Abstract
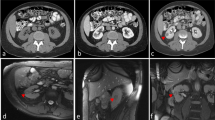
This study was conducted to test and demonstrate the feasibility of magnetic resonance (MR)-guided radiofrequency (RF) ablation of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) using a 1.5 T whole-body scanner equipped with a wide-bore superconductive magnet. Two patients with contrast-enhancing renal masses were treated with multipolar RF ablation (Celon ProSurge). Applicator navigation and near real-time ablation monitoring were performed in a wide-bore 1.5 T scanner using adapted fluoroscopic and diagnostic sequences. In addition to T2-weighted imaging for ablation monitoring, perfusion-weighted images acquired with an arterial spin-labeling technique (FAIR-TrueFISP) were applied. Results were compared to a previous study on 12 patients performed at 0.2 T. Navigation and monitoring of RF ablation using the wide-bore system operating at 1.5 T were clearly improved compared to former experiences on a 0.2 T MR unit. Fluoroscopic and diagnostic images for MR guidance could be acquired with distinctly higher image quality and shorter acquisition time resulting in higher accuracy of applicator placement and shorter treatment time. Spin-labeling perfusion imaging exhibited good image quality, potentially providing additional clinically important information. MR-guided RF ablation of RCC can safely be performed in a 1.5 T wide-bore scanner offering higher image quality, shorter acquisition time, and new monitoring modalities not feasible at 0.2 T.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lewin JS, Nour SG, Connell CF, Sulman A, Duerk JL, Resnick MI, Haaga JR (2004) Phase II clinical trial of interactive MR imaging-guided interstitial radiofrequency thermal ablation of primary kidney tumors: initial experience. Radiology 232:835–845
Boss A, Clasen S, Kuczyk M, Anastasiadis A, Schmidt D, Graf H, Schick F, Claussen CD, Pereira PL (2005) Magnetic resonance-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of renal cell carcinomas: a pilot clinical study. Invest Radiol 40(9):583–590
Farrell MA, Charboneau WJ, DiMarco DS, Chow GK, Zincke H, Callstrom MR, Lewis BD, Lee RA, Reading CC (2003) Imaging-guided radiofrequency ablation of solid renal tumors. AJR Am J Roentgenol 18:1509–1513
Mayo-Smith WW, Dupuy DE, Parikh PM, Pezzullo JA, Cronan JJ (2003) Imaging-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of solid renal masses: techniques and outcomes of 38 treatment sessions in 32 consecutive patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180(6):1503–1508
Gervais DA, Arellano RS, Mueller PR (2005) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Radiol 15(5):960–967
Mahnken AH, Günther RW, Tacke J (2004) Radiofrequency ablation of renal tumors. Eur Radiol 14(8):1449–1455
Memarsadeghi M, Schmook T, Remzi M, Weber M, Potscher G, Lammer J, Kettenbach J (2006) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of renal tumors: midterm results in 16 patients. Eur J Radiol 59:183–189
Arzola J, Baughman SM, Hernandez J, Bishoff JT (2006) Computed tomography-guided, resistance-based, percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of renal malignancies under conscious sedation at two years of follow-up. Urology 68:983–987
Veltri A, Calvo A, Tosetti I, Pagano E, Genovesio A, Virzì V, Ferrando U, Fontana D, Gandini G (2006) Experiences in US-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of 44 renal tumors in 31 patients: analysis of predictors for complications and technical success. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 29:811–818
Clark TW, Malkowicz B, Stavropoulos SW, Sanchez R, Soulen MC, Itkin M, Patel A, Mondschein JI, Wein AJ (2006) Radiofrequency ablation of small renal cell carcinomas using multitined expandable electrodes: preliminary experience. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17:513–519
Zhang Q, Chung YC, Lewin JS, Duerk JL (1998) A method for simultaneous RF ablation and MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 8:110–114
Boss A, Clasen S, Kuczyk M, Schick F, Pereira PL (2007) Image-guided radiofrequency ablation of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Radiol 17:725–733
Martirosian P, Klose U, Mader I, Schick F (2004) FAIR true-FISP perfusion imaging of the kidneys. Magn Reson Med 51:353–361
Boss A, Martirosian P, Schraml C, Clasen S, Fenchel M, Anastasiadis A, Claussen CD, Pereira PL, Schick F (2006) Morphological, contrast-enhanced and spin labeling perfusion imaging for monitoring of relapse after RF ablation of renal cell carcinomas. Eur Radiol 16:1226–1236
Clasen S, Schmidt D, Boss A, Dietz K, Krober SM, Claussen CD, Pereira PL (2006) Multipolar radiofrequency ablation with internally cooled electrodes: experimental study in ex vivo bovine liver with mathematic modeling. Radiology 238:881–890
Terraz S, Constantin C, Majno PE, Spahr L, Mentha G, Becker CD (2007) Image-guided multipolar radiofrequency ablation of liver tumours: initial clinical results. Eur Radiol 17:2253–2261
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boss, A., Rempp, H., Martirosian, P. et al. Wide-bore 1.5 Tesla MR imagers for guidance and monitoring of radiofrequency ablation of renal cell carcinoma: initial experience on feasibility. Eur Radiol 18, 1449–1455 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-0894-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-0894-0