Abstract
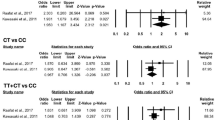
The results from previous studies on association of IL-6 −174 G/C and −572 G/C polymorphisms with the risk of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) remained inconsistent. Therefore, a meta-analysis was performed to assess the association between these two polymorphisms and SLE susceptibility. A literature-based search was conducted to identify all relevant studies. Pooled data were estimated by fixed- and random-effects models when appropriate. Nine publications were included in the meta-analysis, seven for −174 G/C polymorphism and three for −572 G/C polymorphism. The results indicated that IL-6 −174 G/C polymorphism was significantly associated with SLE risk for recessive model and allele analysis in overall populations (OR 1.64, 95 % CI 1.10–2.45, P = 0.016; and 1.34, 1.05–1.72, P = 0.019, respectively, for recessive model and allele analysis) or in Caucasians (OR 1.37, 95 % CI 1.04–1.82, P = 0.027; and 1.27, 1.04–1.54, P = 0.018, respectively, for recessive model and allele analysis). Also, significant association between IL-6 −572 G/C polymorphism and SLE was found under recessive model (OR 1.49, 95 % CI 1.10–2.01, P = 0.009), but not under dominant model and allele analysis (OR 1.05, 95 % CI 0.77–1.43, P = 0.750; and 1.21, 1.00–1.48, P = 0.054, respectively, for dominant model and allele analysis). Additionally, our meta-analysis showed that IL-6 −174 G/C polymorphism was significantly associated with discoid skin lesions (P < 0.05). The present study indicates that IL-6 −174 G/C and −572 G/C polymorphisms could be candidates for susceptibility to SLE. Furthermore, a large number of studies should be performed to explore the association of IL-6 polymorphisms with the risk and clinical characteristics of SLE patients in different ethnics.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yasutomo K (2003) Pathological lymphocyte activation by defective clearance of self-ligands in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 42:214–222
Wakeland EK, Liu K, Graham RR, Behrens TW (2001) Delineating the genetic basis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunity 15:397–408
Ruiz-Narvaez EA, Fraser PA, Palmer JR, Cupples LA, Reich D, Wang YA, Rioux JD, Rosenberg L. MHC region and risk of systemic lupus erythematosus in African American women. Hum Genet. 2011 Jun 22. Epub ahead of print
Lessard CJ, Adrianto I, Kelly JA, Kaufman KM, Grundahl KM, Adler A, Williams AH, Gallant CJ, Marta E et al (2011) Identification of a systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility locus at 11p13 between PDHX and CD44 in a multiethnic study. Am J Hum Genet 88(1):83–91
Han JW, Zheng HF, Cui Y, Sun LD, Ye DQ, Hu Z, Xu JH, Cai ZM et al (2009) Genome-wide association study in a Chinese Han population identifies nine new susceptibility loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 41(11):1234–1237
Kiberd BA (1993) Interleukin-6 receptor blockage ameliorates murine lupus nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 4:58–61
Cash H, Relle M, Menke J, Brochhausen C, Jones SA, Topley N, Galle PR, Schwarting A (2010) Interleukin 6 (IL-6) deficiency delays lupus nephritis in MRL-Fas lpr mice: the IL-6 pathway as a new therapeutic target in treatment of autoimmune kidney disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 37:60–70
Chun HY, Chung JW, Kim HA, Yun JM, Jeon JY, Ye YM et al (2007) Cytokine IL-6 and IL-10 as biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Immunol 27:461–466
Mellor-Pita S, Citores MJ, Castejon R, Yebra-Bango M, Tutor-Ureta P, Rosado S et al (2009) Monocytes and T lymphocytes contribute to a predominance of interleukin 6 and interleukin 10 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 76B:261–270
Illei GG, Shirota Y, Yarboro CH, Daruwalla J, Tackey E, Takada K et al (2010) Tocilizumab in systemic lupus erythematosus: data on safety, preliminary efficacy, and impact on circulating plasma cells from an open-label phase I dosage-escalation study. Arthritis Rheum 62:542–552
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21:589–624
