Abstract
Key message
Marker-free transgenic plants can be generated with high efficiency by using the Cre/ lox P self-excision system controlled by the pollen- and embryo-specific Arabidopsis DLL promoter.
Abstract
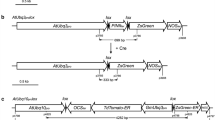
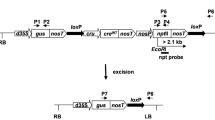
In this work, we aimed to study the feasibility of using the pollen- and embryo-specific DLL promoter of the At4g16160 gene from Arabidopsis thaliana in a Cre/loxP self-excision strategy. A Cre/loxP self-excision cassette controlled by the DLL promoter was introduced into the tobacco genome via Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. No evidence for premature activation of the Cre/loxP system was observed in primary transformants. The efficiency of nptII removal during pollen and embryo development was investigated in transgenic T1 progenies derived from eight self- and four cross-pollinated T0 lines, respectively. Segregation and rooting assays were performed to select recombined T1 plants. Molecular analyses of these plants confirmed the excision event in all analysed T0 lines and marker-free transgenic T1 plants were obtained with efficiency of up to 96.2 %. The Arabidopsis DLL promoter appears to be a strong candidate to drive Cre-mediated recombination not only in tobacco as a model plant, but also in other plant species.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai X, Wang Q, Chu C (2008) Excision of a selective marker in transgenic rice using a novel Cre/loxP system controlled by a floral specific promoter. Transgenic Res 17:1035–1043
Boszorádová E, Libantová J, Matušíková I, Moravčíková J (2014) Application of Arabidopsis tissue-specific CRUC promoter in the Cre/loxP self-excision strategy for generation of marker-free oilseed rape: potential advantages and drawbacks. Acta Physiol Plant 36:1399–1409
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chakraborti D, Sarkar A, Mondal HA, Schuermann D, Hohn B, Sarmah BK, Das S (2008) Cre/lox system to develop selectable marker-free transgenic tobacco plants conferring resistance against sap sucking homopteran insect. Plant Cell Rep 27:1623–1633
Chen J, Greenblatt IM, Dellaporta SL (1992) Molecular analysis of Ac transposition and DNA-replication. Genetics 130:665–676
Chong-Perez B, Reyes M, Rojas L, Ocana B, Ramos A, Kosky RG, Angenon G (2013) Excision of a selectable marker gene in transgenic banana using a Cre/lox system controlled by an embryo specific promoter. Plant Mol Biol 83:143–152
Coppoolse ER, de Vroomen MJ, Roelofs D, Smit J, van Gennip F, Hersmus BJM, Nijkamp HJJ, van Haaren MJJ (2003) Cre recombinase expression can result in phenotypic aberrations in plants. Plant Mol Biol 51:263–279
Costa-Font M, Gil JM, Traill WB (2008) Consumer acceptance, valuation of and attitudes towards genetically modified food: review and implications for food policy. Food Policy 33:99–111
Cuellar W, Gaudin A, Solorzano D, Casas A, Nopo L, Chudalayandi P, Medrano G, Kreuze J, Ghislain M (2006) Self-excision of the antibiotic resistance gene nptII using a heat inducible Cre–loxP system from transgenic potato. Plant Mol Biol 62:71–82
Dale EC, Ow DW (1991) Gene-transfer with subsequent removal of the selection gene from the host genome. P Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10558–10562
Drea SC, Lao NT, Wolfe KH, Kavanagh TA (2006) Gene duplication, exon gain and neofunctionalization of OEP16-related genes in land plants. Plant J 46:723–735
García-Almodóvar R, Petri C, Padilla I, Burgos L (2014) Combination of site-specific recombination and a conditional selective marker gene allows for the production of marker-free tobacco plants. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 116:205–215
Gidoni D, Srivastava V, Carmi N (2008) Site-specific excisional recombination strategies for elimination of undesirable transgenes from crop plants. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 44:457–467
Gilbertson L (2003) Cre–lox recombination: cre-active tools for plant biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 21:550–555
