Abstract
Key message
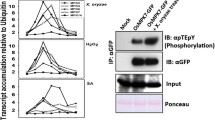
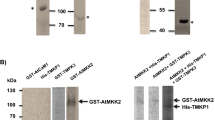
OsMPK3 is a TEY-type rice MAPK belonging to Group C and directly phosphorylates OsbHLH65 in the nucleus. OsMPK3 and OsbHLH65 are induced by biotic stress and defense-related hormones.
Abstract
Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) are involved in the majority of signaling pathways that regulate plant development and stress tolerance via the phosphorylation of target molecules. Plant MAPKs are classified into two subtypes, TEY and TDY, according to the TxY (x = E or D) motif in their activation loop, and the TDY motif is unique to plant MAPKs. In rice, 17 MAPKs have been classified into six groups. To date, the functions of many TDY-type rice MAPKs have been characterized, but little is known of the TEY-type MAPKs in Group C and their possible target substrates. In the study reported here, we determined that a TEY-type rice MAPK belonging to subgroup C, named OsMPK3, phosphorylates its substrate OsbHLH65 in the nucleus. Our electrophoresis mobility shift assay results revealed that OsbHLH65 specifically binds to the E-box cis-element, but not to the G-box. Both OsMPK3 and OsbHLH65 were induced by treatments with rice blast (Magnaporthe grisea), brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens), and defense-related hormones, such as methyl jasmonic acid and salicylic acid. Our results suggest the possibility that OsMPK3 contributes to the defense signal transduction by phosphorylating the basic helix–loop–helix transcription factor.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MAPK (MPK):
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- BPH:
-
Brown planthopper
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- CD:
-
Common docking site
- TF:
-
Transcription factor
- bHLH:
-
Basic helix–loop–helix
References
Agrawal GK, Rakwal R, Iwahashi H (2002) Isolation of novel rice (Oryza sativa L.) multiple stress responsive MAP kinase gene, OsMSRMK2, whose mRNA accumulates rapidly in response to environmental cues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 294:1009–1016
Agrawal GK, Agrawal SK, Shibato J, Iwahashi H, Rakwal R (2003) Novel rice MAP kinases OsMSRMK3 and OsWJUMK1 involved in encountering diverse environmental stresses and developmental regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 300:775–783
Atchley WR, Terhalle W, Dress A (1999) Positional dependence, cliques, and predictive motifs in the bHLH protein domain. J Mol Evol 48:501–516
Carretero-Paulet L, Galstyan A, Roig-Villanova I, Martínez-García JF, Bilbao-Castro JR, Robertson DL (2010) Genome-wide classification and evolutionary analysis of the bHLH family of transcription factors in Arabidopsis, poplar, rice, moss, and algae. Plant Physiol 153:1398–1412
Cho S, Jung K, Jeung J, Kang K, Shim K, You M, Yoo K, Ok S, Shin J (2005) Analysis of differentially expressed transcripts from planthopper-infested wild rice (Oryza minuta). Plant Cell Rep 24:59–67
Cristina MS, Petersen M, Mundy J (2010) Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:621–649
Dóczi R, Ökrész L, Romero AE, Paccanaro A, Bögre L (2012) Exploring the evolutionary path of plant MAPK networks. Trends Plant Sci 17:518–525
Fernández-Calvo P, Chini A, Fernández-Barbero G, Chico J-M, Gimenez-Ibanez S, Geerinck J, Eeckhout D, Schweizer F, Godoy M, Franco-Zorrilla JM (2011) The Arabidopsis bHLH transcription factors MYC3 and MYC4 are targets of JAZ repressors and act additively with MYC2 in the activation of jasmonate responses. Plant Cell 23:701–715
Fu S-F, Chou W-C, Huang D-D, Huang H-J (2002) Transcriptional regulation of a rice mitogen-activated protein kinase gene, OsMAPK4, in response to environmental stresses. Plant Cell Physiol 43:958–963
Gan PH, Dodds PN, Hardham AR (2012) Plant infection by biotrophic fungal and oomycete pathogens. In: Signal commun plant symbiosis. Springer, Berlin, pp 183–212
Hamel L-P, Nicole M-C, Sritubtim S, Morency M-J, Ellis M, Ehlting J, Beaudoin N, Barbazuk B, Klessig D, Lee J (2006) Ancient signals: comparative genomics of plant MAPK and MAPKK gene families. Trends Plant Sci 11:192–198