Galbraith RF (1988) A note on graphical presentation of estimated odds ratios from several clinical trials. Stat Med 7:889–894
Egger M, Davey SG, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in metaanalysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634
Begg CB, Mazumdar M (1994) Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50:1088–1101
Linker-Israeli M, Wallace DJ, Prehn J, Michael D, Honda M, Taylor KD, Paul-Labrador M, Fischel-Ghodsian N, Fraser PA, Klinenberg JR (1999) Association of IL-6 gene alleles with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and with elevated IL-6 expression. Genes Immun 1:45–52
Chua KH, Kee BP, Tan SY, Lian LH (2009) Interleukin-6 promoter polymorphisms (−174 G/C) in Malaysian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Braz J Med Biol Res 42(6):551–555
Godarzi EM, Sarvestani EK, Aflaki E, Amirghofran Z (2011) Interleukin-6 gene polymorphism in Iranian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 30:179–184
Santos MJ, Fernandes D, Capela S, da Silva JC, Fonseca JE (2011) Interleukin-6 promoter polymorphism −174 G/C is associated with nephritis in Portuguese Caucasian systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Clin Rheumatol 30:409–413
Hrycek A, Siekiera U, Cieślik P, Szkróbka W (2005) HLA-DRB1 and -DQB1 alleles and gene polymorphisms of selected cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int 26:1–6
Schotte H, Schlüter B, Rust S, Assmann G, Domschke W, Gaubitz M (2001) Interleukin-6 promoter polymorphism (–174 G/C) in Caucasian German patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 40:393–400
Guarnizo-Zuccardi P, Lopez Y, Giraldo M, Garcia N, Rodriguez L, Ramirez L, Uribe O, Garcia L, Vasquez G (2007) Cytokine gene polymorphisms in Colombian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Tissue Antigens 70:376–382
Huang CM, Huo AP, Tsai CH, Chen CL, Tsai FJ (2006) Lack of association of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 gene polymorphisms in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Lab Anal 20:255–259
Jeon JY, Kim HA, Kim SH, Park HS, Suh CH (2010) Interleukin 6 gene polymorphisms are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in Koreans. J Rheumatol 37:2251–2258
Ripley BJ, Goncalves B, Isenberg DA, Latchman DS, Rahman A (2005) Raised levels of interleukin 6 in systemic lupus erythematosus correlate with anaemia. Ann Rheum Dis 64:849–853
Lee YH, Lee HS, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG (2012) The association between interleukin-6 polymorphisms and systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis. Lupus 21:60–67
Nurnberg W, Haas N, Schadendorf D, Czarnetzki BM (1995) Interleukin-6 expression in the skin of patients with lupus erythematosus. Exp Dermatol 4:52–57
Muller-Steinhardt M, Fricke L, Muller B, Ebel B, Kirchner H, Hartel C (2004) Cooperative influence of the interleukin-6 promoter polymorphisms -597, -572 and -174 on long-term kidney allograft survival. Am J Transpl 4:402–406
Hamid YH, Rose CS, Urhammer SA, Glumer C, Nolsoe R, Kristiansen OP, Mandrup-Poulsen T, Borch-Johnsen K, Jorgensen T, Hansen T, Pedersen O (2005) Variations of the interleukin-6 promoter are associated with features of the metabolic syndrome in Caucasian Danes. Diabetologia 48:251–260
Cussigh A, Falleti E, Fabris C, Bitetto D, Cmet S, Fontanini E, Bignulin S, Fornasiere E, Fumolo E, Minisini R, Pirisi M, Toniutto P (2011) Interleukin 6 promoter polymorphisms influence the outcome of chronic hepatitis C. Immunogenetics 63:33–41
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants from the China National Natural Science Foundation Council (81001333 and 81102262) and Changzheng Hospital Funds for Young Scholar (2011CZQN06).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Zaixing Yang, Yan Liang and Baodong Qin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Liang, Y., Qin, B. et al. A meta-analysis of the association of IL-6 −174 G/C and −572 G/C polymorphisms with systemic lupus erythematosus risk. Rheumatol Int 34, 199–205 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2855-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2855-4