Abstract
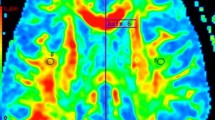
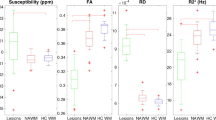
Fifteen multiple sclerosis patients were examined by diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to determine fractional anisotropy (FA) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) in a superventricular volume of interest of 8×8×2 cm3 containing gray matter (GM) and white matter (WM) tissue. Point resolved spectroscopy 2D-chemical shift imaging of the same volume was performed without water suppression. The water contents and DTI parameters in 64 voxels of 2 cm3 were compared. The water content was increased in patients compared with controls (GM: 244±21 vs. 194±10 a.u.; WM: 245±32 vs. 190±11 a.u.), FA decreased (GM: 0.226±0.038 vs. 0.270±0.020; WM: 0.337±0.044 vs. 0.402±0.011) and ADC increased [GM: 1134±203 vs. 899±28 (×10−6 mm2/s); WM: 901±138 vs. 751±17 (×10−6 mm2/s)]. Correlations of water content with FA and ADC in WM were strong (r=−0.68, P<0.02; r=0.75; P<0.01, respectively); those in GM were weaker (r=−0.50, P<0.05; r=0.45, P<0.1, respectively). Likewise, FA and ADC were more strongly correlated in WM (r=−0.88; P<0.00001) than in GM (r=−0.69, P<0.01). The demonstrated relationship between DTI parameters and water content in multiple sclerosis patients suggests a potential for therapy monitoring in normal-appearing brain tissue.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basser PJ, Mattiello J, Le Bihan D (1994) Estimation of the effective self-diffusion tensor from the NMR spin echo. J Magn Reson B 103:247–254
Mori S, van Zijl PCM (2002) Fibre tracking: principles and strategies-a technical review. NMR Biomed 15:468–480
Terajima K, Nakada T (2002) EZ-tracing: a new ready-to-use algorithm for magnetic resonance tractography. J Neurosci Methods 116:147–155
Eichler FS, Itoh R, Barker PB, Mori S, Garrett ES, van Zijl PC, Moser HW, Raymond GV, Melhem ER (2002) Proton MR spectroscopic and diffusion tensor brain MR imaging in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: initial experience. Radiology 225:245–252
Clark C, Werring D, Miller D (2000) Diffusion imaging of the spinal cord in vivo: estimation of the principal diffusion and application to multiple sclerosis. Magn Reson Med 43:133–138
De Stefano N, Iannucci G, Sormani MP, Guidi L, Bartelozzi ML, Comi G, Federico A, Filippi M (2002) MR correlates of cerebral atrophy in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 249:1072–1077
Ciccarelli O, Werring DJ, Barker GJ, Griffin CM, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Miller DH, Thompson AJ (2003) A study of the mechanisms of normal-appearing white matter damage in multiple sclerosis using diffusion tensor imaging-evidence of Wallerian degeneration. J Neurol 250:287–292
Oh J, Henry RG, Genain C, Nelson SJ, Pelletier D (2004) Mechanisms of normal appearing injury related to pericallosal T1 lesions in multiple sclerosis using directional diffusion tensor and H-1 MRS imaging. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:1281–1286
Sijens PE, Irwan R, Potze JH, Mostert JP, De Keyser J, Oudkerk M (2005) Analysis of the human brain in primary progressive multiple sclerosis with mapping of the spatial distributions using 1H MR spectroscopy and diffusion tensor imaging. Eur Radiol. Aug;15(8):1686–1693. Epub2005 Apr22. PMID: 15846494 [PubMed-in process]
Laule C, Vavasour IM, Moore GRW, Oger J, Li DKB, Paty DW, MacKay AL (2004) Water content and myelin water fraction in multiple sclerosis; a T1 relaxation study. J Neurol 251: 284–293
Tourtellotte W, Parker J (1968) Some spaces and barriers in postmortem multiple sclerosis. Prog Brain Res 29:493–525
Sappey-Marinier D (1990) High-resolution NMR spectroscopy of cerebral white matter in multiple sclerosis. Magn Reson Med 15:229–239
McDonald WI, Compston A, Edan G, Goodkin D, Hartung H-P, Lublin FD, McFarland HF, Paty DW, Polman CH, Reingold SC, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Sibley W, Thompson A, Van Den Noort S, Weinshenker BY, Wolinsky JS (2001) Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines from the international panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 50:121–127
Miller DH, Barkhof F, Frank JA, Parker GJM, Thompson AJ (2002) Measurement of atrophy in multiple sclerosis; pathological basis, methodological aspects and clinical relevance. Brain 125:1676–1695
Sijens PE, Mostert JP, Oudkerk M, De Keyser J (2005) 1H MR Spectroscopy of the brain in multiple sclerosis subtypes with analysis of the metabolite concentrations in gray and white matter: initial findings. Eur Radiol Jul 19; [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 16028056 [PubMed-as supplied by publisher]
Irwan R, Sijens PE, Potze JH, Oudkerk M (2005) Correlation of MR spectroscopy and diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 23:851–858
Irwan R, Sijens PE, Kappert P, Oudkerk M. Phase correction for eight-channel head coil in MR spectroscopy. In: Proceedings ISMRM Twelfth Scientific Meeting and Exhibition 2004
Sijens PE, van den Bent MJ, Nowak PJCM, van Dijk P, Oudkerk M (1997) Chemical shift imaging reveals loss of brain tumor choline signal after administration of Gd-contrast agent. Magn Reson Med 37:222–225
Spiegel MR (1961) Theory and problems of statistics. Schaum's Outline Series. McGraw-Hill, New York, 359 pp. ISBN: 0070602344
Papanikolaou N, Papadiki E, Karampekios S, Spilioti M, Maris T, Prassopoulos P, Gourtsoyiannis N (2004) T2 relaxation time analysis in patients with multiple sclerosis: correlation with magnetization transfer ratio. Eur Radiol 4:115–122
Helms G, Piringer A (2001) Magntization transfer of water T2 relaxation components in human brain: implications for T2 based segmentation of spectroscopic volumes. Magn Reson Imaging 19:803–811
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sijens, P.E., Irwan, R., Potze, J.H. et al. Relationships between brain water content and diffusion tensor imaging parameters (apparent diffusion coefficient and fractional anisotropy) in multiple sclerosis. Eur Radiol 16, 898–904 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-0033-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-0033-0