Hoa TTC, Bong BB, Huq E, Hodges TK (2002) Cre/lox site-specific recombination controls the excision of a transgene from the rice genome. Theor Appl Genet 104:518–525
Honys D, Twell D (2004) Transcriptome analysis of haploid male gametophyte development in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol 5:R85
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) Gus fusions—beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher-plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Jopcik M, Bauer M, Moravcikova J, Boszoradova E, Matusikova I, Libantova J (2013) Plant tissue-specific promoters can drive gene expression in Escherichia coli. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 113:387–396
Jopcik M, Moravcikova J, Matusikova I, Libantova J (2014) Spacer length-dependent protection of specific activity of pollen and/or embryo promoters from influence of CaMV 35S promoter/enhancer in transgenic plants. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 118:507–518
Kopertekh L, Schiemann J (2005) Agroinfiltration as a tool for transient expression of cre recombinase in vivo. Transgenic Res 14:793–798
Kopertekh L, Broer I, Schiemann J (2009) Developmentally regulated site-specific marker gene excision in transgenic B. napus plants. Plant Cell Rep 28:1075–1083
Kopertekh L, Saint Paul V, Krebs E, Schiemann J (2012) Utilization of PVX-Cre expression vector in potato. Transgenic Res 21:645–654
Li Z, Xing A, Moon BP, Burgoyne SA, Guida AD, Liang H, Lee C, Caster CS, Barton JE, Klein TM, Falco SC (2007) A Cre/loxP-mediated self-activating gene excision system to produce marker gene free transgenic soybean plants. Plant Mol Biol 65:329–341
Liu HK, Yang C, Wei ZM (2005) Heat shock-regulated site-specific excision of extraneous DNA in transgenic plants. Plant Sci 168:997–1003
Luo K, Duan H, Zhao D, Zheng X, Deng W, Chen Y, Stewart CN Jr, McAvoy R, Jiang X, Wu Y, He A, Pei Y, Li Y (2007) GM-gene-deletor: fused loxP-FRT recognition sequences dramatically improve the efficiency of FLP or CRE recombinase on transgene excision from pollen and seed of tobacco plants. Plant Biotech J 5:263–274
Ma BG, Duan XY, Ma CX, Niu JX, Zhang HP, Pan LZ (2008) Salicylic-acid-induced self-excision of the marker gene nptII from transgenic tomato using the Cre–loxP system. Plant Mol Biol Rep 26:199–212
Ma BG, Duan XY, Niu JX, Ma C, Hao QN, Zhang LX, Zhang HP (2009) Expression of stilbene synthase gene in transgenic tomato using salicylic acid-inducible Cre/loxP recombination system with self-excision of selectable marker. Biotechnol Lett 31:163–169
Marjanac G, De Paepe A, Peck I, Jacobs A, De Buck S, Depicker A (2008) Evaluation of CRE-mediated excision approaches in Arabidopsis thaliana. Transgenic Res 17:239–250
Matzke AJM, Matzke MA (1998) Position effects and epigenetic silencing of plant transgenes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 1:142–148
Mlynarova L, Nap JP (2003) A self-excising Cre recombinase allows efficient recombination of multiple ectopic heterospecific lox sites in transgenic tobacco. Transgenic Res 12:45–57
Mlynarova L, Loonen A, Heldens J, Jansen RC, Keizer P, Stiekema WJ, Nap JP (1994) Reduced position effect in mature transgenic plants conferred by the chicken lysozyme matrix-associated region. Plant Cell 6:417–426
Mlynarova L, Conner AJ, Nap JP (2006) Directed microspore-specific recombination of transgenic alleles to prevent pollen-mediated transmission of transgenes. Plant Biotech J 4:445–452
Moravcikova J, Vaculkova E, Bauer M, Libantova J (2008) Feasibility of the seed specific cruciferin C promoter in the self excision Cre/loxP strategy focused on generation of marker-free transgenic plants. Theor Appl Genet 117:1325–1334
Murashige I, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Plant Physiol 15:473–497
Nicolia A, Manzo A, Veronesi F, Rosellini D (2014) An overview of the last 10 years of genetically engineered crop safety research. Crit Rev in Biotechnol 34:77–88
Odell J, Caimi P, Sauer B, Russell S (1990) Site-directed recombination in the genome of transgenic tobacco. Mol Gen Genet 223:369–378
