Abstract
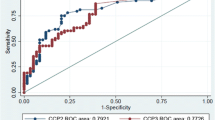
Citrulline antibody, nowadays, is a new item which has been the center of attention due to its much more specificity to diagnose RA. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the efficacy and accuracy of anti-citrulline antibody test in RA diagnosis among hospitalized patients in Iran. Through a case–control study, we tried to calculate the accuracy of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody (anti-CCP) test used in the diagnosis of RA enrolling 200 participants divided into two groups of the patients with RA, on the one hand, and other diseases, on the other. Anti-CCP was measured by ELISA technique through which titers more than 15 were defined as high titer. Of all the studied population, 81 (81 %) were in active phase of RA, which had anti-CCP >15 U/ml, while only 25 controls (25 %) experienced these levels. The average anti-CCP was 144 U/ml in cases and 16.05 U/ml in controls with a P value <0.001, which confirmed significant difference between the two. Considering different comments on this matter besides our findings in the present research, we offer a combination of anti-citrulline antibody test rather than anti-CCP and RF to get the best results in RA diagnosis, discrimination and prognosis because of 97 % specificity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raptopoulou A, Sidiropoulos P, Katsouraki M, Boumpas D (2007) Anti-citrulline antibodies in the diagnosis and prognosis of rheumatoid arthritis: Evolving concepts. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 44:339–363
Bizzaro N, Mazzanti G, Tonutti E, Villalta D, Tozzoli R (2001) Diagnostic accuracy of the anti-citrulline antibody assay for rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chem 47:1089–1093
Morrow J, Nelson L, Watts R (1999) Isenberg D (1999) autoimmune rheumatic disease, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 104–146
Nienhuis RLF, Mandema EA (1964) A new serum factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The antiperinuclear factor. Ann Rheum Dis 23:3025
Young BJ, Mallya RK, Leslie RD, Clark CJ, Hamblin TJ (1976) Antikeratin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J 2:97–99
Citrulline antibody (2009) Medicine.net. available from: http://www.medicinenet.com/citrullineantibody/article.htm#tocb. Accessed 16 Nov
Schellekens GA, de Jong BAW, van den Hoogen FHJ, van de Putte LBA, van Venrooij WJ (1998) Citrulline is an essential constituent of antigenic determinants recognized by rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantibodies. J Clin Invest 101:273–281
FDA clears new test to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis in early stages. Available from: http://www.highbeam.come/doc/1G1-153386873.html. Accessed 14 Sep 2009
Kroot E, de Jong BA, van Leeuwen MA et al (2000) The prognostic value of the anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with recent onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43:1831–1835
Schellekens GA, Visser H, de Jong BA et al (2000) The diagnostic properties of rheumatoid arthritis antibodies recognizing a cyclic citrullinated peptide. Arthritis Rheum 43:155–163
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ et al (2010) Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1580–1588
Nishimura K, Sugiyama D, Kogata Y et al (2007) Meta-analysis: diagnostic accuracy of anti–cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med 146:797–808
Bell DA (2006) Can we rely on anti-citrulline antibody determination for the diagnosis of early rheumatoid arthritis? J Rheumatol 33:2369–2371
Matsui T, Shimada K, Ozawa N et al (2006) Diagnostic utility of anticyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies for very early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 33:2390–2397
Symmons DPM, Hazes JMW, Silman AJ (2003) Cases of early inflammatory polyarthritis should not be classified as having rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 30:902–904
Niewold TB, Harrison MJ, Paget SA (2007) Anti-CCP antibody testing as a diagnostic and prognostic tool in rheumatoid arthritis. QJM 100:193–201
Avouac J, Gossec L, Dougados M (2006) Diagnostic and predictive value of anti-cyclic citrullinated protein antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic literature review. Ann Rheum Dis 65:845–851
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate Dr. Gelareh Vahdati who participated in the study actively. Also, we would like to express our sincere gratitude to Farzan Institute for Research & Technology for technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
Authors did not declare any conflicts of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abolghasemi, S., Gitipour, A. & Morteza, A. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of anti-citrulline antibody test in diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 33, 1027–1030 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-012-2469-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-012-2469-2