Ichimura K, Shinozaki K, Tena G, Sheen J, Henry Y, Champion A, Kreis M, Zhang S, Hirt H, Wilson C (2002) Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plants: a new nomenclature. Trends Plant Sci 7:301–308
Jeong H-J, Shin JS, Ok SH (2011) Barley DNA-binding methionine aminopeptidase, which changes the localization from the nucleus to the cytoplasm by low temperature, is involved in freezing tolerance. Plant Sci 180:53–60
Kim S-H, Oikawa T, Kyozuka J, Wong HL, Umemura K, Kishi-Kaboshi M, Takahashi A, Kawano Y, Kawasaki T, Shimamoto K (2012) The bHLH Rac immunity1 (RAI1) is activated by OsRac1 via OsMAPK3 and OsMAPK6 in rice immunity. Plant Cell Physiol 53:740–754
Li X, Duan X, Jiang H, Sun Y, Tang Y, Yuan Z, Guo J, Liang W, Chen L, Yin J (2006) Genome-wide analysis of basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 141:1167–1184
Liu Q, Xue Q (2007) Computational identification and phylogenetic analysis of the MAPK gene family in Oryza sativa. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:6–14
Miyamoto K, Shimizu T, Lin F, Sainsbury F, Thuenemann E, Lomonossoff G, Nojiri H, Yamane H, Okada K (2012) Identification of an E-box motif responsible for the expression of jasmonic acid-induced chitinase gene OsChia4a in rice. J Plant Physiol 169:621–627
Pires N, Dolan L (2010) Origin and diversification of basic-helix-loop-helix proteins in plants. Mol Biol Evol 27:862–874
Reyna NS, Yang Y (2006) Molecular analysis of the rice MAP kinase gene family in relation to Magnaporthe grisea infection. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19:530–540
Rohila JS, Yang Y (2007) Rice mitogen-activated protein kinase gene family and its role in biotic and abiotic stress response. J Integr Plant Biol 49:751–759
Sailsbery JK, Dean RA (2012) Accurate discrimination of bHLH domains in plants, animals, and fungi using biologically meaningful sites. BMC Evol Biol 12:154
Sharrocks AD, Yang S-H, Galanis A (2000) Docking domains and substrate-specificity determination for MAP kinases. Trends Biochem Sci 25:448–453
Shim K, Cho S, Jeung J, Jung K, You M, Ok S, Chung Y, Kang K, Hwang H, Choi H (2004) Identification of fungal (Magnaporthe grisea) stress-induced genes in wild rice (Oryza minuta). Plant Cell Rep 22:599–607
Singh R, Lee M-O, Lee J-E, Choi J, Park JH, Kim EH, Yoo RH, Cho J-I, Jeon J-S, Rakwal R (2012) Rice mitogen-activated protein kinase interactome analysis using the yeast two-hybrid system. Plant Physiol 160:477–487
Song F, Goodman RM (2002) OsBIMK1, a rice MAP kinase gene involved in disease resistance responses. Planta 215:997–1005
Song D, Chen J, Song F, Zheng Z (2006) A novel rice MAPK gene, OsBIMK2, is involved in disease-resistance responses. Plant Biol 8:587–596
Walter M, Chaban C, Schütze K, Batistic O, Weckermann K, Näke C, Blazevic D, Grefen C, Schumacher K, Oecking C (2004) Visualization of protein interactions in living plant cells using bimolecular fluorescence complementation. Plant J 40:428–438
Wang Q, Li J, Hu L, Zhang T, Zhang G, Lou Y (2013) OsMPK3 positively regulates the JA signaling pathway and plant resistance to a chewing herbivore in rice. Plant Cell Rep 32:1075–1084
Xiong L, Yang Y (2003) Disease resistance and abiotic stress tolerance in rice are inversely modulated by an abscisic acid—inducible mitogen-activated protein kinase. Plant Cell 15:745–759
You MK, Oh S, Ok SH, Cho SK, Shin HY, Jeung JU, Shin JS (2007) Identification of putative MAPK kinases in Oryza minuta and O. sativa responsive to biotic stresses. Mol Cell 23:108
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant (2011-0015848) from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology and by a Grant (PJ008160) from the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program funded by the Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Y.-I. Park.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, HY., You, M.K., Jeung, J.U. et al. OsMPK3 is a TEY-type rice MAPK in Group C and phosphorylates OsbHLH65, a transcription factor binding to the E-box element. Plant Cell Rep 33, 1343–1353 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-014-1620-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-014-1620-9