Abstract
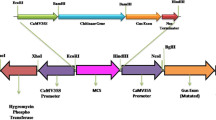
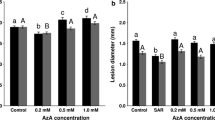
Transgenic tobacco plants producing chloroperoxidase (CPO-P), encoded by a novel gene from Pseudomonas pyrrocinia, were obtained by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Successful transformation was shown by PCR, Southern, northern and western blot analyses, and assays of CPO-P enzyme activity. Extracts from plants transformed with the CPO-P gene significantly reduced Aspergillus flavus colonies by up to 100% compared with extracts from control plants transformed with pBI121. Compared with controls, the transformed plants showed increased disease resistance in planta against a fungal pathogen, Colletotrichum destructivum, the causal agent of tobacco anthracnose.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 March 1999 / Revision received: 22 June 1999 · Accepted: 5 July 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajasekaran, K., Cary, J., Jacks, T. et al. Inhibition of fungal growth in planta and in vitro by transgenic tobacco expressing a bacterial nonheme chloroperoxidase gene. Plant Cell Reports 19, 333–338 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050736
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050736