Abstract
Key message
Cell growth medium composition has profound impacts on the O -glycosylation of a “designer” arabinogalactan protein-based module; full glycosylation is essential in directing efficient extracellular secretion of the tagged recombinant protein.
Abstract
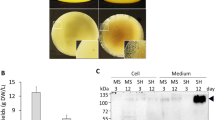
Expression of recombinant proteins in plant cells as fusion with a de novo designed hydroxyproline (Hyp)-O-glycosylated peptide (HypGP) tag, termed HypGP engineering technology, resulted in dramatically increased secreted protein yields. This is due to the function of the HypGP tag as a molecular carrier in promoting efficient transport of conjoined proteins into culture media. To optimize the cell culture to achieve the best secreted protein yields, the medium effects on the cell growth and protein secretion were investigated using as a model system the tobacco BY-2 cell expressing enhanced green fluorescence protein (EGFP) fused with a (SP)32 tag (32 tandem repeats of “Ser-Pro” motif). The (SP)32 tag was found to undergo two-stage Hyp-O-glycosylation in plant cells with the dramatic secretion of the conjoined EGFP correlating with the triggering of the second-stage glycosylation. The BY-2 cell culture in SH medium generated a high secreted protein yield (125 mg/L) with a low cell biomass accumulation (~7.5 gDW/L). In contrast, very low secreted protein yields (~1.5 mg/L) with a high cell biomass accumulation (13.5 gDW/L) were obtained in MS medium. The macronutrients, specifically, the nitrogen supply greatly impacted the glycosylation of the (SP)32 tag and subsequent protein secretion. Modified MS medium with reduced nitrogen levels boosted the secreted EGFP yields to 168 mg/L. This study demonstrates the profound impacts of medium composition on the secreted yields of a HypGP-tagged protein, and provides a basis for medium design to achieve the highest productivity of the HypGP engineering technology.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
An G (1985) High efficiency transformation of cultured tobacco cells. Plant Physiol 79:568–570
De Loose M, Gheysen G, Tire C, Gielen J, Villarroel R, Genetello C, Van Montagu M, Depicker A, Inze D (1991) The extensin signal peptide allows secretion of a heterologous protein from protoplasts. Gene 99:95–100
Dolan MC, Wu D, Cramer CL, Xu J (2014) Hydroxyproline-O-glycosylated peptide tags enhance recombinant protein yields in tobacco transient expression. Process Biochem 29:490–495
Doran PM (2000) Foreign protein production in plant tissue cultures. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11:199–204
Dunstan DI, Short KC (1977) Improved growth of tissue cultures of the onion, Allium cepa. Physiol Plant 41:70–72
Fischer R, Vasilev N, Twyman RM, Schillberg S (2015) High-value products from plants: the challenges of process optimization. Curr Opin Biotechnol 32:156–162
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima O (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cell. Exp Cell Res 50:151
Grimes HD, Hodges TK (1990) The inorganic NO3 –/NH4 + ratio influences plant regeneration and auxin sensitivity in primary callus derived from immature embryos of indica rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Plant Physiol 136:362–367
Hakkinen ST, Raven N, Henquet M, Laukkanen ML, Anderlei T, Pitkanen JP, Twyman RM, Bosch D, Oksman-Caldentey KM, Schillberg S, Ritala A (2014) Molecular farming in tobacco hairy roots by triggering the secretion of a pharmaceutical antibody. Biotechnol Bioeng 111:336–346
Hellwig S, Drossard J, Twyman RM, Fischer R (2004) Plant cell cultures for the production of recombinant proteins. Nat Biotechnol 22:1415–1422
Hijazi M, Velasquez SM, Jamet E, Estevez JM, Albenne C (2014) An update on post-translational modifications of hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins: toward a model highlighting their contribution to plant cell wall architecture. Front Plant Sci 5:395
Holland T, Sack M, Rademacher T, Schmale K, Altmann F, Stadlmann J, Fischer R, Hellwig S (2010) Optimal nitrogen supply as a key to increased and sustained production of a monoclonal full-size antibody in BY-2 suspension culture. Biotechnol Bioeng 107:278–289
Huang TK, McDonald KA (2009) Bioreactor engineering for recombinant protein production in plant cell suspension cultures. Biochem Eng J 45:168–184
