Abstract
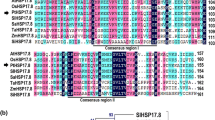
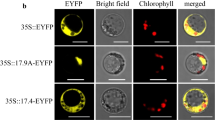
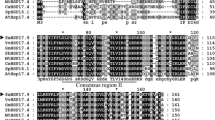
In plants, small heat shock proteins (sHSPs) are unusually abundant and diverse proteins involved in various abiotic stresses, but their functions in seed vigor remain to be fully explored. In this study, we report the isolation and functional characterization of a sHSP gene, NnHSP17.5, from sacred lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) in seed germination vigor and seedling thermotolerance. Sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis indicate that NnHSP17.5 is a cytosolic class II sHSP, which was further supported by the cytosolic localization of the NnHSP17.5-YFP fusion protein. NnHSP17.5 was specifically expressed in seeds under normal conditions, and was strongly up-regulated in germinating seeds upon heat and oxidative stresses. Transgenic Arabidopsis seeds ectopically expressing NnHSP17.5 displayed enhanced seed germination vigor and exhibited increased superoxide dismutase activity after accelerated aging treatment. In addition, improved basal thermotolerance was also observed in the transgenic seedlings. Taken together, this work highlights the importance of a plant cytosolic class II sHSP both in seed germination vigor and seedling thermotolerance.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
Accelerated aging
- ACD:
-
α-Crystallin domain
- DAP:
-
Days after pollination
- EST:
-
Expressed sequence tag
- MV:
-
Methyl viologen
- NBT:
-
Nitro blue tetrazolium
- RACE:
-
Rapid amplification of cDNA ends
- RH:
-
Relative humidity
- sHSPs:
-
Small heat shock proteins
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- YFP:
-
Yellow fluorescent protein
References
Almoguera C, Prieto-Dapena P, Díaz-Martín J, Espinosa JM, Carranco R, Jordano J (2009) The HaDREB2 transcription factor enhances basal thermotolerance and longevity of seeds through functional interaction with HaHSFA9. BMC Plant Biol 9:75
Bailly C, Benamar A, Corbineau F, Come D (1996) Changes in malondialdehyde content and in superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione reductase activities in sunflower seeds as related to deterioration during accelerated aging. Physiol Plantarum 97:104–110
Bailly C, El-Maarouf-Bouteau H, Corbineau F (2008) From intracellular signaling networks to cell death: the dual role of reactive oxygen species in seed physiology. C R Biol 331:806–814
Banti V, Loreti E, Novi G, Santaniello A, Alpi A, Perata P (2008) Heat acclimation and cross-tolerance against anoxia in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 31:1029–1037
Basha E, Lee GJ, Breci LA, Hausrath AC, Buan NR, Giese KC, Vierling E (2004) The identity of proteins associated with a small heat shock protein during heat stress in vivo indicates that these chaperones protect a wide range of cellular functions. J Biol Chem 279:7566–7575
Byrd HW, Delouche JC (1971) Deterioration of soybean seed in storage. Proc Assoc Off Seed Analysts 61:41–57
Cabiscol E, Bellí G, Tamarit J, Echave P, Herrero E, Ros J (2002) Mitochondrial Hsp60, resistance to oxidative stress, and the labile iron pool are closely connected in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 277:44531–44538
Catusse J, Meinhard J, Job C, Strub JM, Fischer U, Pestsova E, Westhoff P, van Dorsselaer A, Job D (2011) Proteomics reveals potential biomarkers of seed vigor in sugarbeet. Proteomics 11:1569–1580
Charng Y, Liu H, Liu N, Hsu F, Ko S (2006) Arabidopsis Hsa32, a novel heat shock protein, is essential for acquired thermotolerance during long recovery after acclimation. Plant Physiol 140:1297–1305
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Coca MA, Almoguera C, Jordano J (1994) Expression of sunflower low-molecular-weight heat-shock proteins during embryogenesis and persistence after germination: localization and possible functional implications. Plant Mol Biol 25:479–492
Dafny-Yelin M, Tzfira T, Vainstein A, Adam Z (2008) Non-redundant functions of sHSP-CIs in acquired thermotolerance and their role in early seed development in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 67:363–373
DeRocher AE, Vierling E (1994) Developmental control of small heat shock protein expression during pea seed maturation. Plant J 5:93–102
Dickson MH (1980) Genetic aspects of seed quality. Hort Sci 15:771–774
Ding Y, Cheng H, Song S (2008) Changes in extreme high-temperature tolerance and activities of antioxidant enzymes of sacred lotus seeds. Sci China Ser C Life Sci 51:842–853
Guo SJ, Zhou HY, Zhang XS, Li XG, Meng QW (2007) Overexpression of CaHSP26 in transgenic tobacco alleviates photoinhibition of PSII and PSI during chilling stress under low irradiance. J Plant Physiol 164:126–136
Haslbeck M, Franzmann T, Weinfurtner D, Buchner J (2005) Some like it hot: the structure and function of small heat-shock proteins. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12:842–846
Huang S, Tang X, Zhang L, Fu J (2003) Thermotolerance and activity of antioxidative enzymes in lotus seeds. J Plant Physiol Mol Biol 29:421–424 (in Chinese)
Jiang C, Xu J, Zhang H, Zhang X, Shi J, Li M, Ming F (2009) A cytosolic class I small heat shock protein, RcHSP17.8, of Rosa chinensis confers resistance to a variety of stresses to Escherichia coli, yeast and Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ 32:1046–1059