Odell JT, Hoopes JL, Vermerris W (1994) Seed-specific gene activation mediated by the Cre/lox site-specific recombination system. Plant Physiol 106:447–458
Ow DW (2007) GM maize from site-specific recombination technology, what next? Curr Opin in Biotech 18:115–120
Petri C, Lopez-Noguera S, Wang H, Garcia-Almodovar C, Alburquerque N, Burgos L (2012) A chemical-inducible Cre–LoxP system allows for elimination of selection marker genes in transgenic apricot. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 110:337–346
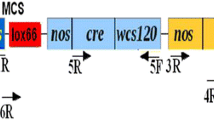
Polóniová Z, Jopčík M, Matušíková I, Libantová J, Moravčíková J (2012) Preparation of plant transformation vector containing “self-excision” Cre/loxP system. J Microbiol Biotech Food Sci 1:563–572
Roy SD, Saxena M, Bhomkar PS, Pooggin M, Hohn T, Bhalla-Sarin N (2008) Generation of marker-free salt tolerant transgenic plants of Arabidopsis thaliana using the gly I gene and cre gene under inducible promoters. Plant Cell Tiss Org 95:1–11
Russell SH, Hoopes JL, Odell JT (1992) Directed excision of a transgene from the plant genome. Mol Gen Genet 234:49–59
Scutt CP, Zubko E, Meyer P (2002) Techniques for the removal of marker genes from transgenic plants. Biochimie 84:1119–1126
Sreekala C, Wu L, Gu K, Wang D, Tian D, Yin Z (2005) Excision of a selectable marker in transgenic rice (Oryza sativa L.) using a chemically regulated Cre/loxP system. Plant Cell Rep 24:86–94
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL-W—improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Tuteja N, Verma S, Sahoo RK, Raveendar S, Reddy INBL (2012) Recent advances in development of marker-free transgenic plants: regulation and biosafety concern. Journal Biosci 37:167–197
Vaculkova E, Moravcikova J, Matusikova I, Bauer M, Libantova J (2007) A modified low copy number binary vector pUN for Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation. Biol Plantarum 51:538–540
Verweire D, Verleyen K, De Buck S, Claeys M, Angenon G (2007) Marker-free Transgenic plants through genetically programmed auto-excision. Plant Physiol 145:1220–1231
Wang Y, Chen BJ, Hu YL, Li JF, Lin ZP (2005) Inducible excision of selectable marker gene from transgenic plants by the Cre/lox site-specific recombination system. Transgen Res 14:605–614
Will E, Klump H, Heffner N, Schwieger M, Schiedlmeier B, Ostertag W, Baum C, Stocking C (2002) Unmodified Cre recombinase crosses the membrane. Nucl Acid Res 30(12):e59
Woo H-J, Suh S-C, Cho Y-G (2011) Strategies for developing marker-free transgenic plants. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 16:1053–1064
Zhang W, Subbarao S, Addae P, Shen A, Armstrong C, Peschke V, Gilbertson L (2003) Cre/lox-mediated marker gene excision in transgenic maize (Zea mays L.) plants. Theor Appl Genet 107:1157–1168
Zhang YY, Li HX, Bo OY, Lu YG, Ye ZB (2006) Chemical-induced autoexcision of selectable markers in elite tomato plants transformed with a gene conferring resistance to lepidopteran insects. Biotechnol Lett 28:1247–1253
Zhang Y, Liu H, Li B, Zhang JT, Li YZ, Zhang HX (2009) Generation of selectable marker-free transgenic tomato resistant to drought, cold and oxidative stress using the Cre/loxP DNA excision system. Transgen Res 18:607–619
Zuo JR, Niu QW, Moller SG, Chua NH (2001) Chemical-regulated, site-specific DNA excision in transgenic plants. Nat Biotechnol 19:157–161
Acknowledgments
Authors thank Anna Fábelová for in vitro plant care. Funding was supported by Scientific Grant Agency of the Ministry of Education of Slovak Republic and Slovak Academy of Sciences VEGA 2-0090-14.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Zeng-Yu Wang.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Polóniová, Z., Jopčík, M., Matušíková, I. et al. The pollen- and embryo-specific Arabidopsis DLL promoter bears good potential for application in marker-free Cre/loxP self-excision strategy. Plant Cell Rep 34, 469–481 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-014-1726-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-014-1726-0