Abstract
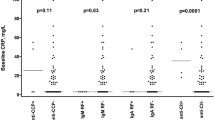
The prevalence and clinical relevance of IgM and IgA RF detected by ELISA were studied in 91 patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) and 45 healthy children. IgM and IgA RF were detected, respectively, in 33 and 44% of the patients, compared to 6.7 and 15.6% of the healthy children (p = 0.001 and 0.0006, respectively). The frequency of IgM RF was significantly higher in patients with polyarticular (52%) as compared to systemic onset JRA (21%; p = 0.04). Five out of ninety-one patients and none of the control group were IgM RF positive by the latex test. High levels of IgM RF were detected more frequently in patients with active disease (p = 0.01) and positive latex agglutination test (p < 0.001) and had a marginally significant association with severe radiological deformities (p = 0.05). The presence of IgA RF was associated with active disease in polyarticular onset JRA children (p = 0.04). In conclusion, high levels of IgM RF and the detection of IgA RF can be useful in assessing clinical activity in a subset of patients with JRA.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bywaters EGL (1959) Differential agglutination title (DAT) in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 18:225
Eichenfield AH, Athreya BH, Doughty RA, Cebul RD (1986) Utility of rheumatoid factor in the diagnosis of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Pediatrics 78:480–484
Cassidy JT, Petty RE (2001) Textbook of pediatric rheumatology. Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. 4th ed., WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 214–321
Minden K, Nierwerth M, Listing J, Biedermann T, Bollow M, Schöntube M, Zink A (2002) Long-term outcome in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 46:2392–2401
Schaller JG (1997) Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Pediatr Rev 18:337–49
Davidson J (2000) Juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a clinical overview. Eur J Radiol 33:128–134. Review
Alvarez Garcia J, Blanco Quiros A, Solis Sanchez P, Telleria Orriols JJ, Lapena Lopez de Armentia S (1989) Measurement and comparison of the rheumatoid factors class IgG, IgM and IgA in chronic juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. An Esp Pediatr 31:554–558. Review Spanish
Walker SM, Shaham B, McCurdy DK, Wietting H, Arora Y K, Hanson V, Bernstein B (1990) Prevalence and concentration of IgM rheumatoid factor in polyarticular onset disease as compared to systemic or pauciarticular onset disease in active juvenile rheumatoid arthritis as measured by ELISA. J Rheumatol 17:936–940
Jarvis JN, Pousak T, Krenz M (1992) Detection of IgM rheumatoid factors by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in children with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: correlation with articular disease and laboratory abnormalities. Pediatrics 90:945–949
Varbanova BB, Baleva M, Nikolov K, Mihallova D (1999) Prevalence of IgM, IgA and IgG rheumatoid factors in seronegative polyarticular disease compared to pauciarticular disease in juvenile chronic arthritis as measured by ELISA. Adv Exp Med Biol 455:61–68
Salusbury FT (1990) Prevalence of IgM, IgA and IgG rheumatoid factors in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 8:513–517
Walker SM, McCurdy DK, Shaham B, Brik R, Wietting H, Arora Y, Lehman TJ, Hanson V, Bernstein B (1990) High prevalence of IgA rheumatoid factor in severe polyarticular-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, but not in systemic-onset or pauciarticular-onset disease. Arthritis Rheum 33:199–204
Ramakrishnan TP, Ilowite NT, Wedgwood JF, Hatam L, Valacer DJ, Bonagura VR (1991) The major factor cross reactive idiotype and IgA rheumatoid factor in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 18:1068–1072
Bas S, Perneger T V, Kunzle E, Vischer T L (2002) Comparative study of different enzyme immunoassays for measurement of IgM and IgA rheumatoid factors. Ann Rheum Dis 61:505–510
Aggarwal A, Dabadghao S, Naik S, Misra R (1994) Serum IgM rheumatoid factor by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) delineates a subset of patients with deforming joint disease in seronegative juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 14:135 –138
Bharadwaj A, Aggarwal A, Misra R (1999) Clinical relevance of IgA rheumatoid factor in children with Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 19:47–49
Ferreira RA, Ferriani VPL, Sopelete MC, Silva DAO, Mineo JR, Kiss MHB, Silva CHM (2002) Immunoglobulin E-rheumatoid factor in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Rev Hosp Clín Fac Med Sao Paulo 57:209–216
Brewer EJ Jr, Bass J, Baum J, Cassidy JT, Fink C, Jacobs J, Hanson V, Levinson JE, Schaller J, Stillman JS (1977) Current proposed revision of JRA criteria. JRA criteria subcommittee of the diagnostic and therapeutic criteria committee of the American rheumatism section of the arthritis foundation. Arthritis Rheum 20:195–199
Cassidy JT, Levinson JE, Bass JC, Baum J, Brewer EJ Jr, Fink CW, Hanson V, Jacobs JC, Masi AT, Schaller JG et al (1986) A study of classification criteria for a diagnosis of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 29:274–281
Steinbroker O, Traeger CH, Batterman RE (1949) Therapeutic criteria in rheumatoid arthritis. JAMA 140:659–662
Moore TL, Dorner RW, Alexander RL, Osborn TG (1988) Enzyme linked (ELISA) immunoadsorbent assay for the detection of hidden 19S rheumatoid factors in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 15:87–90
Wilson MB, Nakane PK (1978) Antibody conjugated to horse -radish peroxidase. In: Kanpp K, Nolubar GW (Eds) Immunofluorescence and related staining technique. Elsevier North’s Holland Biomedical, pp 215–224
Triola, M.F (1999) Introdução à estatística. 7.ed. Rio de Janeiro: LTC (Livro Técnico e Científico) E.S.A. 410p
Jonsson T, Steinsson K, Jonsson H, Geirsson A J, Thorsteinsson J, Valdimarsson H (1998) Combined elevation of IgM e IgA rheumatoid factor has high diagnostic specificity for rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 18:119–122
Jonsson T, Thorsteinsson J, Kolbeinsson A, Jonasdottir E, Sigfusson N, Valdimarsson H (1992) Population study of the importance of rheumatoid factor isotypes in adults. Ann Rheum Dis 51:863–868
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreira, R.A., Silva, C.H.M., Silva, D.A.O. et al. Is measurement of IgM and IgA rheumatoid factors (RF) in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis clinically useful?. Rheumatol Int 27, 345–349 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-006-0221-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-006-0221-5