Kieliszewski MJ, Shpak E (2001) Synthetic genes for the elucidation of glycosylation codes for arabinogalactan-proteins and other hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins. Cell Mol Life Sci 58:1386–1398
Kieliszewski MJ, Xu J, Meyer G (2015) Nucleic acid for plant expression of a fusion protein comprising hydroxyproline O-glycosylation glycomodule. United States Patent. No. 9006410
Mayo KJ, Gonzales BJ, Mason HS (2006) Genetic transformation of tobacco NT1 cells with Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Nat Protoc 1:1105–1111
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio-assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Santos RB, Abranches R, Fischer R, Sack M, Holland T (2016) Putting the spotlight back on plant suspension cultures. Front Plant Sci 7:297
Schenk RU, Hildebrandt AC (1972) Medium and techniques for induction and growth of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plant cell cultures. Can J Bot 50:199–204
Schillberg S, Raven N, Fischer R, Twyman RM, Schiermeyer A (2013) Molecular farming of pharmaceutical proteins using plant suspension cell and tissue cultures. Curr Pharm Des 19:5531–5542
Shpak E, Leykam JF, Kieliszewski MJ (1999) Synthetic genes for glycoprotein design and the elucidation of hydroxyproline-O-glycosylation codes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:14736–14741
Su WW, Lee KT (2007) Plant cell and hairy-root cultures-process characteristics, products, and application. In: Yang ST (ed) Bioprocessing for value-added products from renewable resources. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 263–292
Tekoah Y, Shulman A, Kizhner T, Ruderfer I, Fux L, Nataf Y, Bartfeld D, Ariel T, Gingis-Velitski S, Hanania U, Shaaltiel Y (2015) Large-scale production of pharmaceutical proteins in plant cell culture-the protalix experience. Plant Biotechnol J 13:1199–1208
Tsoi BM, Doran PM (2002) Effect of medium properties and additives on antibody stability and accumulation in suspended plant cell cultures. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 35:171–180
Ullisch DA, Muller CA, Maibaum S, Kirchhoff J, Schiermeyer A, Schillberg S, Roberts JL, Treffenfeldt W, Buchs J (2012) Comprehensive characterization of two different Nicotiana tabacum cell lines leads to doubled GFP and HA protein production by media optimization. J Biosci Bioeng 113:242–248
Wilson SA, Roberts SC (2012) Recent advances towards development and commercialization of plant cell culture processes for the synthesis of biomolecules. Plant Biotechnol J 10:249–268
Xu J, Zhang N (2014) On the way to commercializing plant cell culture platform for biopharmaceuticals: present status and prospect. Pharm Bioprocess 2:499–518
Xu J, Tan L, Goodrum KJ, Kieliszewski MJ (2007) High-yields and extended serum half-life of human interferon alpha2b expressed in tobacco cells as arabinogalactan-protein fusions. Biotechnol Bioeng 97:997–1008
Xu J, Tan L, Lamport DTA, Showalter AM, Kieliszewski MJ (2008) The O-Hyp glycosylation code in tobacco and Arabidopsis and a proposed role of Hyp-glycans in secretion. Phytochemistry 69:1631–1640
Xu J, Okada S, Tan L, Goodrum KJ, Kopchick JJ, Kieliszewski MJ (2010) Human growth hormone expressed in tobacco cells as an arabinogalactan-protein fusion glycoprotein has a prolonged serum life. Transgenic Res 19:849–867
Xu J, Ge X, Dolan MC (2011) Towards high-yield production of pharmaceutical proteins with plant cell suspension cultures. Biotechnol Adv 29:278–299
Zhang N, Gonzalez M, Savary B, Xu J (2016) High-yield secretion of recombinant proteins expressed in tobacco cell culture with a designer glycopeptide tag: Process development. Biotechnol J 11:497–506
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Science Foundation under Grant No. 1605564, and the Arkansas Biosciences Institute, the major research component of the Arkansas Tobacco Settlement Proceeds Act of 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by B. Li.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, N., Dolan, M., Wu, D. et al. Dramatic secretion of recombinant protein expressed in tobacco cells with a designer glycopeptide tag is highly impacted by medium composition. Plant Cell Rep 35, 2513–2522 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-016-2051-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-016-2051-6