Abstract
Key message
Insertion of a solo LTR, which possesses strong bidirectional, stem-specific promoter activities, is associated with the evolution of a dwarfing apple spur mutation.
Abstract
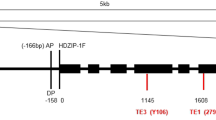
Spur mutations in apple scions revolutionized global apple production. Since long terminal repeat (LTR) retrotransposons are tightly related to natural mutations, inter-retrotransposon-amplified polymorphism technique and genome walking were used to find sequences in the apple genome based on these LTRs. In ‘Red Delicious’ spur mutants, a novel, 2190-bp insertion was identified as a spur-specific, solo LTR (sLTR) located at the 1038th nucleotide of another sLTR, which was 1536 bp in length. This insertion-within-an-insertion was localized within a preexisting Gypsy-50 retrotransposon at position 3,762,767 on chromosome 4. The analysis of transcriptional activity of the two sLTRs (the 2190- and 1536-bp inserts) indicated that the 2190-bp sLTR is a promoter, capable of bidirectional transcription. GUS expression in the 2190-bp-sense and 2190-bp-antisense transgenic lines was prominent in stems. In contrast, no promoter activity from either the sense or the antisense strand of the 1536-bp sLTR was detected. From ~150 kb of DNA on each side of the 2190 bp, sLTR insertion site, corresponding to 300 kb of the ‘Golden Delicious’ genome, 23 genes were predicted. Ten genes had predicted functions that could affect shoot development. This first report, of a sLTR insertion associated with the evolution of apple spur mutation, will facilitate apple breeding, cloning of spur-related genes, and discovery of mechanisms behind dwarf habit.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACX1:
-
Acyl-coenzyme A oxidase 1
- ACO:
-
1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase
- CIPK:
-
CBL-interacting protein kinase
- ERF:
-
Ethylene-responsive transcription factor
- IRAP:
-
Inter-retrotransposon amplified polymorphism
- LTR:
-
Long terminal repeat
- LRNs:
-
LTR retrotransposons
- ORFs:
-
Open reading frames
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- IPCR:
-
Reverse PCR
- S-SAP:
-
Sequence-specific amplification polymorphism
- sLTR:
-
Solo LTR
- TAIL-PCR:
-
Thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR
References
Barkan A, Small I (2014) Pentatricopeptide repeat proteins in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 65:415–442. doi:10.1146/annurev-arplant-050213-040159
Burge C, Karlin S (1997) Prediction of complete gene structures in human genomic DNA. J Mol Biol 268:78–94
Butelli E, Licciardello C, Zhang Y et al (2012) Retrotransposons control fruit-specific, cold-dependent accumulation of anthocyanins in blood oranges. Plant Cell 24:1242–1255. doi:10.1105/tpc.111.095232
Chagné D, Lin-Wang K, Espley RV et al (2013) An ancient duplication of apple MYB transcription factors is responsible for novel red fruit-flesh phenotypes. Plant Physiol 161:225–239. doi:10.1104/pp.112.206771
Cui L, Feng K, Wang M et al (2016) Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of AP2/ERF transcription factors family in Brachypodium distachyon. BMC Genomics 17:636. doi:10.1186/s12864-016-2968-8
Grandbastien MA (1998) Activation of plant retrotransposons under stress conditions. Trends Plant Sci 3:181–187. doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(98)01232-1
Grandbastien MA (2015) LTR retrotransposons, handy hitchhikers of plant regulation and stress response. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 1849:403–416. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.07.017
Guo M, Thomas J, Collins G, Timmermans MCP (2008) Direct repression of KNOX loci by the ASYMMETRIC LEAVES1 complex of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20:48–58. doi:10.1105/tpc.107.056127
Harrison N, Harrison RJ, Barber-perez N et al (2016) A new three-locus model for rootstock-induced dwarfing in apple revealed by genetic mapping of root bark percentage. J Exp Bot 67:1871–1881. doi:10.1093/jxb/erw001
Hashimoto K, Kudla J (2011) Calcium decoding mechanisms in plants. Biochimie 93:2054–2059. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2011.05.019
