Abstract.
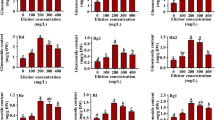
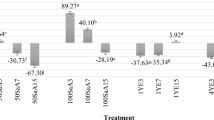
This study was initiated to investigate the impacts of elicitor concentration and elicitor-adding time on the saponin synthesis and the cell growth of Panax ginseng cell suspensions. Both of the elicitors tested, yeast extract and methyl jasmonate, significantly improved saponin production. The highest additive level of the seven ginsenosides tested was 2.07% (dry weight basis), which was 28-fold higher than that in the control. The optimum time to add either elicitor was found to be on the day of inoculation. The addition of either elicitor did not show as significant an influence on cell growth as on saponin production. It was advisable to remove 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) from the medium when methyl jasmonate was used as the elicitor as methyl jasmonate interacts antagonistically with 2,4-D. These results suggest that the addition of an elicitor to ginseng cell suspension cultures could stimulate saponin production.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Revision received: 13 June 2001
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, M., Wong, H. & Teng, W. Effects of elicitation on the production of saponin in cell culture of Panax ginseng . Plant Cell Rep 20, 674–677 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990100378
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990100378