Abstract
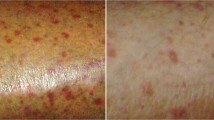
Effects of a dual endothelin receptor antagonist, bosentan on peripheral circulatioin and skin lesions as well as pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) were investigated in Japanese patients with connective tissue diseases (CTD). Fifteen patients with PAH associated with CTD [systemic sclerosis (SSc) 13, mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) 2] were treated with bosentan for 40–96 weeks, and changes of exercise capacity (6-min walk distance and Borg’s dyspnea scale), cardio-pulmonary hemodynamics (right ventricular pressure, specific activity scale and cardiac index), Raynaud’s phenomenon, digital ulcers and dermal sclerosis were observed. Bosentan improved exercise capacity, had a positive effect on hemodynamic parameters, and was well tolerated as previously reported. After a median 8 weeks of treatment, 13 out of 15 patients had improved Raynaud’s phenomenon. Digital ulcers also improved after a median 12 weeks’ treatment in all of 8 patients. Modified Rodnan total skin score decreased from 21.0 ± 5.9 to 11.5 ± 3.9 in diffuse cutaneous SSc and from 17.0 ± 6.5 to 9.5 ± 4.5 in limited cutaneous SSc after 24 months’ treatment, reaching significance after 6 months in both groups. These data suggest that bosentan is effective for both PAH and peripheral vascular diseases in Japanese patients with CTD. The pathological background to the improvement in dermal sclerosis observed in this study should be further investigated.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi-Simab K, Hellmich B, Gross WL (2006) Bosentan for severe pulmonary arterial hypertension related to systemic sclerosis with interstitial lung disease. Eur J Clin Invest 36(Suppl 3):4–8
Cozzi F, Montisci R, Marotta H et al (2006) Bosentan therapy of pulmonary arterial hypertension in connective tissue diseases. Eur J Clin Invest 36(Suppl 3):49–53. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.2006.01684.x
Oldfield V, Lyseng-Williamson KA (2006) Bosentan: a review of its use in pulmonary arterial hypertension and systemic sclerosis. Am Cardiovasc Drugs 6:189–208. doi:10.2165/00129784-200606030-00006
Galie N, Manes A, Branzi A (2004) The endothelin system in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Cardiovasc Res 61:227–237. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2003.11.026
Schulze-Neick I, Gilbert N, Ewert R et al (2005) Adult patients with congenital heart disease and pulmonary arterial hypertension: first open prospective multicenter study of bosentan therapy. Am Heart J 150:716
Sitbon O, Gressin V, Speich R et al (2004) Bosentan for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170:1212–1217. doi:10.1164/rccm.200404-445OC
Korn JH, Mayers M, Matucci CM et al (2004) Digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis: prevention by with bosentan, an oral endothelin receptor antagonist. Arthritis Rheum 50:3985–3993. doi:10.1002/art.20676
Masi AT, Rodnan GP, Medsger TA Jr et al (1980) Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Arthritis Rheum 15:202–205
Shrap GC, Irvin WS, Tan EM et al (1972) Mixed connective tissue disease—an apparently distinct rheumatic disease syndrome associated with a specific antibody to an extractable nuclear antigen (ENA). Am J Med 52:148–159. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(72)90064-2
Goldman L, Hashimoto B, Cook EF, Loscalzo A (1981) Comparative reproducibility and validity of systems for assessing cardiovascular functional class: advantages of a new specific activity scale. Circulation 64:1227–1234
Borg GA (1982) Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med Sci Sports Exerc 14:377–381
Clements PJ, Lachenbruch PA, Seibold JR et al (1995) Inter and intraobserver variability of total skin thickness score (modified Rodnan TSS) in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 22:1281–1285
Oldfield V, Lyseng Williamson KA (2006) Bosentan: a review of its use in pulmonary arterial hypertension and systemic sclerosis. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs 6:189–208. doi:10.2165/00129784-200606030-00006
Humbert M, Cabane J (2003) Successful treatment of systemic sclerosis digital ulcers and pulmonary arterial hypertension with endothelin receptor antagonist bosentan. Rheumatology 42:191–193
Jain M, Varga J (2006) Bosentan for the treatment of systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension, pulmonary fibrosis and digital ulcers. Expert Opin Pharmacother 7:1487–1501. doi:10.1517/14656566.7.11.1487
Launay D, Diot E, Pasquir E et al (2006) Bosentan for treatment of active digital ulcers in patients with systemic sclerosis (9 cases). Presse Med 35:587–592. doi:10.1016/S0755-4982(06)74645-0
Maugars YM, Berthelot JM, Abbas A et al (1996) Long-term prognosis of 69 patients with dermatomyositis or polymyositis. Clin Exp Rheum 14:263–274
Song E, Ouyang N, Horbelt M et al (2000) Influence of alternatively and classically activated macrophages on fibrogenic activities of human fibroblasts. Cell Immunol 204:19–28. doi:10.1006/cimm.2000.1687
Marshall RP, McAnulty RJ, Laurent GJ (2000) Angiotensin II is mitogenic for human lung fibroblasts via activation of the type 1 receptor. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 161:1999–2004
Funauchi M, Shimadsu H, Tamaki C et al (2006) Role of endothelial damage in the pathogenesis of interstitial pneumonitis in patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. J Rheumatol 33:903–906
Clozel M, Salloukh H (2005) Role of endothelin in fibrosis and anti-fibrotic potential of bosentan. Ann Med 37:2–12. doi:10.1080/07853890410018925
Clements P, Lachenbruch P, Furst D, Paulus H (1993) The course of skin involvement in systemic sclerosis over three years in a trial of chlorambucil versus placebo. Arthritis Rheum 36:1575–1579. doi:10.1002/art.1780361112
Tillon J, Herve F, Chevallier D, Muir JF, Levesque H, Marie I (2006) Successful treatment of systemic sclerosis-related digital ulcers and sarcoidosis with endothelin receptor antagonist (bosentan) therapy. Br J Dermatol 154:1000–1002
Riccardi MT, Chiala A, Lannone F, Grattagliano V, Covelli M, Lapadula G (2007) Treatment of digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis with endothelin-1 receptor antagonist (bosentan). Reumatismo 59:135–139
Chamaillard M, Heliot Hosten I, Constans J, Taïeb A (2007) Bosentan as a rescue therapy in scleroderma refractory digital ulcers. Arch Dermatol 143:125–126. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.1.125
Roldan R, Morote G, Castro-Mdel C, Miranda MD, Moreno JC, Collantes E (2006) Efficacy of bosentan in treatment of unresponsive cutaneous ulceration in disabling pansclerotic morphea in children. J Rheumatol 33:2538–2540
Alegre-Sancho JJ, Roman-Ivorra JA, Chalmeta-Verdejo C, Fernandez-Carballido C, Fernández-Llanio N, Ivorra-Cortes J et al (2007) Bosentan therapy for cutaneous fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis. Curr Med Res Opin 23(suppl 2):S89–S96
Humbert M, Segal ES, Kiely DG, Carlsen J, Schwierin B, Hoepwe MM (2007) Results of European post-marketing surveillance of bosentan in pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 30:338–344. doi:10.1183/09031936.00138706
Acknowledgments
A part of this study was supported by a grant from The Osaka Medical Research Foundation for Incurable Diseases.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Funauchi, M., Kishimoto, K., Shimazu, H. et al. Effects of bosentan on the skin lesions: an observational study from a single center in Japan. Rheumatol Int 29, 769–775 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-008-0789-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-008-0789-z