Prot Dosim 111:289–295
Shrimpton PC, Wall BF (2000) Reference doses for paediatric computed tomography. Radiat Prot Dosim 90:249–252
Martin DR, Semelka RC (2006) Health effects of ionising radiation from diagnostic CT. Lancet 367:1712–1714
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the Swiss National Science Foundation (Grant no. 3200B0-105951) and are thankful to the members of SSPR, in particular: Drs G. Eich, S. Hanquinet, J.-M. Girard, A. Racle, G. Remsei, T. Schraner, P. Waibel, R. Wolf, Mme M. Wyttenbach, M. P. Brégis, and A. Devaud)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verdun, F.R., Gutierrez, D., Vader, J.P. et al. CT radiation dose in children: a survey to establish age-based diagnostic reference levels in Switzerland. Eur Radiol 18, 1980–1986 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-0963-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-0963-4