Hayashi K, Yoshida H (2009) Refunctionalization of the ancient rice blast disease resistance gene Pit by the recruitment of a retrotransposon as a promoter. Plant J 57:413–425. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03694.x
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907. doi:10.1073/pnas.1411926112
Kahyo T, Tao H, Shinmura K et al (2013) Identification and association study with lung cancer for novel insertion polymorphisms of human endogenous retrovirus. Carcinogenesis 34:2531–2538. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgt253
Kashkush K, Khasdan V (2007) Large-scale survey of cytosine methylation of retrotransposons and the impact of readout transcription from long terminal repeats on expression of adjacent rice genes. Genetics 177:1975–1985. doi:10.1534/genetics.107.080234
Kereszt A, Li D, Indrasumunar A et al (2007) Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transformation of soybean to study root biology. Nat Protoc 2:948–952. doi:10.1038/nprot.2007.141
Kohany O, Gentles AJ, Hankus L, Jurka J (2006) Annotation, submission and screening of repetitive elements in Repbase: RepbaseSubmitter and Censor. BMC Bioinform 7:474. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-7-474
Koo AJK, Hoo SC, Kobayashi Y, Howe GA (2006) Identification of a peroxisomal acyl-activating enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of jasmonic acid in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 281:33511–33520. doi:10.1074/jbc.M607854200
Lamesch P, Berardini TZ, Li D et al (2012) The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): improved gene annotation and new tools. Nucleic Acids Res 40:1202–1210. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr1090
Liu YG, Mitsukawa N, Whittier RF (1995) Efficient isolation and map-ping of Arabidopsis thaliana T-DNA insert junctions by thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR. Plant J 8:457–463
Lu QN, Jia DX (1999) Malus Mill Flora, China fruit-plant monographs. China Agricultural Science and Technology Publishing House, China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing
Malumbres M, Manning G, Whyte D et al (2014) Cyclin-dependent kinases. Genome Biol 15:122. doi:10.1186/gb4184
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8(19):4321–4325
Otto D, Petersen R, Brauksiepe B et al (2014) The columnar mutation (“Co gene”) of apple (Malus × domestica) is associated with an integration of a Gypsy-like retrotransposon. Mol Breed 33:863–880. doi:10.1007/s11032-013-0001-3
Oyama RK, Silber MV, Renner SS (2010) A specific insertion of a solo-LTR characterizes the Y-chromosome of Bryonia dioica (Cucurbitaceae). BMC Res Notes 3:166. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-3-166
Pan Y, Bo K, Cheng Z, Weng Y (2015) The loss-of-function GLABROUS 3 mutation in cucumber is due to LTR-retrotransposon insertion in a class IV HD-ZIP transcription factor gene CsGL3 that is epistatic over. BMC Plant Biol 15:302. doi:10.1186/s12870-015-0693-0
Petersen R, Krost C (2013) Tracing a key player in the regulation of plant architecture: the columnar growth habit of apple trees (Malus × domestica). Planta 238:1–22
Qi W, Sun F, Wang Q et al (2011) Rice ethylene-response AP2/ERF factor OsEATB restricts internode elongation by down-regulating a gibberellin biosynthetic gene. Plant Physiol 157:216–228. doi:10.1104/pp.111.179945
Ren H, Gray WM (2015) SAUR proteins as effectors of hormonal and environmental signals in plant growth. Mol Plant 8:1153–1164. doi:10.1016/j.molp.2015.05.003
Ruduś I, Sasiak M, Kepczyński J (2013) Regulation of ethylene biosynthesis at the level of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase (ACO) gene. Acta Physiol Plant 35:295–307. doi:10.1007/s11738-012-1096-6
Schilmiller AL, Koo AJK, Howe GA (2007) Functional diversification of acyl-coenzyme A oxidases in jasmonic acid biosynthesis and action. Plant Physiol 143:812–824. doi:10.1104/pp.106.092916
Studer A, Zhao Q, Ross-Ibarra J, Doebley J (2011) Identification of a functional transposon insertion in the maize domestication gene tb1. Nat Genet 43:1160–1163. doi:10.1038/ng.942
