Abstract
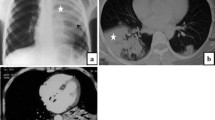
The aim of this study was to determine whether skin ulcer can be used as a predictive and prognostic factor of acute/subacute interstitial lung disease (ILD) in Japanese patients with dermatomyositis (DM). We reviewed the medical records of 39 consecutive DM patients who were admitted to Tokyo Metropolitan Komagome Hospital from January 2000 to December 2009. The mean follow-up period was 63.9 ± 51.6 months. Fifteen patients had acute/subacute ILD and 11 patients had chronic ILD. Seven out of 15 acute/subacute ILD led to respiratory failure and 3 of them died due to ILD. Skin ulcers were observed in 5 out of 15 patients with acute/subacute ILD (33.3 %) and in 2 out of 24 patients without acute/subacute ILD (8.3 %). The presence of skin ulcers was revealed to be a significant predictive factor for acute/subacute ILD among various parameters by multivariate analysis. In the 15 patients with acute/subacute ILD, the presence of skin ulcers was a significant poor prognostic factor (p = 0.0231) and the cumulative survival rate of patients with skin ulcers was 53.3 % for 12 months. Skin ulcer is a significant predictive and prognostic factor of acute/subacute ILD in patients with DM.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Won Huh J, Soon Kim D, Keun Lee C, Yoo B, Bum Seo J, Kitaichi M et al (2007) Two distinct clinical types of interstitial lung disease associated with polymyositis-dermatomyositis. Respir Med 101(8):1761–1769
Kang EH, Lee EB, Shin KC, Im CH, Chung DH, Han SK et al (2005) Interstitial lung disease in patients with polymyositis, dermatomyositis and amyopathic dermatomyositis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 44(10):1282–1286
Chen IJ, Jan Wu YJ, Lin CW, Fan KW, Luo SF, Ho HH et al (2009) Interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Clin Rheumatol 28(6):639–646
Fathi M, Lundberg IE (2005) Interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 17(6):701–706
Marie I, Hachulla E, Cherin P, Dominique S, Hatron PY, Hellot MF et al (2002) Interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheum 47(6):614–622
Gono T, Kawaguchi Y, Hara M, Masuda I, Katsumata Y, Shinozaki M et al (2010) Increased ferritin predicts development and severity of acute interstitial lung disease as a complication of dermatomyositis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 49(7):1354–1360
Kameda H, Nagasawa H, Ogawa H, Sekiguchi N, Takei H, Tokuhira M et al (2005) Combination therapy with corticosteroids, cyclosporin A, and intravenous pulse cyclophosphamide for acute/subacute interstitial pneumonia in patients with dermatomyositis. J Rheumatol 32(9):1719–1726
Ideura G, Hanaoka M, Koizumi T, Fujimoto K, Shimojima Y, Ishii W et al (2007) Interstitial lung disease associated with amyopathic dermatomyositis: review of 18 cases. Respir Med 101(7):1406–1411
Ye S, Chen XX, Lu XY, Wu MF, Deng Y, Huang WQ et al (2007) Adult clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis with rapid progressive interstitial lung disease: a retrospective cohort study. Clin Rheumatol 26(10):1647–1654
Mimori A, Suzuki T, Satoh N, Nara H, Masuyama J, Yoshio T et al (2000) Dermatomyositis and cutaneous necrosis: report of five cases. Mod Rheumatol 10:117–120
Sato S, Hirakata M, Kuwana M, Suwa A, Inada S, Mimori T et al (2005) Autoantibodies to a 140-kd polypeptide, CADM-140, in Japanese patients with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheum 52(5):1571–1576
Nakashima R, Imura Y, Kobayashi S, Yukawa N, Yoshifuji H, Nojima T et al (2010) The RIG-I-like receptor IFIH1/MDA5 is a dermatomyositis-specific autoantigen identified by the anti-CADM-140 antibody. Rheumatology (Oxford) 49(3):433–440
Gerami P, Schope JM, McDonald L, Walling HW, Sontheimer RD (2006) A systematic review of adult-onset clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis (dermatomyositis sine myositis): a missing link within the spectrum of the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. J Am Acad Dermatol 54(4):597–613
American Thoracic Society. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment. International consensus statement. American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000 Feb; 161(2 Pt 1):646–664
Suda T, Fujisawa T, Enomoto N, Nakamura Y, Inui N, Naito T et al (2006) Interstitial lung diseases associated with amyopathic dermatomyositis. Eur Respir J 28(5):1005–1012
Cicuttini FM, Fraser KJ (1989) Recurrent pneumomediastinum in adult dermatomyositis. J Rheumatol 16(3):384–386
Yosipovitch G, Feinmesser M, David M (1998) Adult dermatomyositis with livedo reticularis and multiple skin ulcers. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 11(1):48–50
Jang KA, Kim SH, Choi JH, Sung KJ, Moon KC, Koh JK (1999) Subcutaneous emphysema with spontaneous pneumomediastinum and pneumothorax in adult dermatomyositis. J Dermatol 26(2):125–127
Tsujimura S, Saito K, Tanaka Y (2008) Complete resolution of dermatomyositis with refractory cutaneous vasculitis by intravenous cyclophosphamide pulse therapy. Intern Med 47(21):1935–1940
Yamamoto T, Ohkubo H, Katayama I, Nishioka K (1994) Dermatomyositis with multiple skin ulcers showing vasculitis and membrano-cystic lesion. J Dermatol 21(9):687–689
Scheinfeld NS (2006) Ulcerative paraneoplastic dermatomyositis secondary to metastatic breast cancer. Skinmed 5(2):94–96
Pusceddu V, Frau B, Guerzoni D, Catani G, Murgia M, Murru M et al (2008) Undescribed case of necrotic ulcerative amyopathic dermatomyositis in bone metastatic breast cancer. Breast J 14(6):591–592
Sigurgeirsson B, Lindelof B, Edhag O, Allander E (1992) Risk of cancer in patients with dermatomyositis or polymyositis. A population-based study. N Engl J Med 326(6):363–367
Mukae H, Ishimoto H, Sakamoto N, Hara S, Kakugawa T, Nakayama S et al (2009) Clinical differences between interstitial lung disease associated with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis and classic dermatomyositis. Chest 136(5):1341–1347
Kameda H, Takeuchi T (2006) Recent advances in the treatment of interstitial lung disease in patients with polymyositis/dermatomyositis. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 6(4):409–415
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishigaki, K., Maruyama, J., Hagino, N. et al. Skin ulcer is a predictive and prognostic factor of acute or subacute interstitial lung disease in dermatomyositis. Rheumatol Int 33, 2381–2389 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2735-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2735-y