Kalemba EM, Pukacka S (2008) Changes in late embryogenesis abundant proteins and a small heat shock protein during storage of beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) seeds. Environ Exp Bot 63:274–280
Lee YP, Baek KH, Lee HS, Kwak SS, Bang JW, Kwon SY (2010) Tobacco seeds simultaneously over-expressing Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase display enhanced seed longevity and germination rates under stress conditions. J Exp Bot 61:2499–2506
Les DH, Garvin DK, Wimpee CF (1991) Molecular evolutionary history of ancient aquatic angiosperms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10119–10123
Ma C, Haslbeck M, Babujee L, Jahn O, Reumann S (2006) Identification and characterization of a stress-inducible and a constitutive small heat-shock protein targeted to the matrix of plant peroxisomes. Plant Physiol 141:47–60
Maimbo M, Ohnishi K, Hikichi Y, Yoshioka H, Kiba A (2007) Induction of a small heat shock protein and its functional roles in Nicotiana plants in the defense response against Ralstonia solanacearum. Plant Physiol 145:1588–1599
McDonald MB (1999) Seed deterioration: physiology repair and assessment. Seed Sci Technol 27:177–238
Miao Y, Jiang L (2007) Transient expression of fluorescent fusion proteins in protoplasts of suspension cultured cells. Nat Protoc 2:2348–2353
Murakami T, Matsuba S, Funatsuki H, Kawaguchi K, Saruyama H, Tanida M, Sato Y (2004) Over-expression of a small heat shock protein, sHSP17.7, confers both heat tolerance and UV-B resistance to rice plants. Mol Breed 13:165–175
Neta-Sharir I, Isaacson T, Lurie S, Weiss D (2005) Dual role for tomato heat shock protein 21: protecting photosystem II from oxidative stress and promoting color changes during fruit maturation. Plant Cell 17:1829–1838
Perez DE, Hoyer JS, Johnson AI, Moody ZR, Lopez J, Kaplinsky NJ (2009) BOBBER1 is a noncanonical Arabidopsis small heat shock protein required for both development and thermotolerance. Plant Physiol 151:241–252
Prieto-Dapena P, Castano R, Almoguera C, Jordano J (2006) Improved resistance to controlled deterioration in transgenic seeds. Plant Physiol 142:1102–1112
Rajjou L, Lovigny Y, Groot SPC, Belghazi M, Job C, Job D (2008) Proteome-wide characterization of seed aging in Arabidopsis: a comparison between artificial and natural aging protocols. Plant Physiol 148:620–641
Sabehat A, Lurie S, Weiss D (1998) Expression of small heat-shock proteins at low temperatures. Plant Physiol 117:651–658
Sanmiya K, Suzuki K, Egawa Y, Shono M (2004) Mitochondrial small heat-shock protein enhances thermotolerance in tobacco plants. FEBS Lett 557:265–268
Sattler SE, Gilliland LU, Magallanes-Lundback M, Pollard M, DellaPenna D (2004) Vitamin E is essential for seed longevity and for preventing lipid peroxidation during germination. Plant Cell 16:1419–1432
Scharf KD, Siddique M, Vierling E (2001) The expanding family of Arabidopsis thaliana small heat stress proteins and a new family of proteins containing alpha-crystallin domains (Acd proteins). Cell Stress Chaperones 6:225–237
Shen-Miller J, Mudgett MB, Schopf JW, Clarke S, Berger R (1995) Exceptional seed longevity and robust growth: ancient sacred lotus from China. Am J Bot 82:1367–1380
Shen-Miller J, Schopf JW, Harbottle G, Cao R, Ouyang S, Zhou K, Southon JR, Liu G (2002) Long-living lotus: germination and soil γ-irradiation of centuries-old fruits, and cultivation, growth, and phenotypic abnormalities of offspring. Am J Bot 89:236–247
Sun W, Bernard C, van de Cotte B, van Montagu M, Verbruggen N (2001) At-HSP17.6A, encoding a small heat-shock protein in Arabidopsis, can enhance osmotolerance upon overexpression. Plant J 27:407–415
Sun W, Van Montagu M, Verbruggen N (2002) Small heat shock proteins and stress tolerance in plants. Biochim Biophys Acta 1577:1–9
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr121
Tesnier K, Strookman-Donkers HM, van Pijlen JG, van der Geest AHM, Bino RJ, Groot SPC (2002) A controlled deterioration test for Arabidopsis thaliana reveals genetic variation in seed quality. Seed Sci Technol 30:149–165
Vierling E (1991) The roles of heat shock proteins in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 42:579–620
Volkov RA, Panchuk II, Schöffl F (2005) Small heat shock proteins are differentially regulated during pollen development and following heat stress in tobacco. Plant Mol Biol 57:487–502
Wang W, Vinocur B, Shoseyov O, Altman A (2004) Role of plant heat-shock proteins and molecular chaperones in the abiotic stress response. Trends Plant Sci 9:244–252
Waters ER, Lee GJ, Vierling E (1996) Evolution, structure and function of the small heat shock proteins in plants. J Exp Bot 47:325–338
Wehmeyer N, Hernandez LD, Finkelstein RR, Vierling E (1996) Synthesis of small heat-shock proteins is part of the developmental program of late seed maturation. Plant Physiol 112:747–757
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (30370912), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2006B20101010 and 9151027501000075) and Guangdong Agriculture Science and Technology Team Project to S. Huang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. S. Shin.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Chen, H., Chu, P. et al. NnHSP17.5, a cytosolic class II small heat shock protein gene from Nelumbo nucifera, contributes to seed germination vigor and seedling thermotolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis . Plant Cell Rep 31, 379–389 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1173-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1173-0