Sun J, Fang JG, Wang F et al (2010a) Characterisation of RNaseH-LTR sections of Ty1-copia retrotransposons in apple and fingerprinting of four apple clones by S-SAP analysis. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 85:53–58. doi:10.1080/14620316.2010.11512630
Sun J, Zhou J, Sun Q, Wang K (2010b) IRAP identification of apple red delicious and Fuji bud sport clones. Acta Bot Boreal Occident 10:1952–1958
Światek A, Azmi A, Stals H et al (2004) Jasmonic acid prevents the accumulation of cyclin B1;1 and CDK-B in synchronized tobacco BY-2 cells. FEBS Lett 572:118–122. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.07.018
Tustin DS, Gardiner SE, Foster TM et al (2015) Two quantitative trait loci, Dw1 and Dw2, are primarily responsible for rootstock-induced dwarfing in apple. Hortic Res 2:15001. doi:10.1038/hortres.2015.1
Velasco R, Zharkikh A, Affourtit J et al (2010) The genome of the domesticated apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.). Nat Genet 42:833–839. doi:10.1038/ng.654
Vitte C, Panaud O (2003) Formation of solo-LTRs through unequal homologous recombination counterbalances amplifications of LTR retrotransposons in rice Oryza sativa L. Mol Biol Evol 20:528–540. doi:10.1093/molbev/msg055
Yan F, Hu G, Ren Z et al (2015) Ectopic expression a tomato KNOX Gene Tkn4 affects the formation and the differentiation of meristems and vasculature. Plant Mol Biol 89:589–605. doi:10.1007/s11103-015-0387-x
Yang C-Q, Fang X, Wu X-M et al (2012) Transcriptional regulation of plant secondary metabolism. J Integr Plant Biol 54:703–712. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7909.2012.01161.x
Zhang L, Mao D, Xing F et al (2015) Loss of function of OsMADS3 via the insertion of a novel retrotransposon leads to recessive male sterility in rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Sci 238:188–197. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.06.007
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by two Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the State National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31372043 and 31071776).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Dr. Prakash P. Kumar.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
299_2017_2160_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary material 1 (PDF 105 kb) The schematic of IRAP and genome walking in ‘Red Delicious’ and its two spur mutants, ‘Chinese Marshal 1’ and ‘Oregon spur Delicious’. Red box represents Fragment-1 from the two spur mutants amplified using IRAP technique. Green box represents Sequence-2 from the two spur mutants amplified using TAIL-PCR technique. Yellow box represents Sequence-3 amplified from the two spur mutants using IPCR. The primers LP-1 and LP-2 were designed based on the sequence of the apple genome to amplify the sequence flanking Sequence-1, 2 and 3
299_2017_2160_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Supplementary material 2 (PDF 65 kb) The target site duplication (TSD, red) and inverted repeat (IR, italics) of the 1536-bp sLTR insertion (green) are shown. The TSD and IR of the 2190-bp sLTR insertion (yellow) are boxed and underlined, respectively. The TSD and IR of Gypsy-50 are indicated in red and double underlined. LTRs of Gypsy-50 are indicated in blue. The two ‘CGGGG’ sites are shaded in blue
299_2017_2160_MOESM3_ESM.png
Supplementary material 3 (PNG 4740 kb) The alignment of the 122 LTR-like copies found in apple using the 2190-bp fragment, ranging in size from 1777-bp to 2190-bp
299_2017_2160_MOESM4_ESM.pdf
Supplementary material 4 (PDF 86 kb) Primers used for overlapped amplification of products of PL-1 and PL-2, amplified by primers LP-1 and LP-2
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, M., Sun, Q., Zhou, J. et al. Insertion of a solo LTR retrotransposon associates with spur mutations in ‘Red Delicious’ apple (Malus × domestica). Plant Cell Rep 36, 1375–1385 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-017-2160-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-017-2160-x